Elastic Search: Add search to your website
Overview
Introduction to Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch provides a range of search techniques, starting with BM25, the industry standard for textual search, ensuring precise keyword matching. It also offers semantic search powered by AI models, improving results based on context and intent.
To get started, the best option is to use Elastic Cloud Serverless, where you can effortlessly scale search without managing infrastructure—just index your data and start searching. To see it in action, check out our walkthrough demo: Launch Demo
Let's get started
How to ingest and enrich data for search
Elasticsearch includes a wide range of data ingestion capabilities that help solve your business challenges. Check out this webinar to:
Learn how to bring disparate data into a single place to create search experiences.
Understand tools to use for your specific types of data, including the Elastic web crawler, catalog of connectors, data and ML inference pipelines, and more.
See live demos using customer support datasets.
Create an Elastic Cloud project
Get started with a 14-day trial. Once you go to cloud.elastic.co and create an account, follow the steps below to learn how to launch your first Elasticsearch Serverless project.
Head over Create Project. Let’s create a Serverless project that is Optimized for Vectors, give it a name and create it.
In this example, we will onboard a live website, the Elasticsearch Labs.
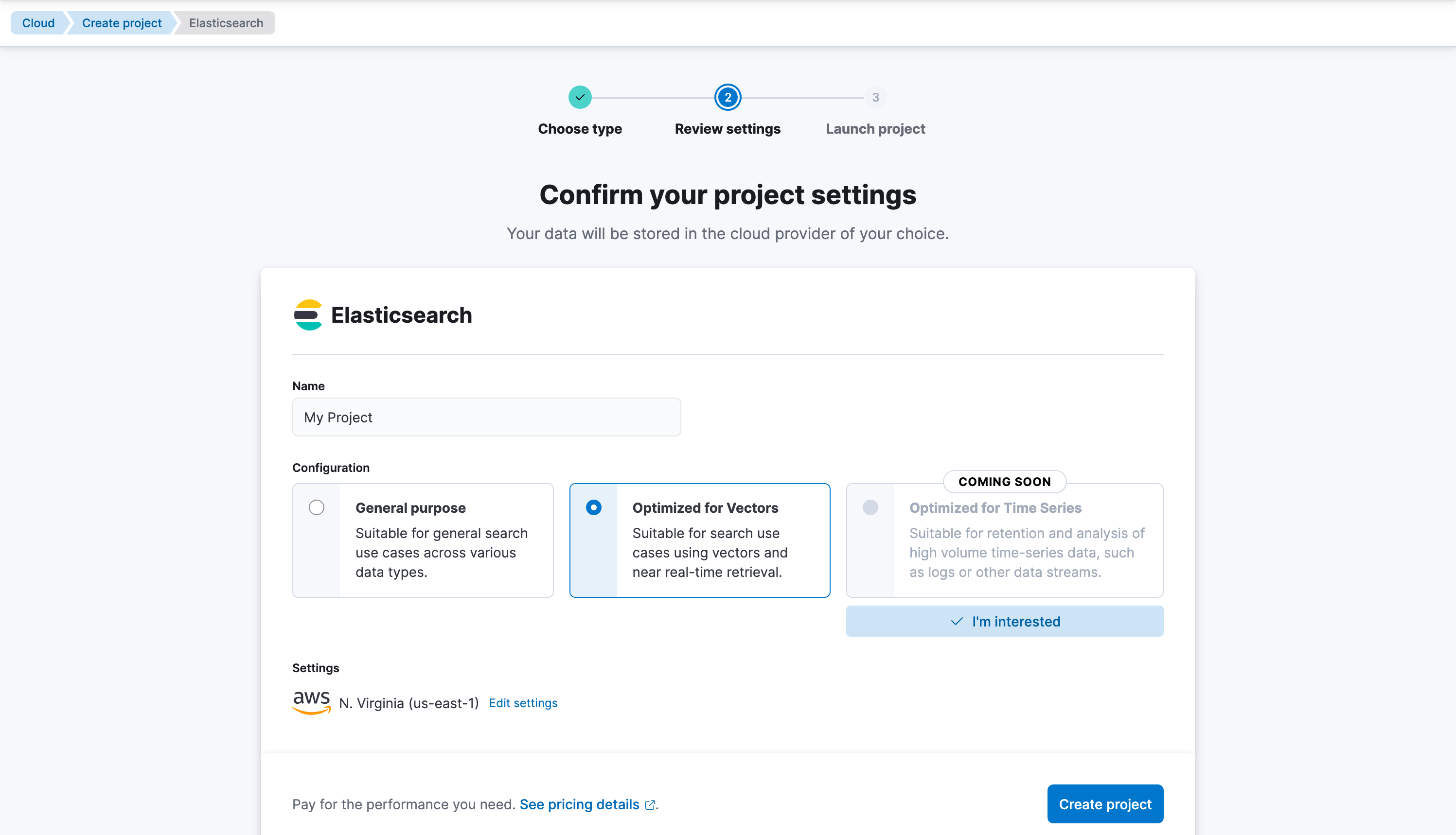
Let’s create our first Elasticsearch index, we can name it elasticsearch-labs-blog. Hit Create my index.
