Email connector and action
The email connector uses the SMTP protocol to send mail messages. Email message text is sent as both plain text and html text.
- For emails to have a footer with a link back to Kibana, set the
server.publicBaseUrlconfiguration setting. - When the
xpack.actions.email.domain_allowlistconfiguration setting is used, the email addresses used for all of the Sender (from), To, CC, and BCC properties must have email domains specified in the configuration setting.
You can create connectors in Stack Management > Connectors or as needed when you’re creating a rule. For example:
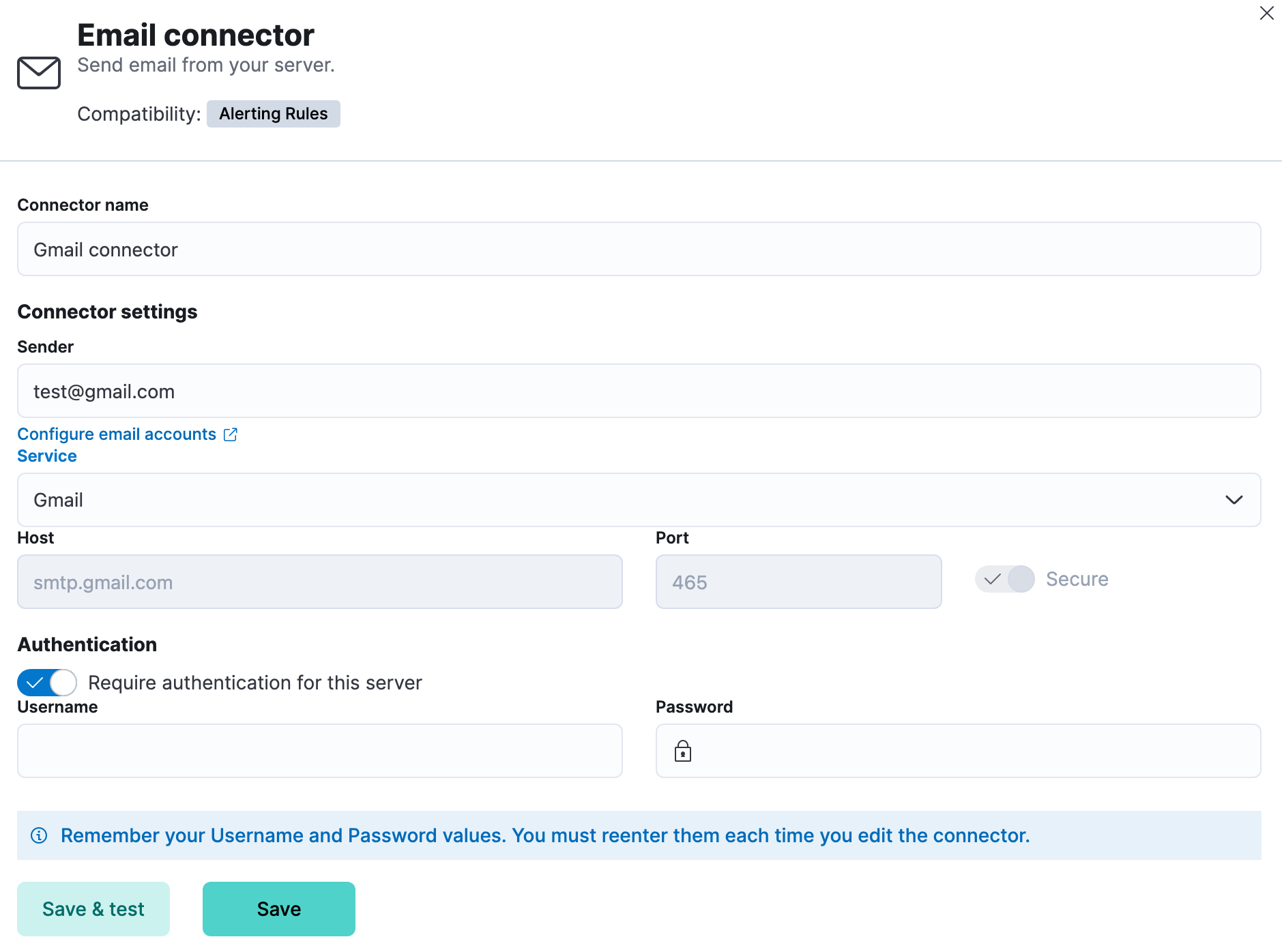
Email connectors have the following configuration properties:
- Name
- The name of the connector. The name is used to identify a connector in the management UI connector listing, or in the connector list when configuring an action.
