Trusted applications
If you use Elastic Defend along with other antivirus (AV) software, you might need to configure the other system to trust Elastic Endpoint. Refer to Allowlist Elastic Endpoint in third-party antivirus apps for more information.
You can add Windows, macOS, and Linux applications that should be trusted, such as other antivirus or endpoint security applications. Trusted applications are designed to help mitigate performance issues and incompatibilities with other endpoint software installed on your hosts. Trusted applications apply only to hosts running the Elastic Defend integration.
To ensure you're using the right feature for your use case, we recommend reviewing Optimize Elastic Defend to understand the differences between trusted applications and alert exceptions.
You must have the Trusted Applications privilege or the appropriate user role to access this feature.
Trusted applications create blindspots for Elastic Defend, because the applications are no longer monitored for threats. One avenue attackers use to exploit these blindspots is by DLL (Dynamic Link Library) side-loading, where they leverage processes signed by trusted vendors — such as antivirus software — to execute their malicious DLLs. Such activity appears to originate from the trusted application’s process.
Trusted applications might still generate alerts in some cases, such as if the application’s process events indicate malicious behavior. To reduce false positive alerts, add an Endpoint alert exception, which prevents Elastic Defend from generating alerts. To compare trusted applications with other endpoint artifacts, refer to Optimize Elastic Defend.
Additionally, trusted applications still generate process events for visualizations and other internal use by the Elastic Stack. To prevent process events from being written to Elasticsearch, use an event filter to filter out the specific events that you don’t want stored in Elasticsearch, but be aware that features that depend on these process events may not function correctly.
By default, a trusted application is recognized globally across all hosts running Elastic Defend. You can also assign a trusted application to a specific Elastic Defend integration policy, enabling the application to be trusted by only the hosts assigned to that policy.
To add a trusted application:
Find Trusted applications in the navigation menu or use the global search field.
Click Add trusted application.
Fill in these fields in the Details section:
Name: Enter a name for the trusted application.Description(Optional): Enter a description for the trusted application.
Select an option in the Conditions section:
Define conditions based on the application's hash, executable path, or signer.
Select operating system: Select the appropriate operating system from the drop-down.Field: Select a field to identify the trusted application:Hash: The MD5, SHA-1, or SHA-256 hash value of the application’s executable.Path: The full file path of the application’s executable.Signature: (Windows and macOS only) The name of the application’s digital signer.TipTo find the signer’s name for an application, go to Discover and query the process name of the application’s executable (for example,
process.name : "mctray.exe"for a McAfee security binary). Then, search the results for theprocess.code_signature.subject_namefield, which contains the signer’s name (for example,McAfee, Inc.).
Operator: Select an operator to define the condition:is: Must be exactly equal toValue; wildcards are not supported. This operator is required for theHashandSignaturefield types.matches: Can include wildcards inValue, such asC:\path\*\app.exe. This option is only available for thePathfield type. Available wildcards are?(match one character) and*(match zero or more characters).NoteUnlike detection rule exceptions, trusted applications do not require escaping special characters.
Value: Enter the hash value, file path, or signer name. To add an additional value, click AND.NoteYou can only add a single field type value per trusted application. For example, if you try to add two
Pathvalues, you’ll get an error message. Also, an application’s hash value must be valid to add it as a trusted application. In addition, to minimize visibility gaps in the Elastic Security app, be as specific as possible in your entries. For example, combineSignatureinformation with a knownPath.
Define more complex conditions, such as trusting specific file paths or remote IP addresses.
Select operating system: Select the appropriate operating system from the drop-down.(Optional) Turn on the Process Descendants toggle to make your exception apply to processes that are descendants of your new trusted application. Field: Select a field to identify the trusted application.Operator: Select an operator to define the condition:isis notis one ofis not one ofmatches|does not match: Allows you to use wildcards inValue, such asC:\path\*\app.exe. Available wildcards are?(match one character) and*(match zero or more characters).NoteUnlike detection rule exceptions, trusted applications do not require escaping special characters.
ImportantUsing wildcards can impact performance. To create a more efficient trusted application using wildcards, use multiple conditions and make them as specific as possible. For example, adding conditions using
process.nameorfile.namecan help limit the scope of wildcard matching.
Value: Enter the value associated with theField. To enter multiple values (when usingis one oforis not one of), enter each value, then press Return.To define multiple conditions, click
ANDand configure a new condition. You can also add nested conditions by selectingAdd nested condition.
Select an option in the Assignment section to assign the trusted application to a specific integration policy:
Global: Assign the trusted application to all integration policies for Elastic Defend.Per Policy: Assign the trusted application to one or more specific Elastic Defend integration policies. Select each policy in which you want the application to be trusted.NoteYou can also select the
Per Policyoption without immediately assigning a policy to the trusted application. For example, you could do this to create and review your trusted application configurations before putting them into action with a policy.