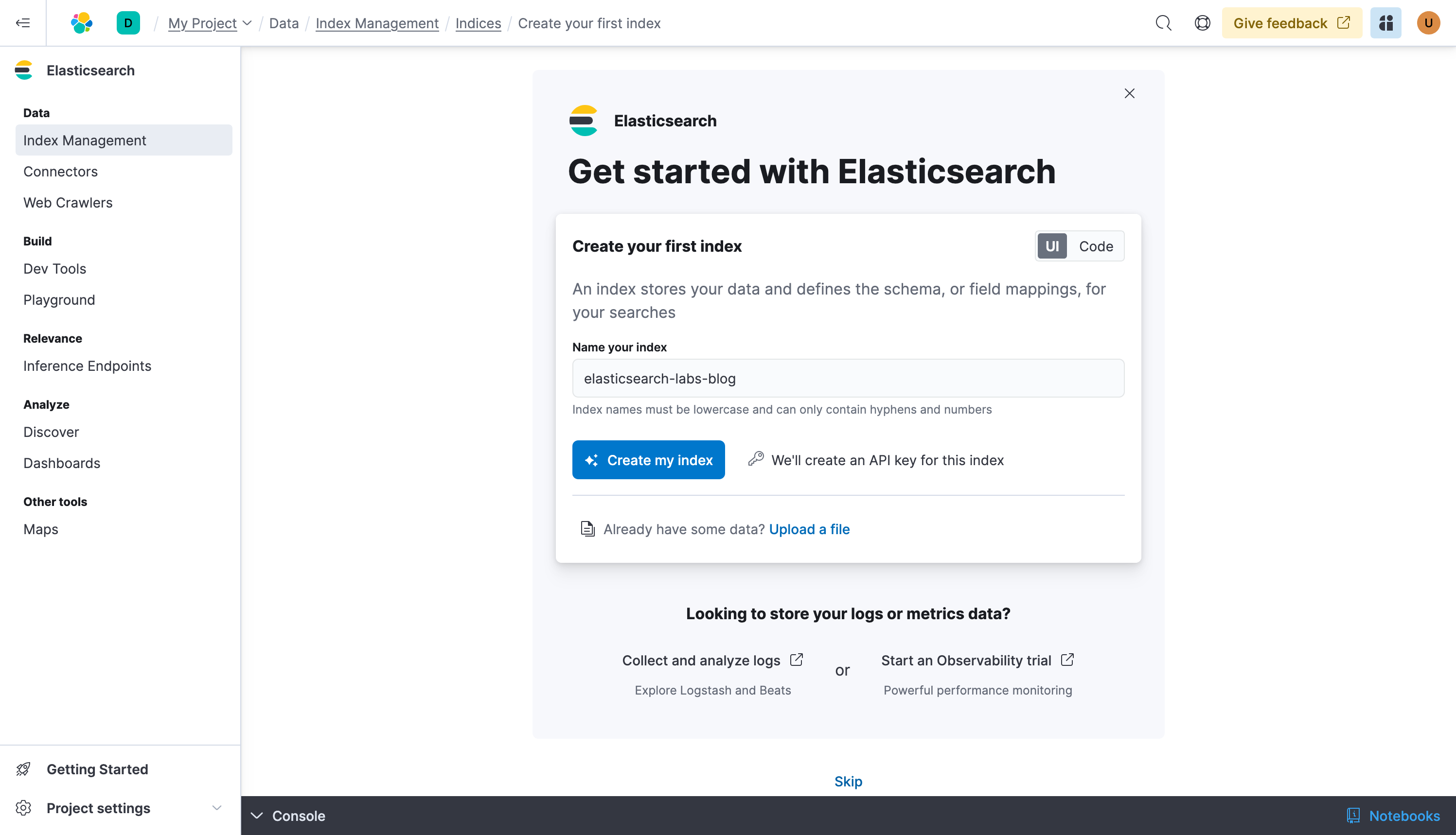
Your index is created, we have now the three things we need:
- The index: our data store
- The Elasticsearch URL: the endpoint to which we will send our data
