Deploy Fleet Server on-premises and Elasticsearch on Elastic Cloud
To use Fleet for central management, a Fleet Server must be running and accessible to your hosts.
Another approach is to deploy a cluster of Fleet Servers on-premises and connect them back to Elastic Cloud with access to Elasticsearch and Kibana. In this deployment model, you are responsible for high-availability, fault-tolerance, and lifecycle management of Fleet Server.
This approach might be right for you if you would like to limit the control plane traffic out of your data center. For example, you might take this approach if you are a managed service provider or a larger enterprise that segregates its networks.
This approach might not be right for you if you don’t want to manage the life cycle of an extra compute resource in your environment for Fleet Server to reside on.
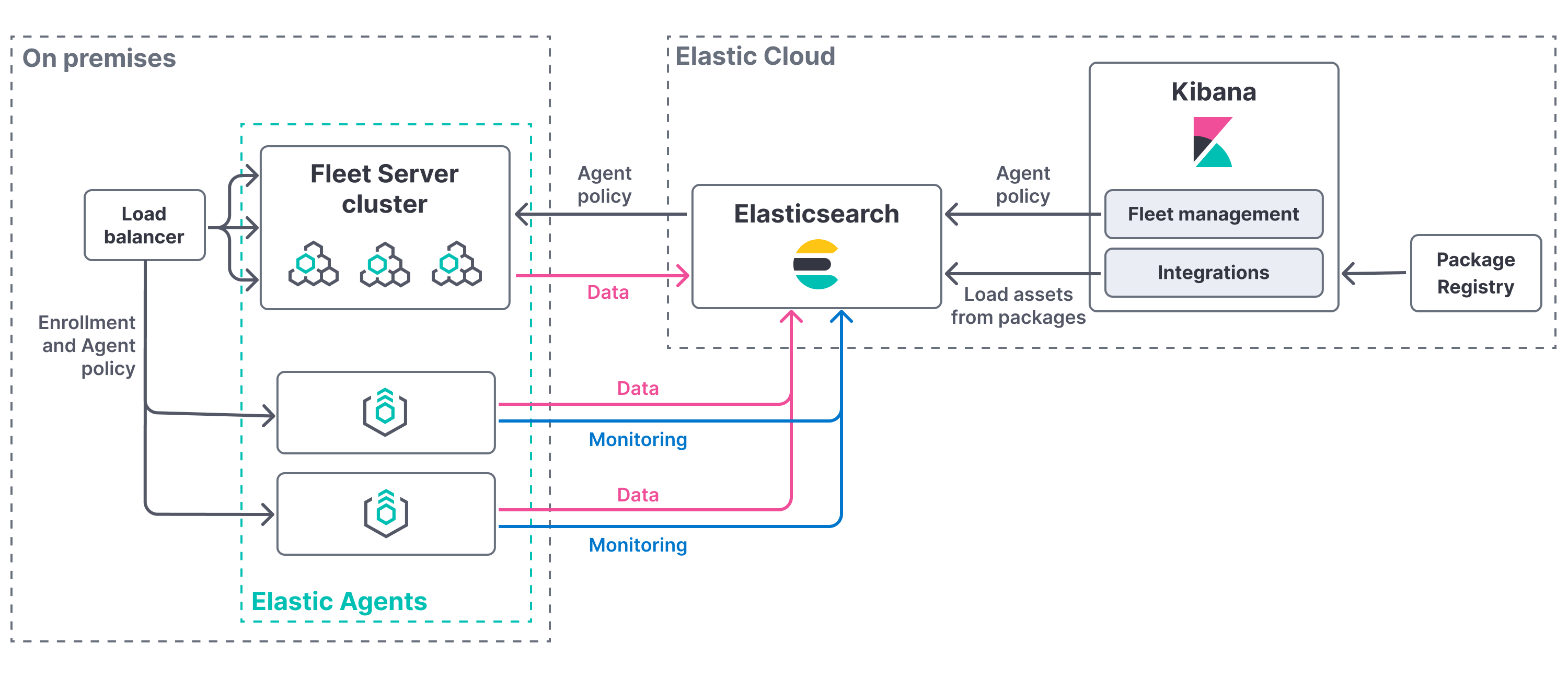
To deploy a self-managed Fleet Server on-premises to work with an Elastic Cloud Hosted deployment, you need to:
- Satisfy all compatibility requirements and prerequisites
- Create a Fleet Server policy
- Add Fleet Server by installing an Elastic Agent and enrolling it in an agent policy containing the Fleet Server integration
Fleet Server is compatible with the following Elastic products:
Elastic Stack 7.13 or later
- For version compatibility, Elasticsearch must be at the same or a later version than Fleet Server, and Fleet Server needs to be at the same or a later version than Elastic Agent (not including patch releases).
- Kibana should be on the same minor version as Elasticsearch
Elastic Cloud Enterprise 2.9 or later—allows you to use a hosted Fleet Server on Elastic Cloud.
- Requires additional wildcard domains and certificates (which normally only cover
*.cname, not*.*.cname). This enables us to provide the URL for Fleet Server ofhttps://.fleet.. - The deployment template must contain an Integrations Server node.
For more information about hosting Fleet Server on Elastic Cloud Enterprise, refer to Manage Integrations Server in Elastic Cloud Enterprise.
- Requires additional wildcard domains and certificates (which normally only cover
Before deploying, you need to:
- Obtain or generate a Cerfiticate Authority (CA) certificate.
- Ensure components have access to the default ports needed for communication.
Before setting up Fleet Server using this approach, you will need a CA certificate to configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt traffic between the Fleet Servers and the Elastic Stack.
