Example: Install standalone Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm
This example shows how to install the standalone Elastic Agent on a Kubernetes system using a Helm chart, collect Kubernetes metrics and logs, and send them to an Elasticsearch cluster in Elastic Cloud for visualization in Kibana.
Although this tutorial uses an Elastic Cloud Hosted deployment, you can adapt the same steps for other deployment types. For self-managed, Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes, or Elastic Cloud Enterprise deployments, you might need to provide the Elasticsearch CA certificate during the Elastic Agent installation, as outlined in the following sections.
For an overview of the Elastic Agent Helm chart and its benefits, refer to Install Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm.
This guide takes you through these steps:
- Add the Elastic Helm repository
- Install Elastic Agents
- Update Elastic Agent configuration examples
- Tidy up
To get started, you need:
- A local install of the Helm Kubernetes package manager.
- An Elastic Cloud Hosted Elasticsearch cluster on version 8.18 or higher. An Elastic Cloud Serverless project also meets this requirement.
- An Elasticsearch API key with the privileges described in the referenced document.
- An active Kubernetes cluster.
The installation and configuration steps shown in this example deploy the following components to monitor your Kubernetes cluster:
A default installation of
kube-state-metrics(KSM), configured as a dependency of the Helm chart. KSM is required by the Kubernetes integration to collect cluster-level metrics.A group of standalone Elastic Agents, deployed as a Kubernetes DaemonSet, and configured to collect the following host level data:
- Host level metrics and logs through the System Integration. This enables the monitoring of your Kubernetes nodes at OS level. Elastic Agent Pods will collect system metrics and logs from their own hosts.
- Kubernetes node-level metrics and logs through the Kubernetes Integration: This integration collects Kubernetes metrics and Pods' logs related to the node where each Elastic Agent Pod runs. It focuses on node-level visibility only, not cluster-wide metrics, which are handled separately.
A standalone Elastic Agent, deployed as a
Deploymentof 1 replica, and configured to collect Kubernetes cluster-level metrics and events through the Kubernetes integration: This complements the node-level data gathered by the DaemonSet, providing full visibility into the cluster's state and workloads. Some of this data is retrieved from kube-state-metrics.
By default, all resources are installed in the namespace defined by your current kubectl context. You can override this by specifying a different namespace using the --namespace option during installation.
Before installing, add the Elastic Helm repository to your local Helm configuration and verify the available versions of the elastic-agent chart. If the repository is already configured, run helm repo update to ensure you have the latest package information.
Set up Helm repository:
helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co/ helm repo updateVerify chart versions:
helm search repo elastic-agent --versionsThe previous command returns something similar to:
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION elastic/elastic-agent 9.0.0 9.0.0 Elastic-Agent Helm Chart elastic/elastic-agent 8.18.0 8.18.0 Elastic-Agent Helm Chart
Open your Elastic Cloud deployment, and from the navigation menu select Manage this deployment.
In the Applications section, copy the Elasticsearch endpoint and make a note of the endpoint value.
Open a terminal shell on your local system where the Helm tool is installed and you have access to the Kubernetes cluster.
Copy and prepare the command to install the chart:
helm install demo elastic/elastic-agent \ --set kubernetes.enabled=true \ --set system.enabled=true \ --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI \ --set outputs.default.url=<ES-endpoint>:443 \ --set outputs.default.api_key="API_KEY"- Substitute <ES-endpoint> with the Elasticsearch endpoint value that you copied earlier. Be sure to include the right port, as the agent might default to port 9200 if no port is specified.
- Substitute API_KEY with your API key in
Beatsformat.