- The API Key: the easiest of the authentication methods
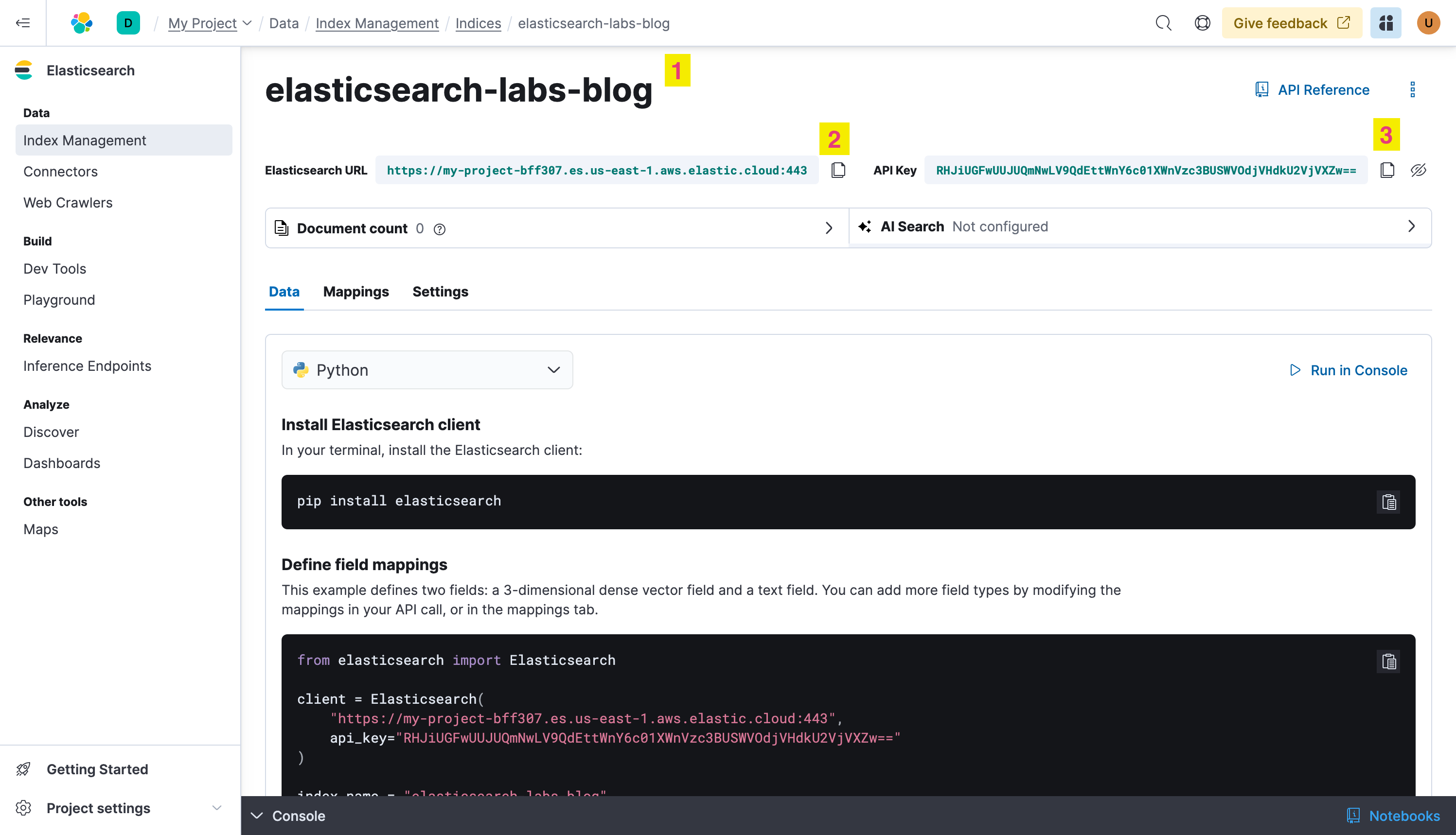
Configure the Elastic Open Web Crawler
You will need Docker to use the Open Web Crawler.
