How Elastic AI Assistant for Security and Amazon Bedrock can empower security analysts for enhanced performance

Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing natural language processing (NLP), offering enhanced conversational AI experiences for customer service and boosting productivity. To meet enterprise needs, it’s important to ensure the responses that are generated are accurate as well as respect the permissions model associated with the underlying content. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) emerges as a key technique, retrieving relevant information from enterprise knowledge bases.
Enterprises are not only in pursuit of high-performance infrastructure but also a secure platform that unlocks the potential of generative AI without jeopardizing sensitive data and intellectual property. Large language models endeavor to comprehend and generate text that mirrors human language, drawing upon the structure, meaning, and context of natural language.
In this blog post, we will provide an overview of how the Elastic AI Assistant for Security and Amazon Bedrock can help security analysts get started in a matter of minutes to elevate their security team’s posture.
Elastic and AI
Elastic Cloud enables users to search, solve, and succeed with one platform, three search-powered solutions, built on a single technology stack. It is designed for any type of data — deployable anywhere — to solve your search, observability, and security challenges. Elastic® users benefit from a unified data analytics platform, which dramatically reduces the cost and complexity of data collection, storage, and analysis.
The integration of Elastic with advanced AI models elevates its capabilities to new heights. By harnessing Elasticsearch®’s retrieval capabilities, LLMs gain access to the most pertinent documents, enabling them to furnish accurate responses. This collaboration between Elasticsearch and Amazon Bedrock ensures users receive answers that are contextually relevant and factually accurate, setting a benchmark for information retrieval and AI-driven assistance.
Elastic stands as a top notch search engine with a plethora of features designed to guarantee exceptional search performance. It supports conventional keyword and text-based searches using the Elasticsearch Relevance Engine™ (ESRE) and Elastic Learned Sparse EncodeR (ELSER) algorithm, alongside AI-ready vector search capabilities with exact match and approximate kNN (k-Nearest Neighbor) search functionalities. These advanced features empower Elasticsearch to retrieve highly pertinent results for queries expressed in natural language. By combining traditional, vector, or hybrid search approaches, Elasticsearch delivers pinpoint accuracy, simplifying the process for users to locate the information they seek.
The Elasticsearch platform seamlessly integrates robust machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities directly into Elastic solutions like the Elastic AI Assistant for Security, providing the tools to create highly sought-after applications and execute tasks with remarkable efficiency. By leveraging these advanced technologies, users unlock the full potential of Elasticsearch, delivering unparalleled user experiences and streamlining workflows.
Elastic Security
Elastic Security combines security information and event management (SIEM) threat detection features with endpoint prevention and response capabilities in one solution. These analytical and protection capabilities, leveraged by the speed and extensibility of Elasticsearch, enable analysts to defend their organization from threats before damage and loss occur.
Use cases
Below are some of the common tasks performed by a cybersecurity operations team.
Alert investigation: Security analysts investigate alerts to determine their validity and severity. They review the information provided in the alert, such as source IP, destination IP, timestamps, and the nature of the event. Based on the investigation, analysts can decide whether the alert represents a legitimate security incident or a false positive. If it's a real threat, they proceed to incident response.
Incident response: Once an alert is confirmed as a security incident, incident response teams take steps to mitigate the threat. This may involve isolating affected systems, collecting evidence, and coordinating with relevant stakeholders to resolve the incident. The goal is to contain and remediate the incident, minimize damage, and prevent it from escalating.