- Sender
- The from address for all emails sent with this connector. This must be specified in
user@host-nameformat. See the Nodemailer address documentation for more information. - Service
- The name of the email service. If
serviceis one of Nodemailer’s well-known email service providers, thehost,port, andsecureproperties are defined with the default values and disabled for modification. IfserviceisMS Exchange Server, thehost,port, andsecureproperties are ignored andtenantId,clientId,clientSecretare required instead. Ifserviceisother, thehostandportproperties must be defined. - Host
- Host name of the service provider. If you are using the
xpack.actions.allowedHostssetting, make sure this hostname is added to the allowed hosts. - Port
- The port to connect to on the service provider.
- Secure
- If true, the connection will use TLS when connecting to the service provider. Refer to the Nodemailer TLS documentation for more information. If not true, the connection will initially connect over TCP, then attempt to switch to TLS via the SMTP STARTTLS command.
- Tenant ID
- The directory tenant that the application plans to operate against, in GUID format.
- Client ID
- The application ID that is assigned to your app, in GUID format. You can find this information in the portal where you registered your app.
- Client Secret
- The client secret that you generated for your app in the app registration portal. The client secret must be URL-encoded before being sent. The Basic auth pattern of providing credentials in the Authorization header, per RFC 6749, is also supported.
- Require authentication
- If true, a username and password for login type authentication must be provided.
- Username
- Username for login type authentication.
- Password
- Password for login type authentication.
You can test connectors as you're creating or editing the connector in Kibana. For example:
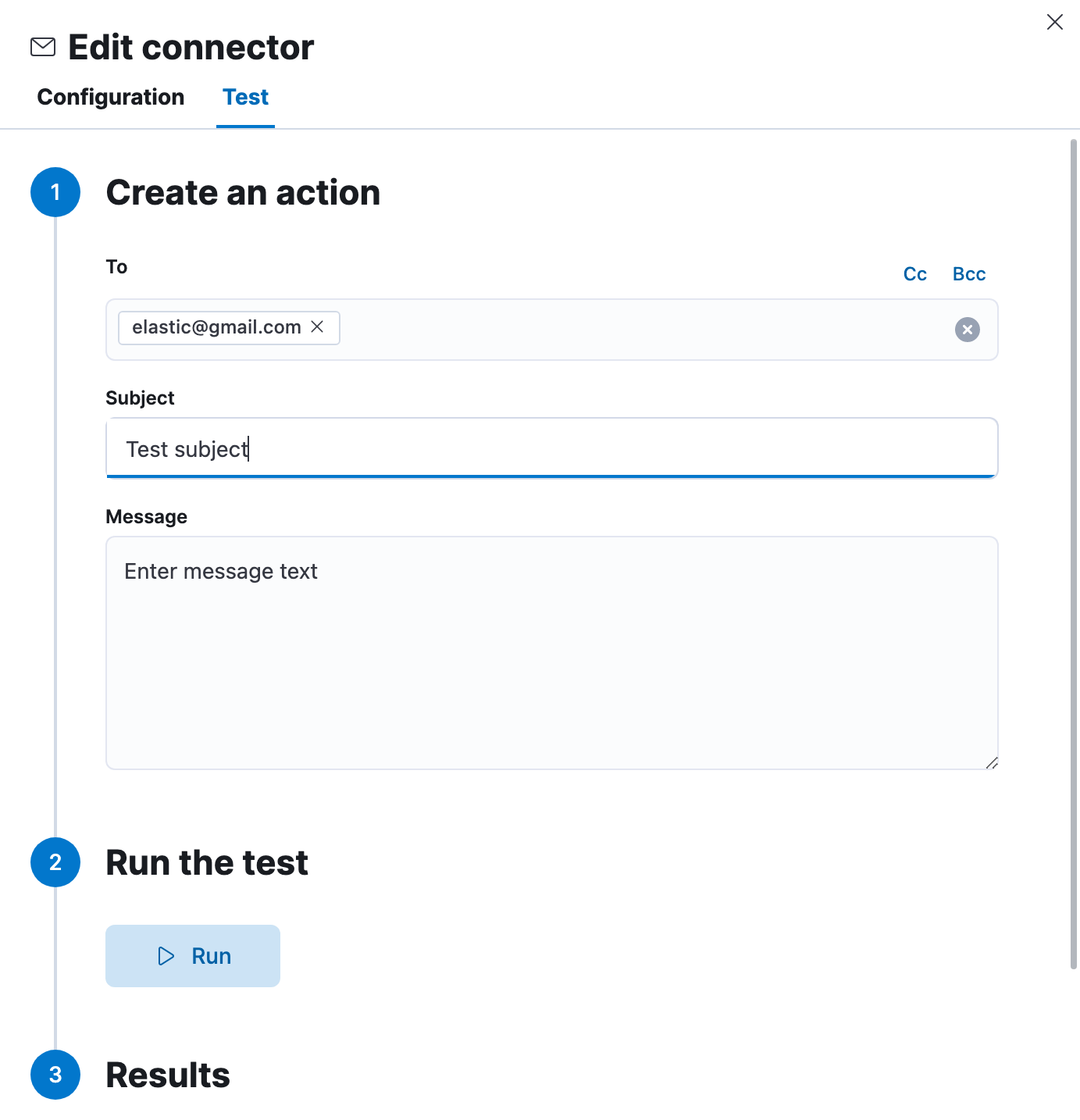
Email actions have the following configuration properties.