The command has these properties:
helm install: Runs the Helm CLI install tool. You can usehelm upgradeto modify or update an installed release.demo: The name for this specific installation of the chart, known as the release name. You can choose any name.elastic/elastic-agent: The name of the chart to install, using the format<repository>/<chart-name>.--set kubernetes.enabled=true: Adds and configures the Kubernetes integration. This setting is enabled by default.--set system.enabled=true: Adds and configures the system integration, which is disabled by default.--set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI: Sets the authentication method for the Elasticsearch output to require an API key. This setting defaults toESPlainAuthBasic.--set outputs.default.api_key="API_KEY": Sets the API key that Elastic Agent will use to authenticate with your Elasticsearch cluster.--set outputs.default.url=<ES-endpoint>:443: Sets the address of the Elasticsearch endpoint, where the Elastic Agent will send all collected data.
After your updates, the command should be similar to:
helm install demo elastic/elastic-agent \ --set kubernetes.enabled=true \ --set system.enabled=true \ --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI \ --set outputs.default.url=https://demo.es.us-central1.gcp.foundit.no:443 \ --set outputs.default.api_key="A6ecaHNTJUFFcJI6esf4:5HJPxxxxxxxPS4KwSBeVEs"TipFor a full list of all available values settings and descriptions, refer to the Elastic Agent Helm Chart Readme and default values.yaml.
The following options could be useful for special use cases:
--namespace <namespace>: Allows to install all resources in a specific namespace.--version <version>: Installs a specific version of the Helm chart and Elastic Agent. Refer to Preparations to check available versions.--set agent.version=<version>: Installs a specific version of Elastic Agent. By default, the chart installs the agent version that matches its own.--set-file 'outputs.default.certificate_authorities[0].value=/local-path/to/es-ca.crt': Specifies the CA certificate that Elastic Agent should trust when connecting to Elasticsearch. This is typically required when Elasticsearch uses a certificate signed by a private CA. Not needed for clusters hosted on Elastic Cloud.--set kube-state-metrics.enabled=false: Prevents the installation of kube-state-metrics. Useful if KSM is already installed in your cluster.--set kubernetes.state.host: Sets the kube-state-metrics endpoint used in the Kubernetes integration input streams. Useful if you already have KSM installed and you are not deploying it with the chart.--set kubernetes.state.enabled=false: Disables all input streams related to kube-state-metrics in the Kubernetes integration configuration.--set kube-state-metrics.fullnameOverride=ksm: Overrides the default release name (kube-state-metrics) used for the KSM deployment. Useful if you already have a KSM instance deployed and want to install a second one with a different name.--set kubernetes.state.agentAsSidecar.enabled=true: Enables KSM autosharding by deploying KSM as aStatefulSetwith Elastic Agents as sidecar containers. This setup is useful and recommended for large Kubernetes clusters to distribute the metric collection load. To scale KSM in this configuration, use thekube-state-metrics.replicassetting.
Run the command.
The command output should confirm that two Elastic Agents have been installed (one
DaemonSetand oneDeployment), along with the Kubernetes and system integrations, and that kube-state-metrics has also been deployed in the same namespace.... Release "demo" is installed at "default" namespace Installed agents: - clusterWide [deployment - standalone mode] - perNode [daemonset - standalone mode] Installed kube-state-metrics at "default" namespace. Installed integrations: - kubernetes [built-in chart integration] - system [built-in chart integration] ...Run the
kubectl get pods -n defaultcommand to confirm that the Elastic Agent pods are running:NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE agent-clusterwide-demo-5fc46c54d5-7vhjz 1/1 Running 0 5m35s agent-pernode-demo-2fp77 1/1 Running 0 5m34s agent-pernode-demo-q9f8n 1/1 Running 0 5m34s agent-pernode-demo-twrtw 1/1 Running 0 5m35s kube-state-metrics-6bc97757c4-x9rkg 1/1 Running 0 5m35sIn your Elastic Cloud deployment, from the Kibana menu open the Integrations page.
Run a search for
Kubernetesand then select the Kubernetes integration card.On the Kubernetes integration Settings page, select Install Kubernetes. This installs the dashboards, Elasticsearch indexes, and other assets used to monitor your Kubernetes cluster.