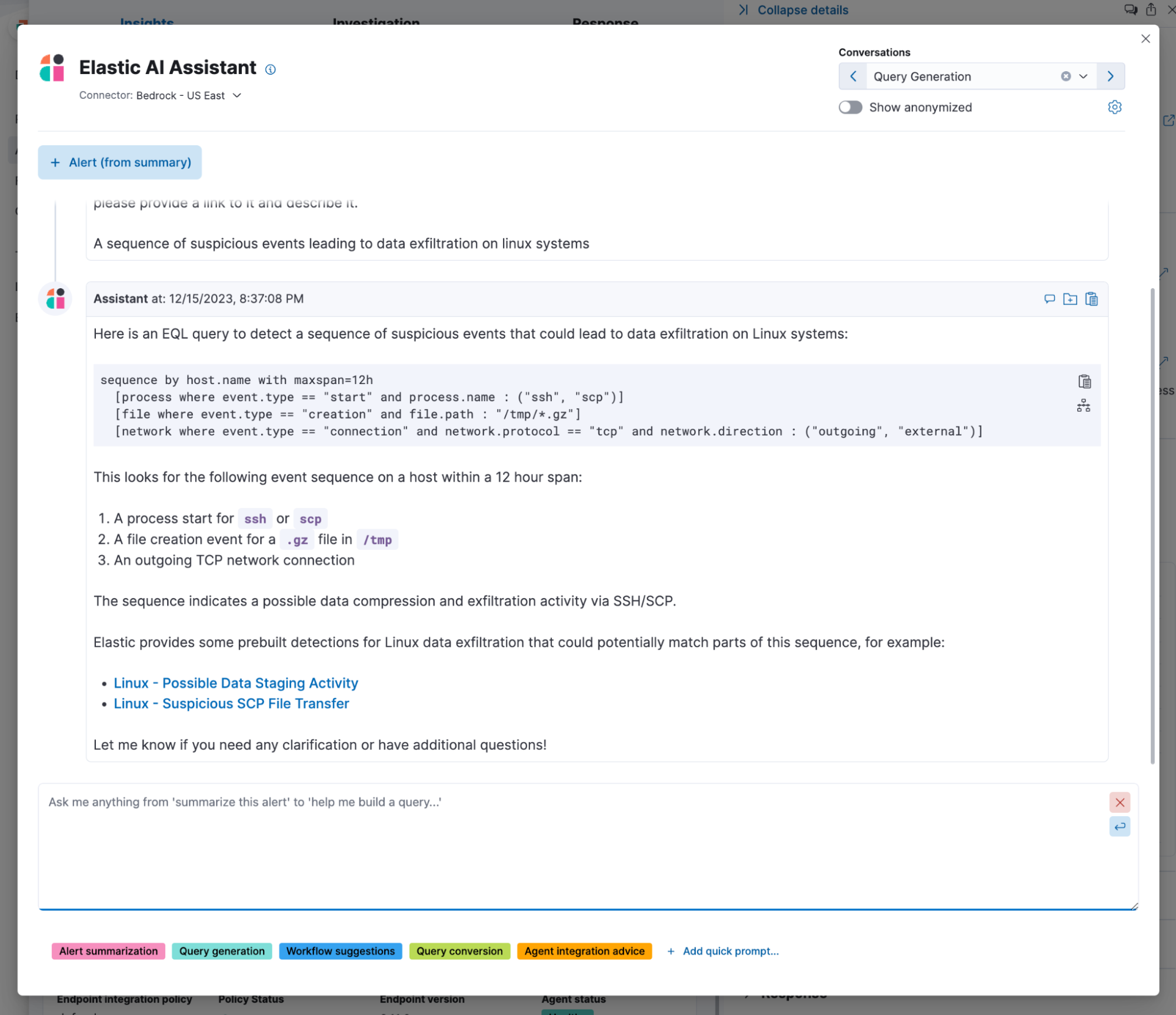
Query generation: Security analysts create custom queries using a SIEM tool's query language or interface to search for specific events or patterns of interest. For example, they might query for all failed login attempts within a specific time frame. Query results provide valuable insights into historical data, helping analysts identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, or patterns of suspicious activity.
Elastic AI Assistant
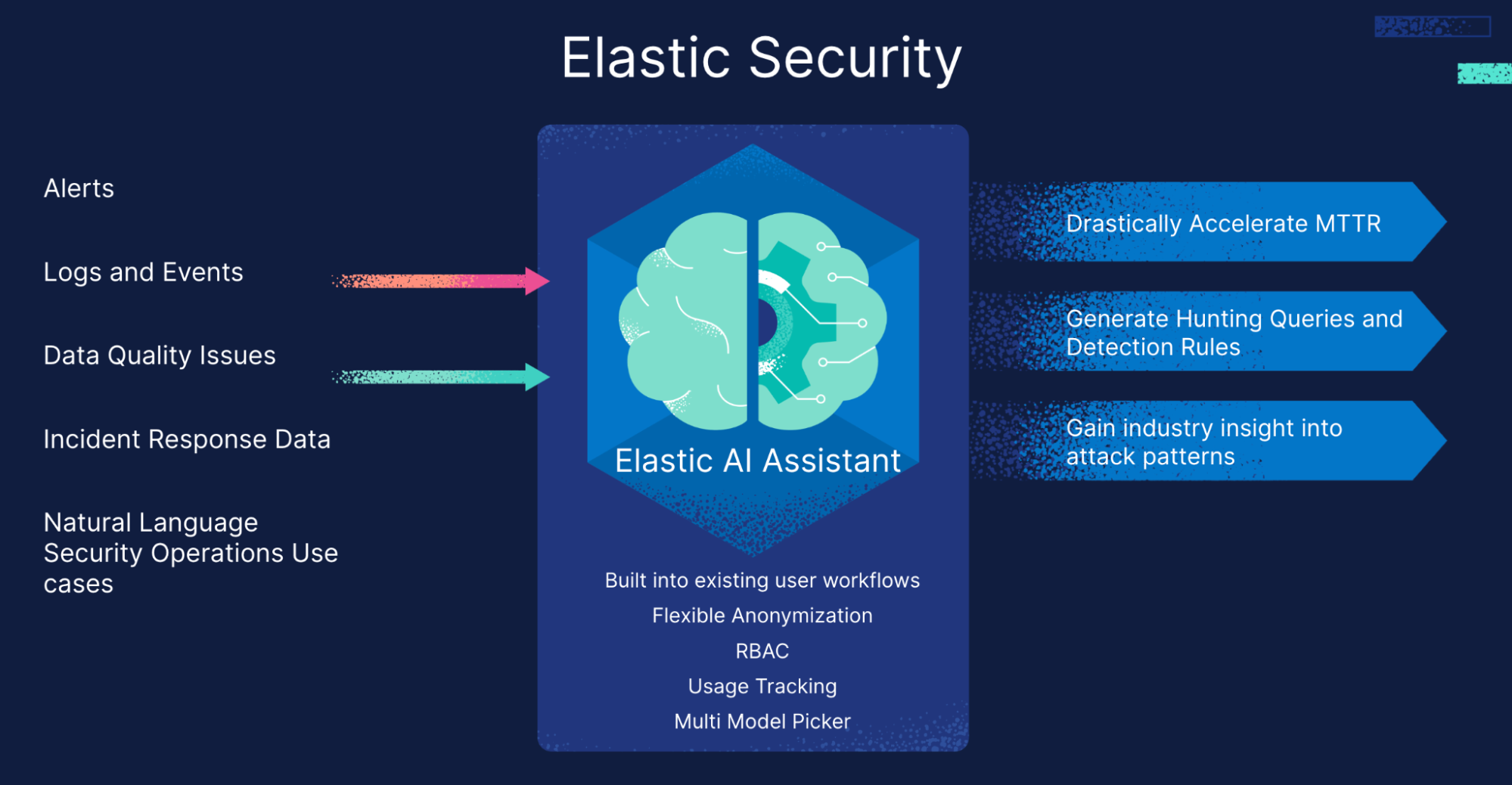
Elastic AI Assistant magnifies this benefit. As an assistant across numerous security use cases, simple built-in prompts allow for use case-specific application, and the freestyle ability provides the power to go beyond what comes prebuilt.
Elastic AI Assistant can be easily invoked with a simple keyboard shortcut or via contextual links in Elastic Security. It offers users prebuilt, recommended prompts as well as specific context for the LLM. Prompts and context are the key to making generative AI applicable to a team. The prompt ensures the answer coming back from the LLM is written for the right user (a tier 1 or 2 security analyst, for example). Users can even create their own prompts to share with their team, allowing Elastic AI Assistant to evolve to best serve a user’s organization. And context is the organization-specific information that tailors the answer to specific problems.
The Elastic AI Assistant bolsters cybersecurity operations teams with generative AI. It allows users to interact with Elastic Security for tasks such as alert investigation, incident response, and query generation or conversion using natural language.