- To, CC, BCC
- Each item is a list of addresses. Addresses can be specified in
user@host-nameformat, inname <user@host-name>format, or using Mustache templates. One of To, CC, or BCC must contain an entry. - Subject
- The subject line of the email.
- Message
- The message text of the email. Markdown format is supported.
Use the Action configuration settings to customize connector networking configurations, such as proxies, certificates, or TLS settings. You can set configurations that apply to all your connectors or use xpack.actions.customHostSettings to set per-host configurations.
The email connector uses an integration of Nodemailer to send email from many popular SMTP email services. For Microsoft Exchange email, it uses the Microsoft Graph API.
For other email servers, you can check the list of well-known services that Nodemailer supports in the JSON file well-known/services.json. The properties of the objects in those files — host, port, and secure — correspond to the same email connector configuration properties. A missing secure property in the "well-known/services.json" file is considered false. Typically, port: 465 uses secure: true, and port: 25 and port: 587 use secure: false.
Use the preconfigured email connector (Elastic-Cloud-SMTP) to send emails from Elastic Cloud.
For more information on the preconfigured email connector, see Elastic Cloud email service limits.
To create a connector that sends email from the Gmail SMTP service, set the Service to Gmail.
If you get an authentication error that indicates that you need to continue the sign-in process from a web browser when the action attempts to send email, you need to configure Gmail to allow less secure apps to access your account.
If two-step verification is enabled for your account, you must generate and use a unique App Password to send email from Kibana. See Sign in using App Passwords for more information.