Here is a simple config file, it tells the crawler to read the https://www.elastic.co/search-labs blog and write it to the elasticsearch-labs-blog index at elasticsearch.host using the elasticsearch.api_key
Copy the following content to a file and call it crawler-config-blog.yml , change host and api_key accordingly:
domains:
- url: https://www.elastic.co
seed_urls:
- https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog
crawl_rules:
- policy: allow
type: begins
pattern: /search-labs/blog
- policy: deny
type: regex
pattern: .*
elasticsearch:
host: https://my-project-bff307.es.us-east-1.aws.elastic.cloud
api_key: RHJiUGFwUUJUQmNwLV9QdEttWnY6c01XWnVzc3BUSWVOdjVHdkU2VjVXZw==
pipeline_enabled: false
Now create a docker-compose.yml file:
services:
crawler:
image: docker.elastic.co/integrations/crawler:latest
volumes:
- ./config:/app/config
stdin_open: true
tty: true
and start the service with:
docker-compose up -d
We are ready to start the crawling process:
docker-compose exec -it crawler bin/crawler crawl crawler-config-blog.yml
After a few minutes we should have the whole Elasticsearch labs blogs indexed to elasticsearch-labs-blog
.Working with Elasticsearch
Leverage Vector Search for building search experiences
Are you considering using vector search as part of your search experience? Elastic has two forms of vector search: "dense" (aka, kNN vector search) and "sparse" such as Elastic's Learned Sparse Encoder (ELSER).
Sparse vector search is the simpler option to get started with. Elastic offers an out-of-the-box model, the Learned Sparse Encoder model, for semantic search. This model outperforms on a variety of datasets, such as financial data, weather records, question-answer pairs, among others. The model is built to provide great relevance across domains, without the need for additional fine tuning.
Check out this interactive demo to see how search results are more relevant when you test Elastic's Learned Sparse Encoder model against Elastic's textual BM25 algorithm.
In addition, Elastic also supports kNN vectors to implement similarity search on unstructured data beyond text, such as videos, images, and audio.
The advantage of semantic search and vector search is that these technologies allow customers to use intuitive language in their search queries. For example, if you wanted to search for workplace guidelines on a second income, you could search for “side hustle”, which is not a term you're likely to see in a formal HR document.
For getting started with building a semantic search experience using vector search, check out this step-by-step guide.
Leverage data to improve your search
Once your search experience is up and running, how do you make it better? Take advantage of behavioral analytics to analyze your users' engagement across your websites and applications. You can use this information to improve the relevance of your search results and identify gaps in your content.
Learn how to get started with behavioral analytics with this guided tour.
Next steps
Thanks for taking the time to connect your databases to Elasticsearch with Elastic Cloud. As you begin your journey with Elastic, understand some operational, security, and data components you should manage as a user when you deploy across your environment.
Ready to get started? Spin up a free 14-day trial on Elastic Cloud or try out these hands-on learning on Search AI 101.