On the Kubernetes integration page, open the Assets tab and select the [Metrics Kubernetes] Nodes dashboard.
On the dashboard, you can view the status of your Kubernetes nodes, including metrics on memory, CPU, and filesystem usage, network throughput, and more.

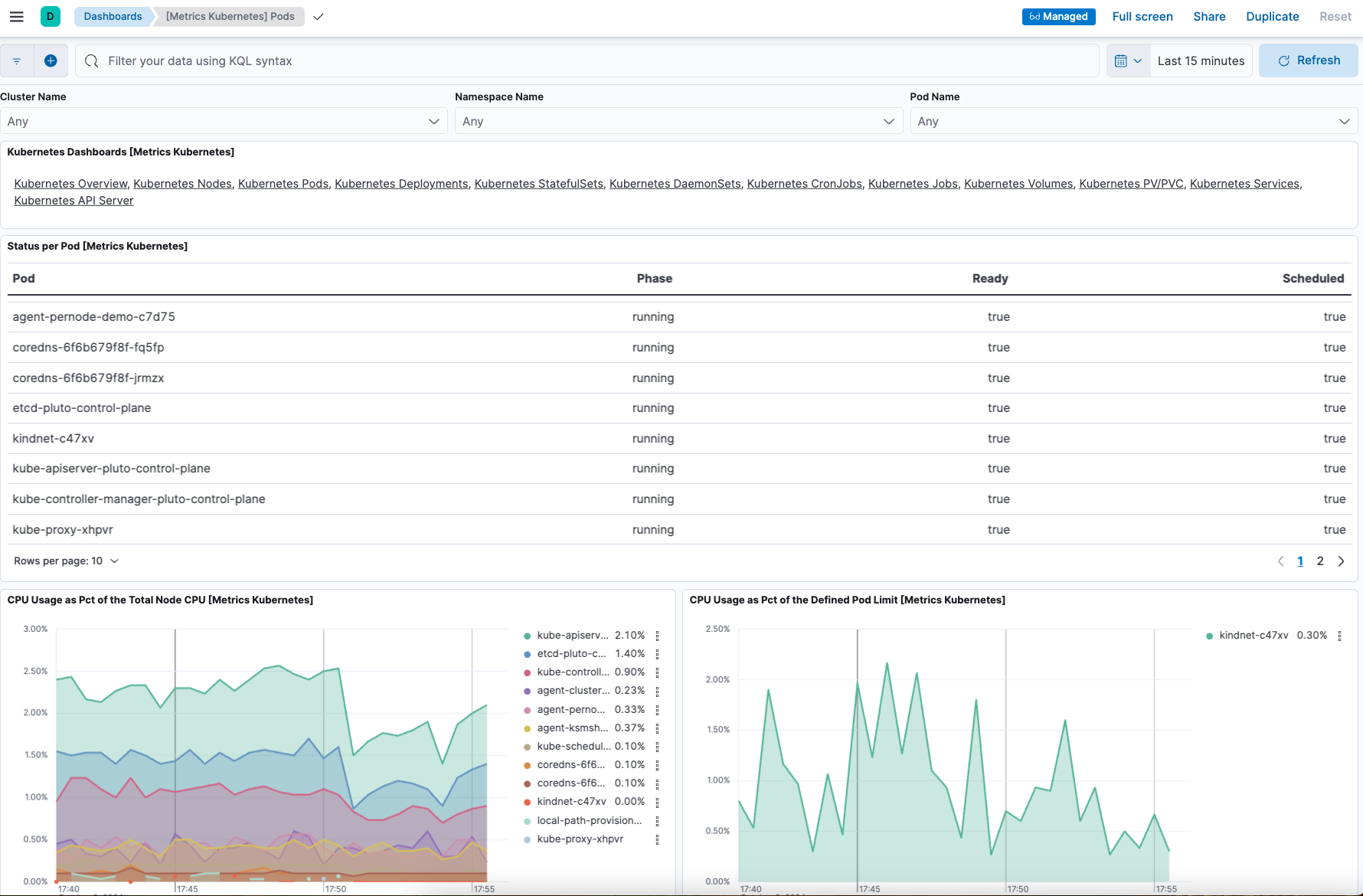
On the Kubernetes integration page, open the Assets tab and select the [Metrics Kubernetes] Pods dashboard. As with the nodes dashboard, on this dashboard you can view the status of your Kubernetes pods, including various metrics on memory, CPU, and network throughput.