To create a connector that sends email from the Outlook.com SMTP service, set the Service to Outlook.
When sending emails, you must provide a from address, either as the default in your connector configuration or as part of the email action in the rule.
You must use a unique App Password if two-step verification is enabled. See App passwords and two-step verification for more information.
To create a connector that sends email from the Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) SMTP service, set the Service to Amazon SES.
You must use your Amazon SES SMTP credentials to send email through Amazon SES. For more information, see Obtaining Your Amazon SES SMTP Credentials. You might also need to verify your email address or your whole domain at AWS.
To prepare for the removal of Basic Auth, you must update all existing Microsoft Exchange connectors with the new configuration based on the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Authentication.
The email connector uses Microsoft Graph REST API v1.0, in particular the sendMail endpoint. It supports only the Microsoft Graph global service root endpoint (https://graph.microsoft.com).
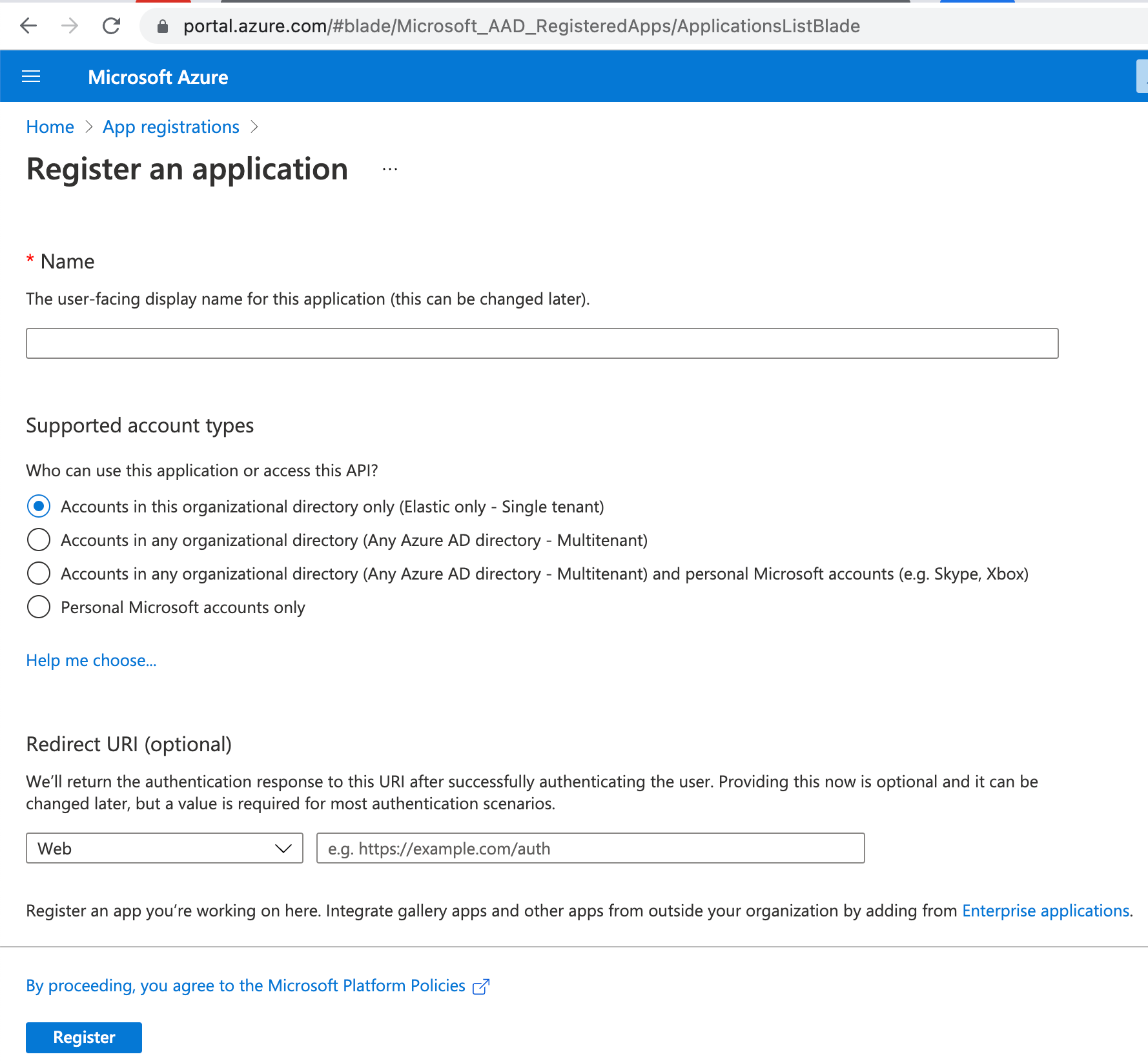
Before you create an email connector for Microsoft Exchange, you must create and register the client integration application on the Azure portal:
Next, open Manage > API permissions, and then define the permissions for the registered application to send emails. Refer to the documentation for the Microsoft Graph API.
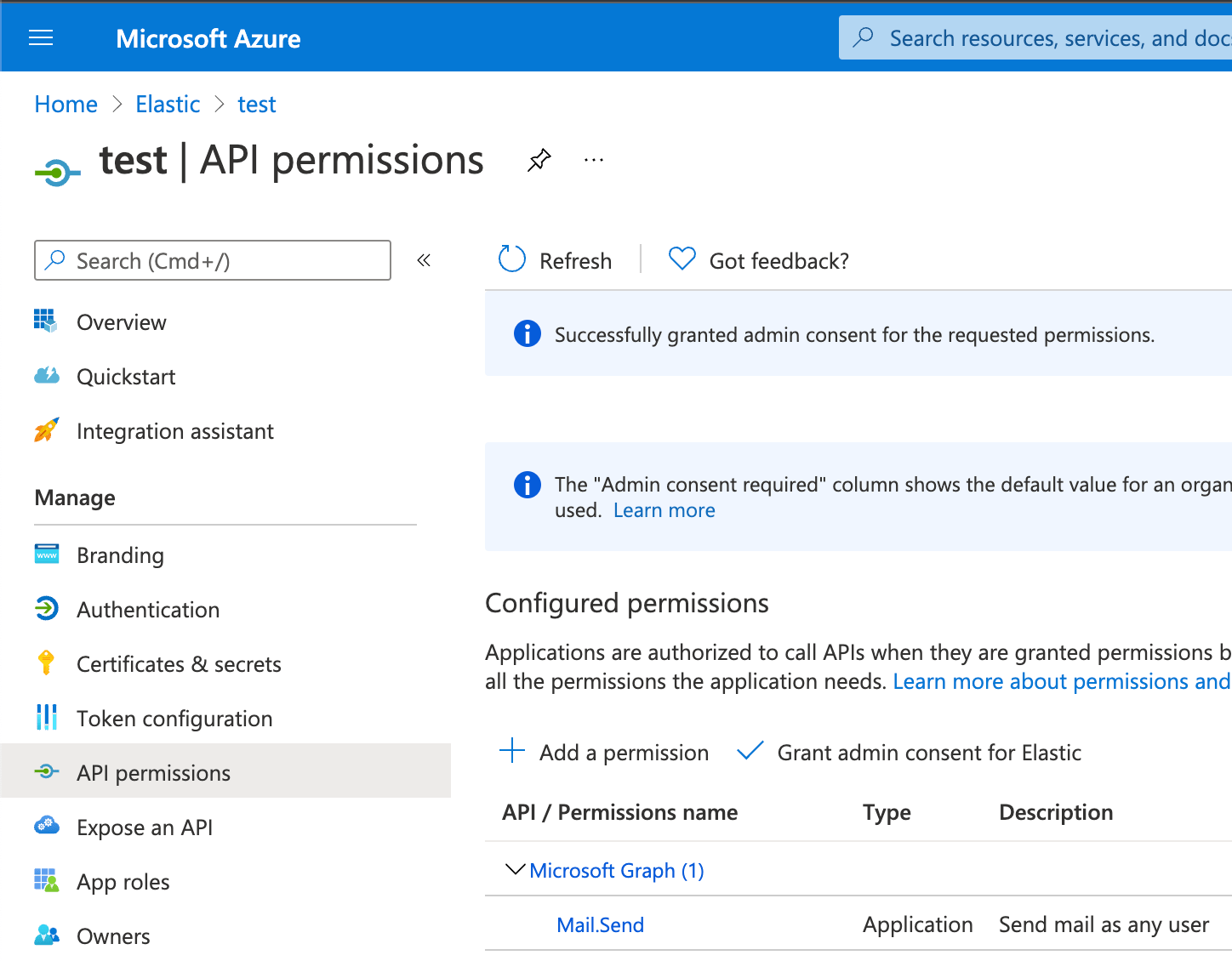
Add the "Mail.Send" permission for Microsoft Graph. The permission appears in the list with the status "Not granted for <your Azure active directory>":
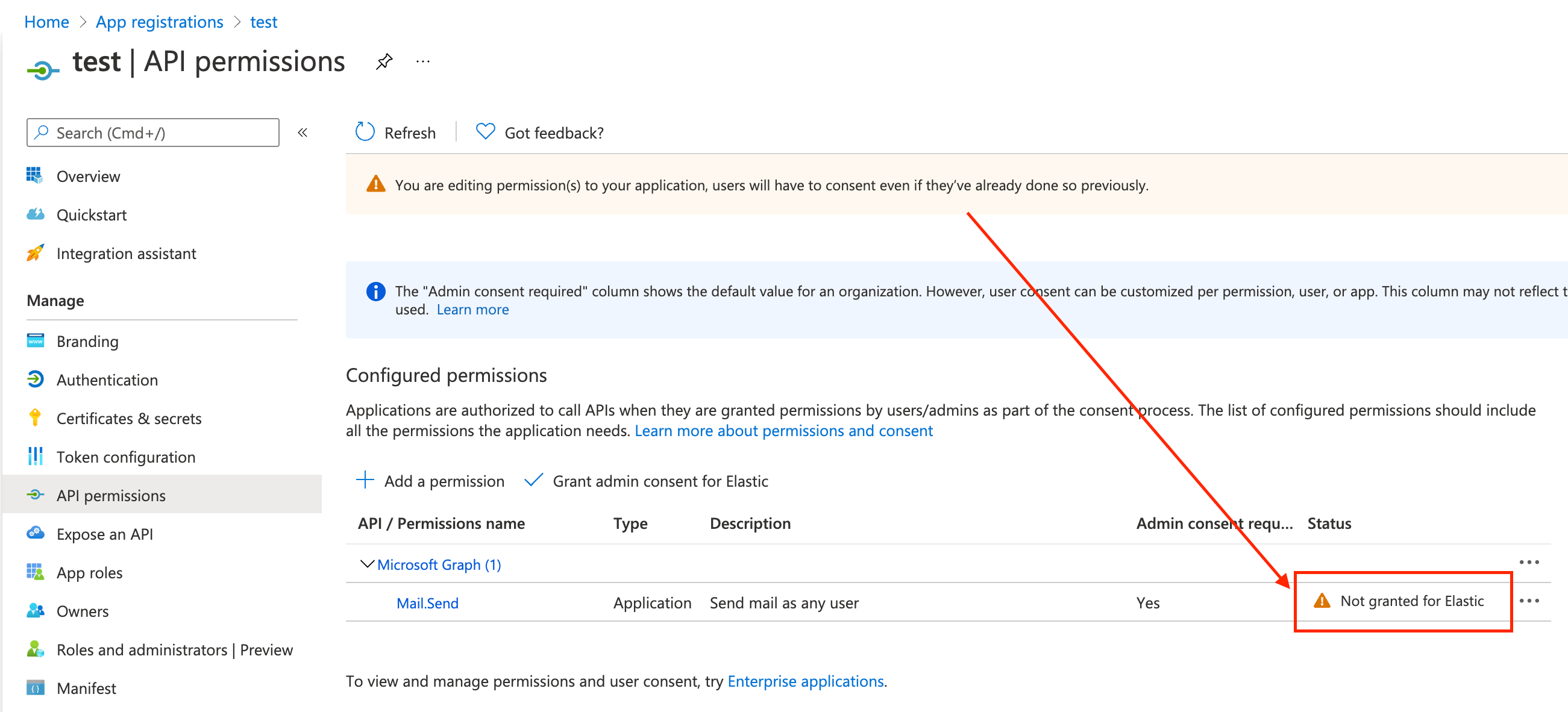
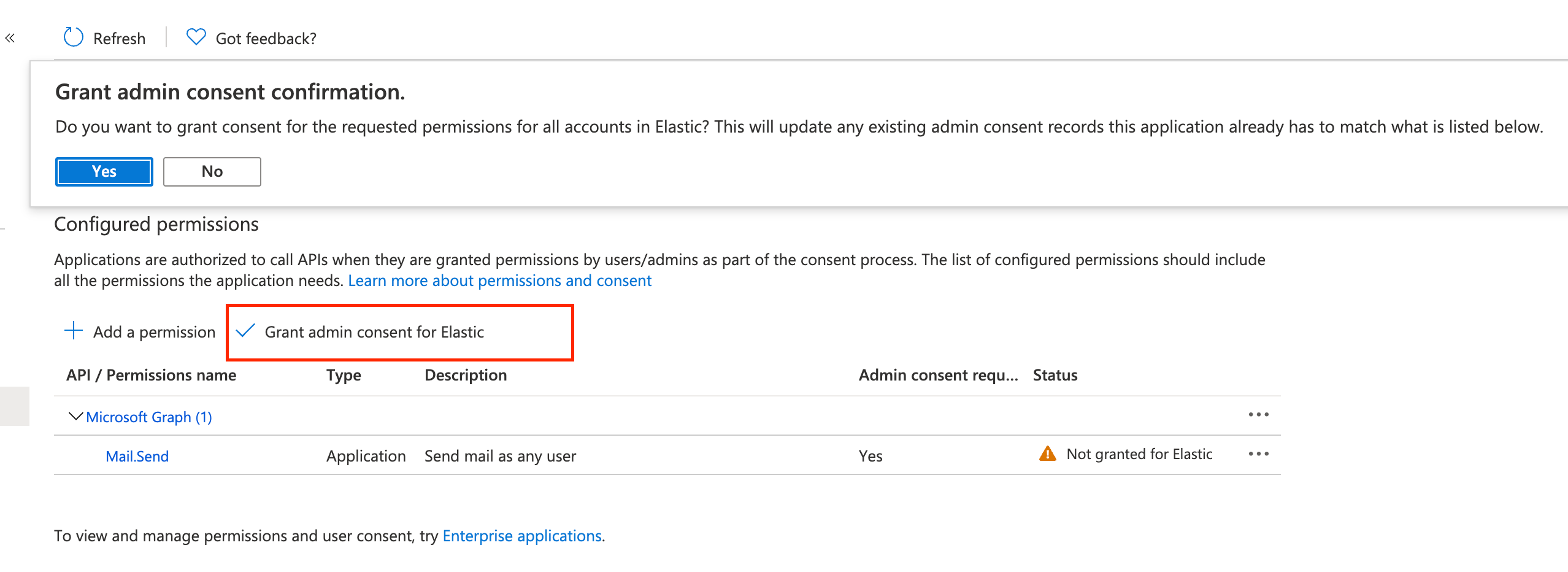
Click Grant admin consent for <your Azure active directory>.
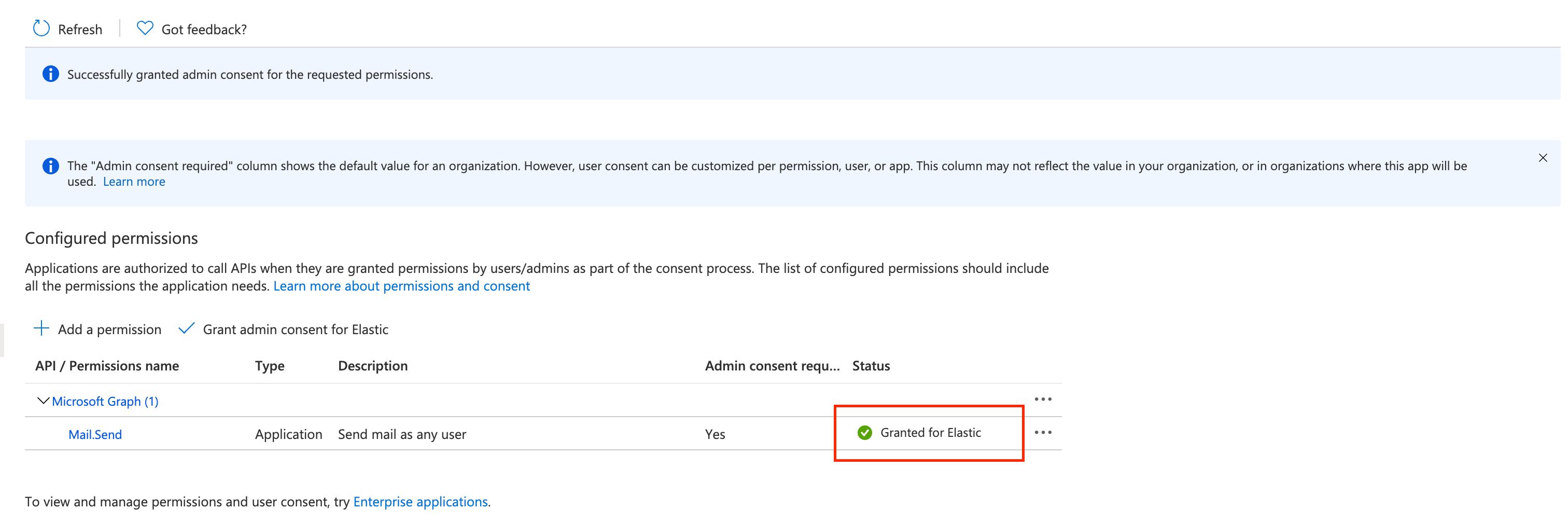
Confirm that the status for the "Mail.Send" permission is now granted.