If your organization already uses the Elastic Stack, you may already have a CA certificate. If you do not have a CA certificate, you can read more about generating one in Configure SSL/TLS for self-managed Fleet Servers.
This is not required when testing and iterating using the Quick start option, but should always be used for production deployments.
When Elasticsearch or Fleet Server are deployed, components communicate over well-defined, pre-allocated ports. You may need to allow access to these ports. See the following table for default port assignments:
| Component communication | Default port |
|---|---|
| Elastic Agent → Fleet Server | 8220 |
| Elastic Agent → Elasticsearch | 443 |
| Elastic Agent → Logstash | 5044 |
| Elastic Agent → Kibana (Fleet) | 443 |
| Fleet Server → Kibana (Fleet) | 443 |
| Fleet Server → Elasticsearch | 443 |
If you do not specify the port for Elasticsearch as 443, the Elastic Agent defaults to 9200.
First, create a Fleet Server policy. The Fleet Server policy manages and configures the Elastic Agent running on the Fleet Server host to launch a Fleet Server process.
To create a Fleet Server policy:
In Fleet, open the Agent policies tab.
Click on the Create agent policy button, then:
- Provide a meaningful name for the policy that will help you identify this Fleet Server (or cluster) in the future.
- Ensure you select Collect system logs and metrics so the compute system hosting this Fleet Server can be monitored. (This is not required, but is highly recommended.)
After creating the Fleet Server policy, navigate to the policy itself and click Add integration.
Search for and select the Fleet Server integration.
Then click Add Fleet Server.
Configure the Fleet Server:
- Expand Change default. Because you are deploying this Fleet Server on-premises, you need to enter the Host address and Port number,
8220. (In our example the Fleet Server will be installed on the host10.128.0.46.) - It’s recommended that you also enter the Max agents you intend to support with this Fleet Server. This can also be modified at a later stage. This will allow the Fleet Server to handle the load and frequency of updates being sent to the agent and ensure a smooth operation in a bursty environment.
- Expand Change default. Because you are deploying this Fleet Server on-premises, you need to enter the Host address and Port number,
Now that the policy exists, you can add Fleet Servers.
A Fleet Server is an Elastic Agent that is enrolled in a Fleet Server policy. The policy configures the agent to operate in a special mode to serve as a Fleet Server in your deployment.
To add a Fleet Server:
In Fleet, open the Agents tab.
Click Add Fleet Server.
This will open in-product instructions for adding a Fleet Server using one of two options. Choose Advanced.
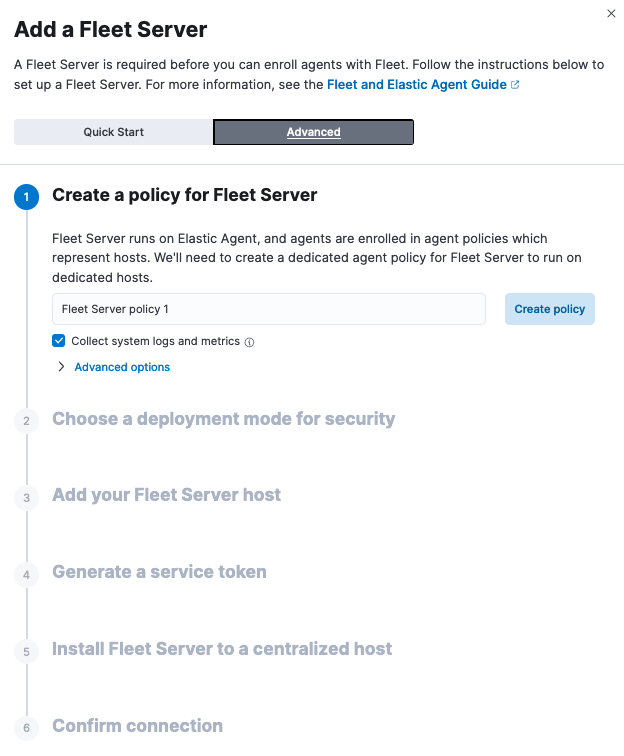
Follow the in-product instructions to add a Fleet Server.
Select the agent policy that you created for this deployment.
Choose Production as your deployment mode.
Production mode is the fully secured mode where TLS certificates ensure a secure communication between Fleet Server and Elasticsearch.
Open the Fleet Server Hosts dropdown and select Add new Fleet Server Hosts. Specify one or more host URLs your Elastic Agents will use to connect to Fleet Server. For example,
https://192.0.2.1:8220, where192.0.2.1is the host IP where you will install Fleet Server.A Service Token is required so the Fleet Server can write data to the connected Elasticsearch instance. Click Generate service token and copy the generated token.
Copy the installation instructions provided in Kibana, which include some of the known deployment parameters.
Replace the value of the
--certificate-authoritiesparameter with your CA certificate.
If installation is successful, a confirmation indicates that Fleet Server is set up and connected.
After Fleet Server is installed and enrolled in Fleet, the newly created Fleet Server policy is applied. You can see this on the Fleet Server policy page.
The Fleet Server agent will also show up on the main Fleet page as another agent whose life-cycle can be managed (like other agents in the deployment).
You can update your Fleet Server configuration in Kibana at any time by going to: Management → Fleet → Settings. From there you can:
- Update the Fleet Server host URL.
- Configure additional outputs where agents will send data.
- Specify the location from where agents will download binaries.
- Specify proxy URLs to use for Fleet Server or Elastic Agent outputs.
Now you’re ready to add Elastic Agents to your host systems. To learn how, see Install Fleet-managed Elastic Agents.
For on-premises deployments, you can dedicate a policy to all the agents in the network boundary and configure that policy to include a specific Fleet Server (or a cluster of Fleet Servers).
Read more in Add a Fleet Server to a policy.