Below are some examples of how the prebuilt prompts in Elastic AI assistant can help to increase the productivity of a cybersecurity operations team:
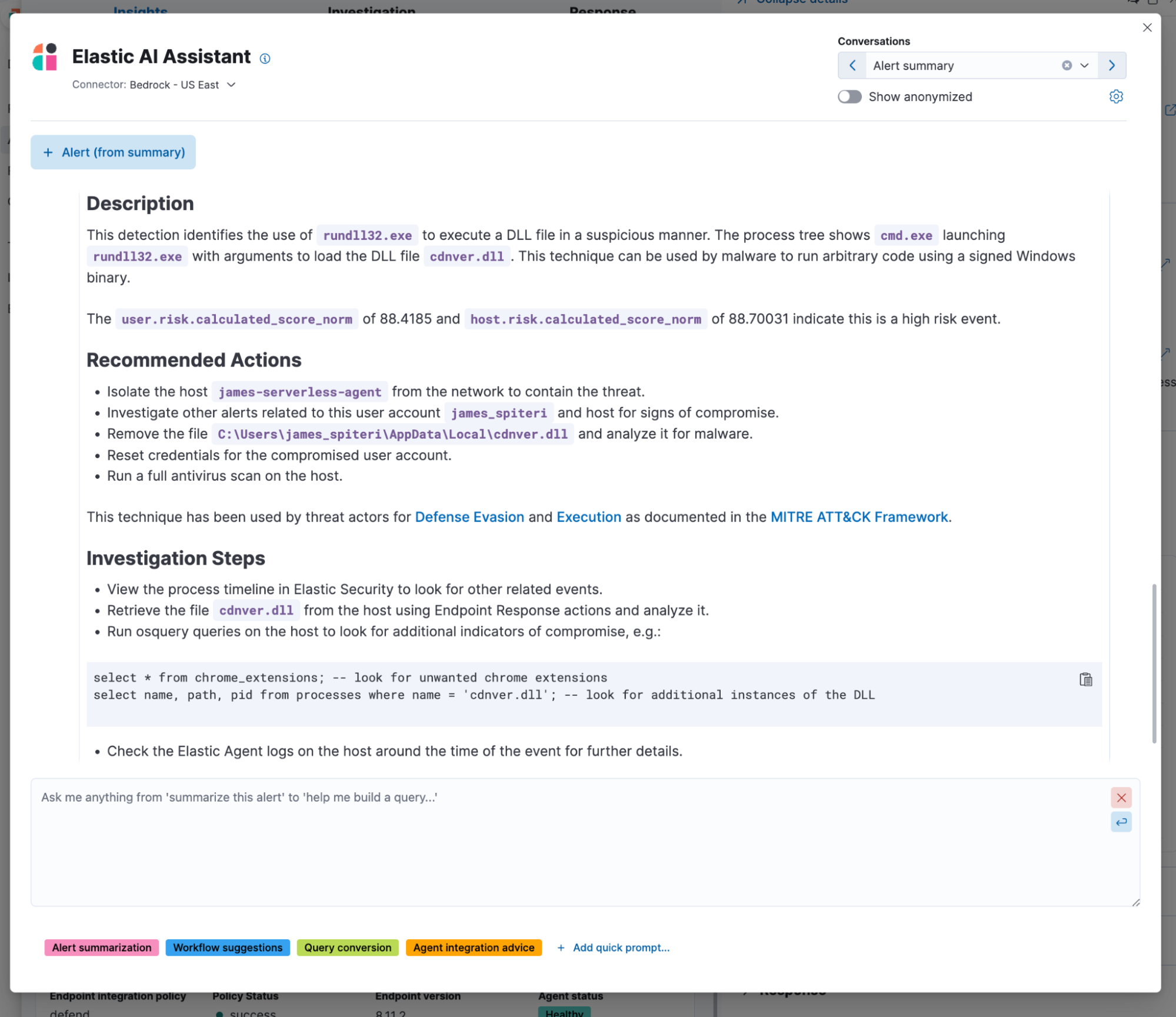
Alert summarization: This prompt provides an alert document as context and returns a detailed description of why the alert triggered and recommended steps to triage and remediate the attack. This type of prompt can generate a dynamic runbook for an organization.
Workflow suggestions: This can provide a step-by-step guide for accomplishing a task within Elastic, such as adding an alert exception or creating a custom dashboard.
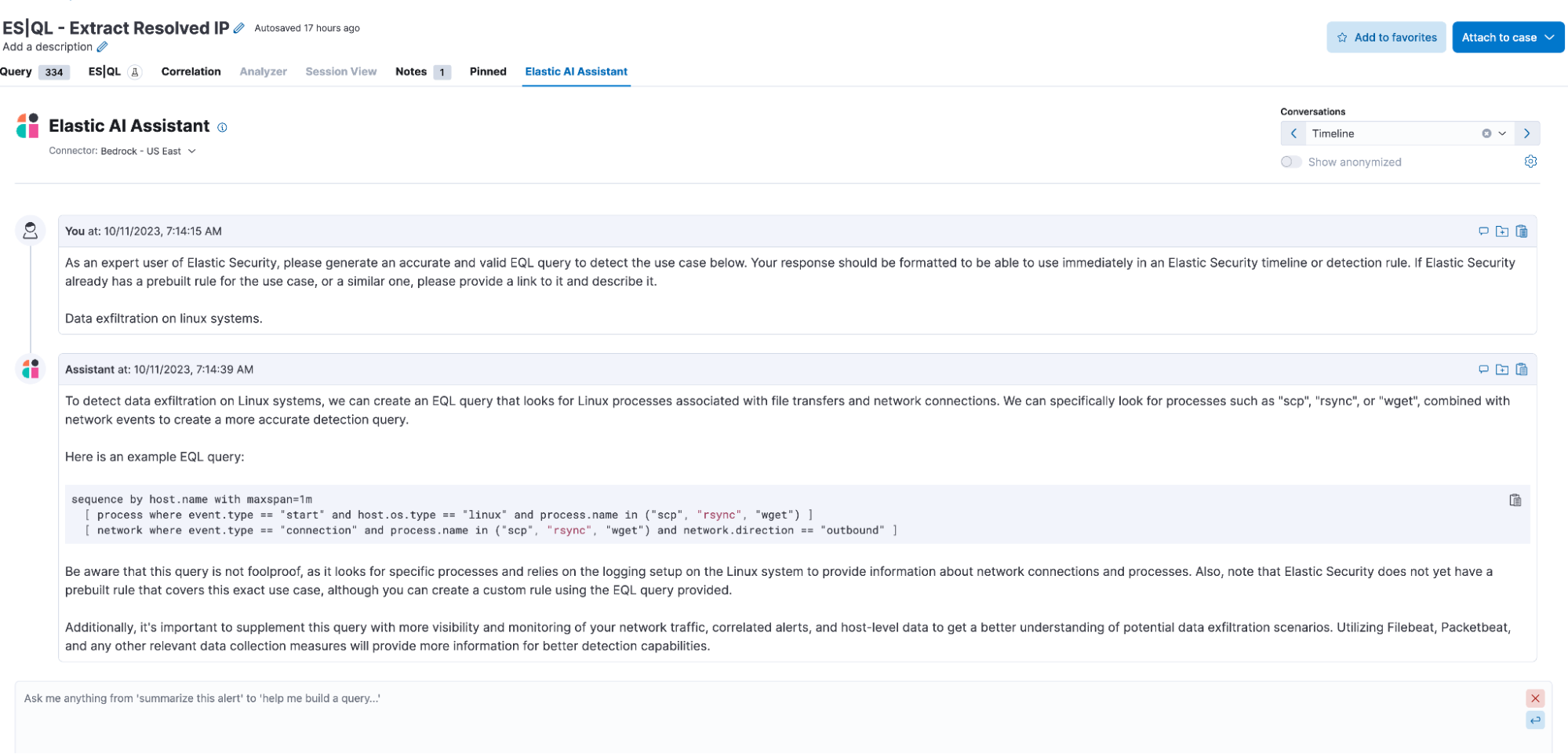
Query conversion: To streamline migration from legacy SIEMs, a user can paste a query from another product and Elastic AI Assistant will convert it into an Elastic query. This process has already been shown to slash the time and cost of SIEM migration.
- Agent integration advice: If a user wants to collect information but is unsure of the best method in Elastic, a user can simply ask Elastic AI Assistant to help.
Integration with Amazon Bedrock
Elastic AI Assistant’s open framework enables users to adapt to the rapidly shifting LLM landscape — easily connecting to new models to facilitate comparison and the adoption of domain-specific models for different applications. Now Elastic users will be able to use large language models through Amazon Bedrock starting with Anthropic Claude 2.
Why Amazon Bedrock?
Amazon Bedrock offers an easy-to-use developer experience to work with a broad range of high-performing foundation models (FMs) from leading AI companies like Anthropic, AI21 Labs, Cohere, Meta, Stability AI, and Amazon. Users can quickly experiment with a variety of FMs in the playground and use a single API for inference regardless of the models they choose, giving them the flexibility to use FMs from different providers and keep up to date with the latest model versions with minimal code changes.