Now that you have Elastic Agent installed, collecting, and sending data successfully, let’s try changing the agent configuration settings.
In the previous installation example, two Elastic Agents, per-node and cluster-wide, were installed, along with kube-state-metrics. Let’s suppose that you don’t need metrics related to kube-state-metrics and would like to upgrade your configuration accordingly.
This is only an example of how to update the configuration of an installed Helm chart. Disabling kube-state-metrics will prevent several Kubernetes dashboards in Kibana from displaying data.
The following values will help achieve that goal:
kubernetes.state.enabled=false: Disables all input streams related to kube-state-metrics in the Kubernetes integration configuration of the cluster-wide Elastic Agent.kube-state-metrics.enabled=false: Prevents the installation of the kube-state-metrics component.
To update the configuration of an installed release:
Start by copying the same command you used previously to install Elastic Agent, for example:
helm install demo elastic/elastic-agent \ --set kubernetes.enabled=true \ --set system.enabled=true \ --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI \ --set outputs.default.url=https://demo.es.us-central1.gcp.foundit.no:443 \ --set outputs.default.api_key="A6ecaHNTJUFFcJI6esf4:5HJPxxxxxxxPS4KwSBeVEs"Update the command as follows:
Replace
installwithupgrade, keeping the same release name (demoin this example).Modify the parameters as needed:
helm upgrade demo elastic/elastic-agent \ --set kubernetes.enabled=true \ --set system.enabled=true \ --set kubernetes.state.enabled=false \ --set kube-state-metrics.enabled=false \ --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI \ --set outputs.default.url=https://demo.es.us-central1.gcp.foundit.no:443 \ --set outputs.default.api_key="A6ecaHNTJUFFcJI6esf4:5HJPxxxxxxxPS4KwSBeVEs"
Run the command.
After running the command, kube-state-metrics will no longer be running, and the
agent-clusterwide-demoinstance will be configured without any state-related data streams.The upgrade output should look similar to the following:
... Installed agents: - clusterWide [deployment - standalone mode] - perNode [daemonset - standalone mode] Installed integrations: - kubernetes [built-in chart integration] - system [built-in chart integration] ...To review the full contents of the installed release, run:
helm get manifest demo
You’ve upgraded your configuration to run without the kube-state-metrics service. You can similarly upgrade your agent to change other settings defined in the in the Elastic Agent values.yaml file.
By default Elastic Agent runs under the elastic user account. For some use cases you may want to temporarily change an agent to run with higher privileges.