To configure the Microsoft Exchange Client secret, open Manage > Certificates & secrets:
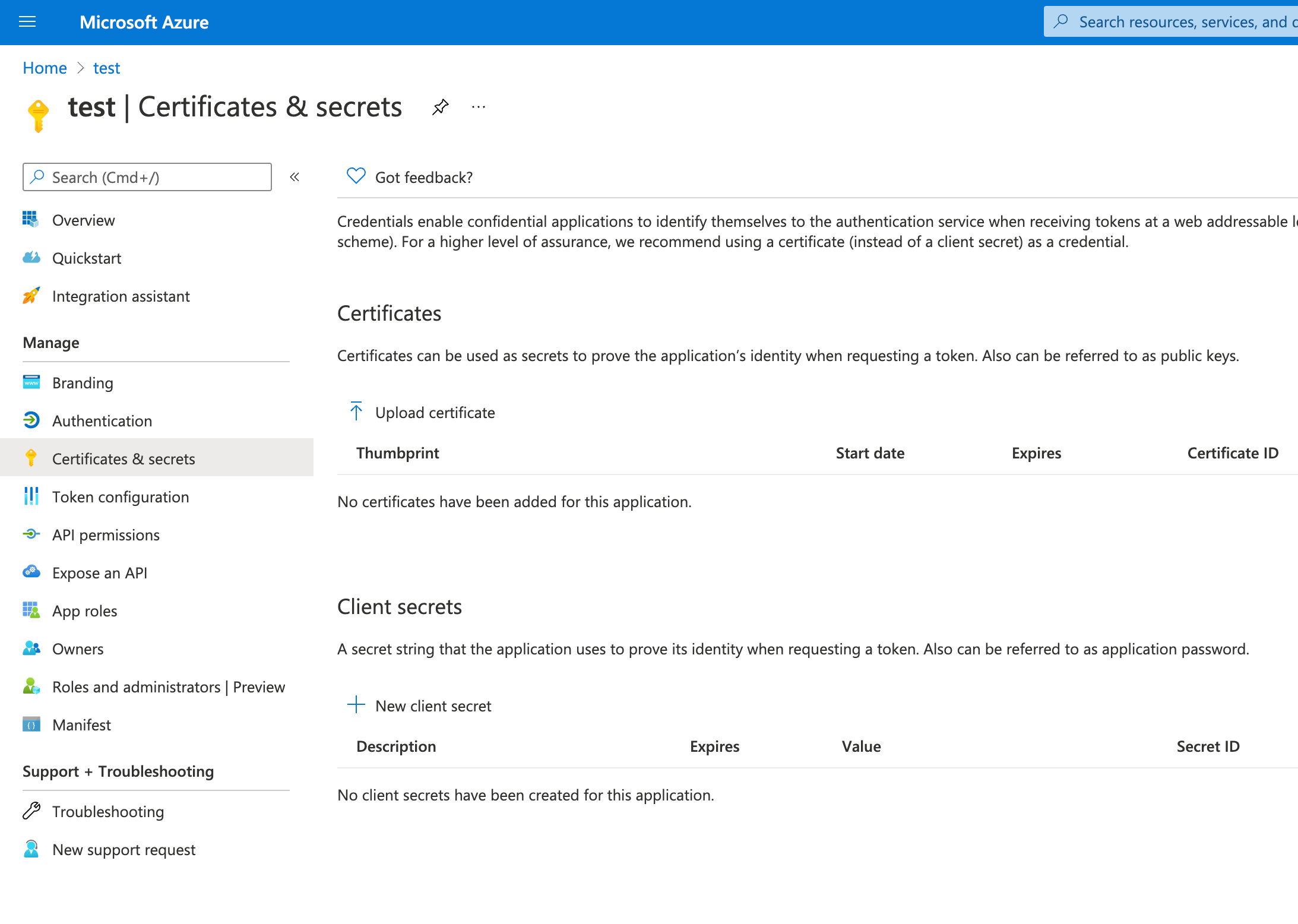
Add a new client secret, then copy the value and put it to the proper field in the Microsoft Exchange email connector.