Click Add trusted application. The application is added to the Trusted applications list.
The Trusted applications page displays all the trusted applications that have been added to the Elastic Security app. To refine the list, use the search bar to search by name, description, or field value.
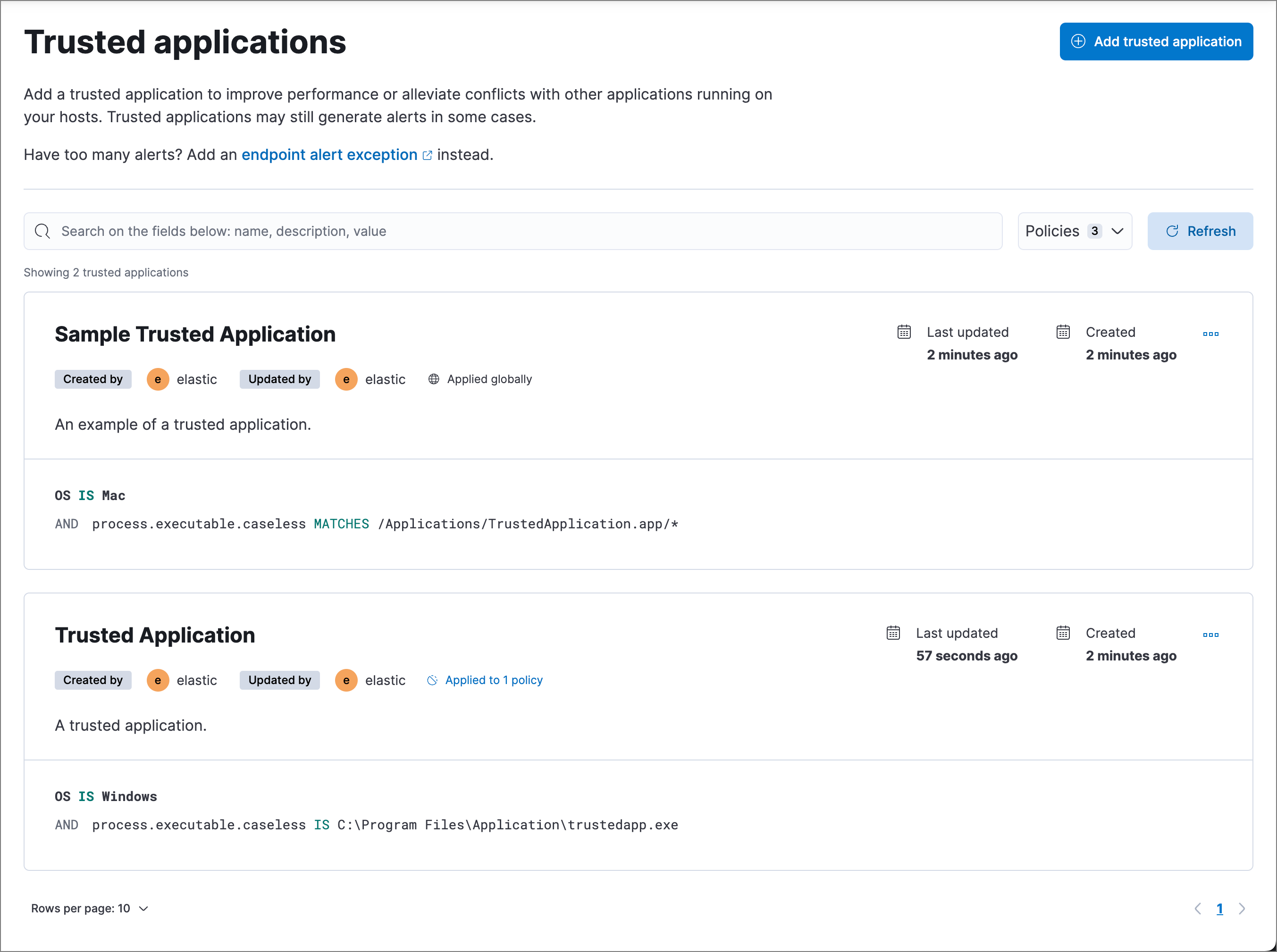
You can individually modify each trusted application. You can also change the policies that a trusted application is assigned to.
To edit a trusted application:
- Click the actions menu (…) on the trusted application you want to edit, then select Edit trusted application.
- Modify details as needed.
- Click Save.
You can delete a trusted application, which removes it entirely from all Elastic Defend integration policies.
To delete a trusted application:
- Click the actions menu (…) on the trusted application you want to delete, then select Delete trusted application.
- On the dialog that opens, verify that you are removing the correct application, then click Delete. A confirmation message appears.