Run the
kubectl get pods -n defaultcommand to view the running Elastic Agent pods:NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE agent-clusterwide-demo-7b5df89b75-sfhd7 1/1 Running 0 14m agent-pernode-demo-fm6tr 1/1 Running 0 14m agent-pernode-demo-hh6xb 1/1 Running 0 14m agent-pernode-demo-szrp9 1/1 Running 0 14mNow, run the
kubectl execcommand to enter one of the running Elastic Agents, substituting the correct pod name returned from the previous command. For example:kubectl exec -it pods/agent-pernode-demo-fm6tr -- bashFrom inside the pod, run the Linux
ps auxcommand to view the running processes.ps auxThe results should be similar to the following:
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND elastic+ 1 0.0 0.0 1936 416 ? Ss 21:04 0:00 /usr/bin/tini -- /usr/local/bin/docker-entrypoint -c /etc/elastic-agent/agent.yml -e elastic+ 10 0.2 1.3 2555252 132804 ? Sl 21:04 0:13 elastic-agent container -c /etc/elastic-agent/agent.yml -e elastic+ 37 0.6 2.0 2330112 208468 ? Sl 21:04 0:37 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E elastic+ 38 0.2 1.7 2190072 177780 ? Sl 21:04 0:13 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat filebeat -E se elastic+ 56 0.1 1.7 2190136 175896 ? Sl 21:04 0:11 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E elastic+ 68 0.1 1.8 2190392 184140 ? Sl 21:04 0:12 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E elastic+ 78 0.7 2.0 2330496 204964 ? Sl 21:04 0:48 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat filebeat -E se elastic+ 535 0.0 0.0 3884 3012 pts/0 Ss 22:47 0:00 bash elastic+ 543 0.0 0.0 5480 2360 pts/0 R+ 22:47 0:00 ps auxIn the command output, Elastic Agent is currently running as the
elasticuser:elastic+ 10 0.2 1.3 2555252 132804 ? Sl 21:04 0:13 elastic-agent container -c /etc/elastic-agent/agent.yml -eRun
exitto leave the Elastic Agent pod.Run the
helm upgradecommand again, this time adding the parameter--set agent.unprivileged=falseto override the defaulttruevalue for that setting.helm upgrade demo elastic/elastic-agent \ --set kubernetes.enabled=true \ --set system.enabled=true \ --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI \ --set outputs.default.url=<ES-endpoint>:443 \ --set outputs.default.api_key="API_KEY" \ --set agent.unprivileged=falseRun the
kubectl get pods -n defaultcommand to view the running Elastic Agent pods:NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE agent-clusterwide-demo-77c65f6c7b-trdms 1/1 Running 0 5m18s agent-pernode-demo-s6s7z 1/1 Running 0 5m18s agent-pernode-demo-v6rf8 1/1 Running 0 5m18s agent-pernode-demo-6zx8l 1/1 Running 0 5m18sRe-run the
kubectl execcommand to enter one of the running Elastic Agents, substituting the correct pod name. For example:kubectl exec -it pods/agent-pernode-demo-s6s7z -- bashFrom inside the pod, run the Linux
ps auxcommand to view the running processes.USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.0 0.0 1936 452 ? Ss 23:10 0:00 /usr/bin/tini -- /usr/local/bin/docker-entrypoint -c /etc/elastic-agent/agent.yml -e root 9 0.9 1.3 2488368 135920 ? Sl 23:10 0:01 elastic-agent container -c /etc/elastic-agent/agent.yml -e root 27 0.9 1.9 2255804 203128 ? Sl 23:10 0:01 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E root 44 0.3 1.8 2116148 187432 ? Sl 23:10 0:00 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E root 64 0.3 1.8 2263868 188892 ? Sl 23:10 0:00 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat metricbeat -E root 76 0.4 1.8 2190136 190972 ? Sl 23:10 0:00 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat filebeat -E se root 100 1.2 2.0 2256316 207692 ? Sl 23:10 0:01 /usr/share/elastic-agent/data/elastic-agent-d99b09/components/agentbeat filebeat -E se root 142 0.0 0.0 3752 3068 pts/0 Ss 23:12 0:00 bash root 149 0.0 0.0 5480 2376 pts/0 R+ 23:13 0:00 ps auxRun
exitto leave the Elastic Agent pod.
You’ve upgraded the Elastic Agent privileges to run as root. To change the settings back, you can re-run the helm upgrade command with --set agent.unprivileged=true to return to the default unprivileged mode.
After you’ve run through this example, run the helm uninstall command to uninstall Elastic Agent.
helm uninstall demo
The uninstall should be confirmed as shown:
release "demo" uninstalled
For full details about using the Elastic Agent Helm chart, refer to the Elastic Agent Helm Chart Readme.
Refer to the examples section of the GitHub repository for advanced use cases.