To find the Microsoft Exchange client and tenant IDs, open the Overview page:
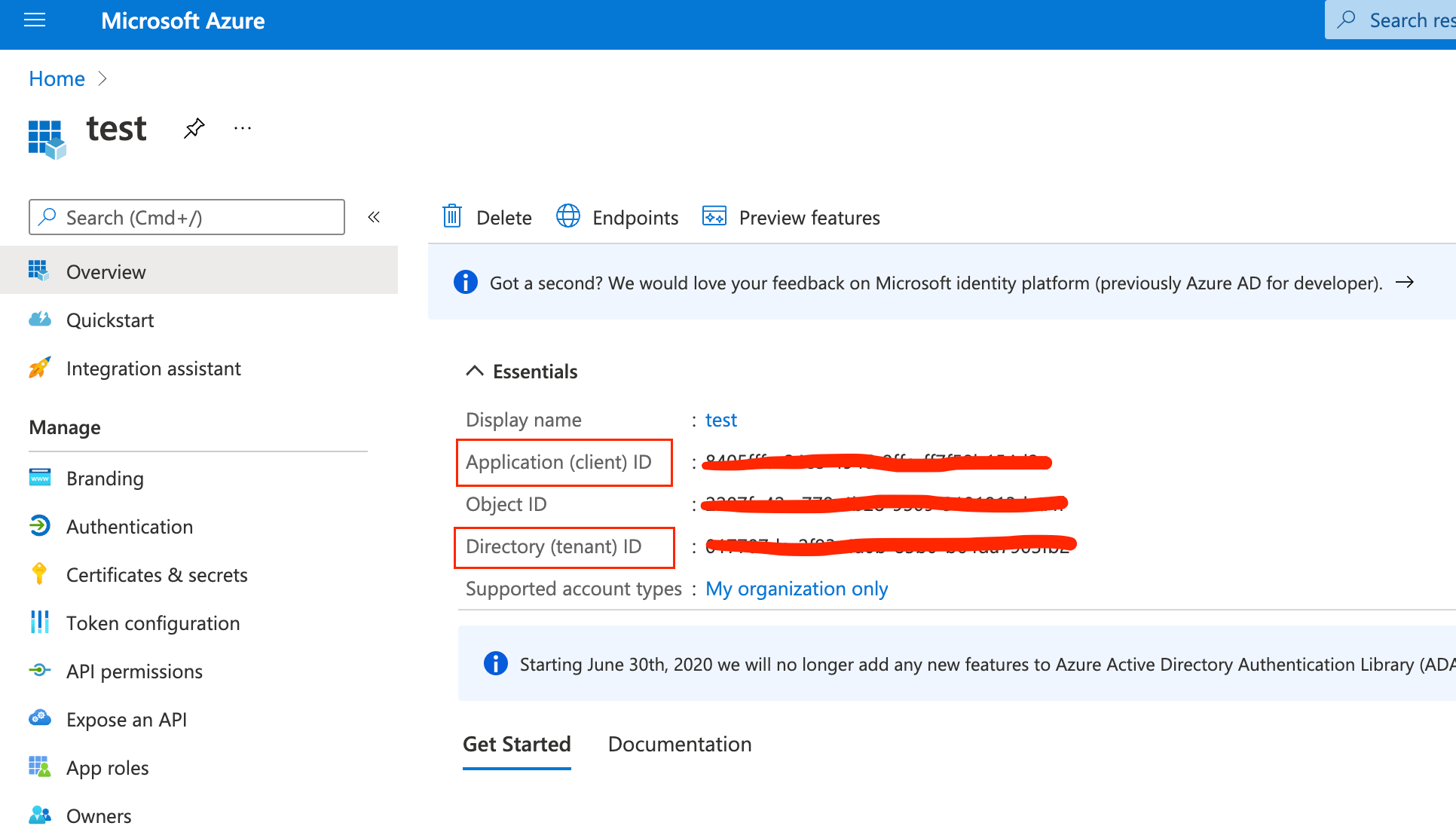
Create a connector and set the Service to MS Exchange Server. Copy and paste the values into the proper fields.