Why Anthropic Claude 2?
Claude 2 is a general-purpose LLM and the most capable system released by Anthropic to date. Claude is based on Anthropic’s research into creating reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI systems. Claude can be used for sophisticated dialogue, creative content generation, complex reasoning, coding, and detailed instruction. It can edit, rewrite, summarize, classify, extract structured data, do Q&A based on the content, and more. Claude is based on Anthropic’s leading safety research and is built with techniques including Constitutional AI. Designed to reduce brand risk, Claude aims to be helpful, honest, and harmless.
This means Claude 2 can read through prolonged log records and surface answers to related security questions.
The role of context
Large language models are astonishing, almost magical. However, to provide an answer that applies well to a specific organization, the LLM needs relevant context. Without this context, a user receives generic information derived from publicly trained models. ESRE helps customers overcome these challenges by providing organizational context, grounding each answer in data that is unique to their organization.
Solution overview
The power of the Elastic AI Assistant lies in its ability to offer specific context, incorporating organization-specific information to address unique challenges. This personalized context ensures that the generated responses are not only accurate but also directly applicable to a team's needs.
Navigating the generative AI landscape is simplified with Elastic AI Assistant's user-friendly interface and one-click prebuilt prompts. Whether a user is seeking quick insights or addressing intricate security issues, the Elastic AI Assistant is designed to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in their daily task.
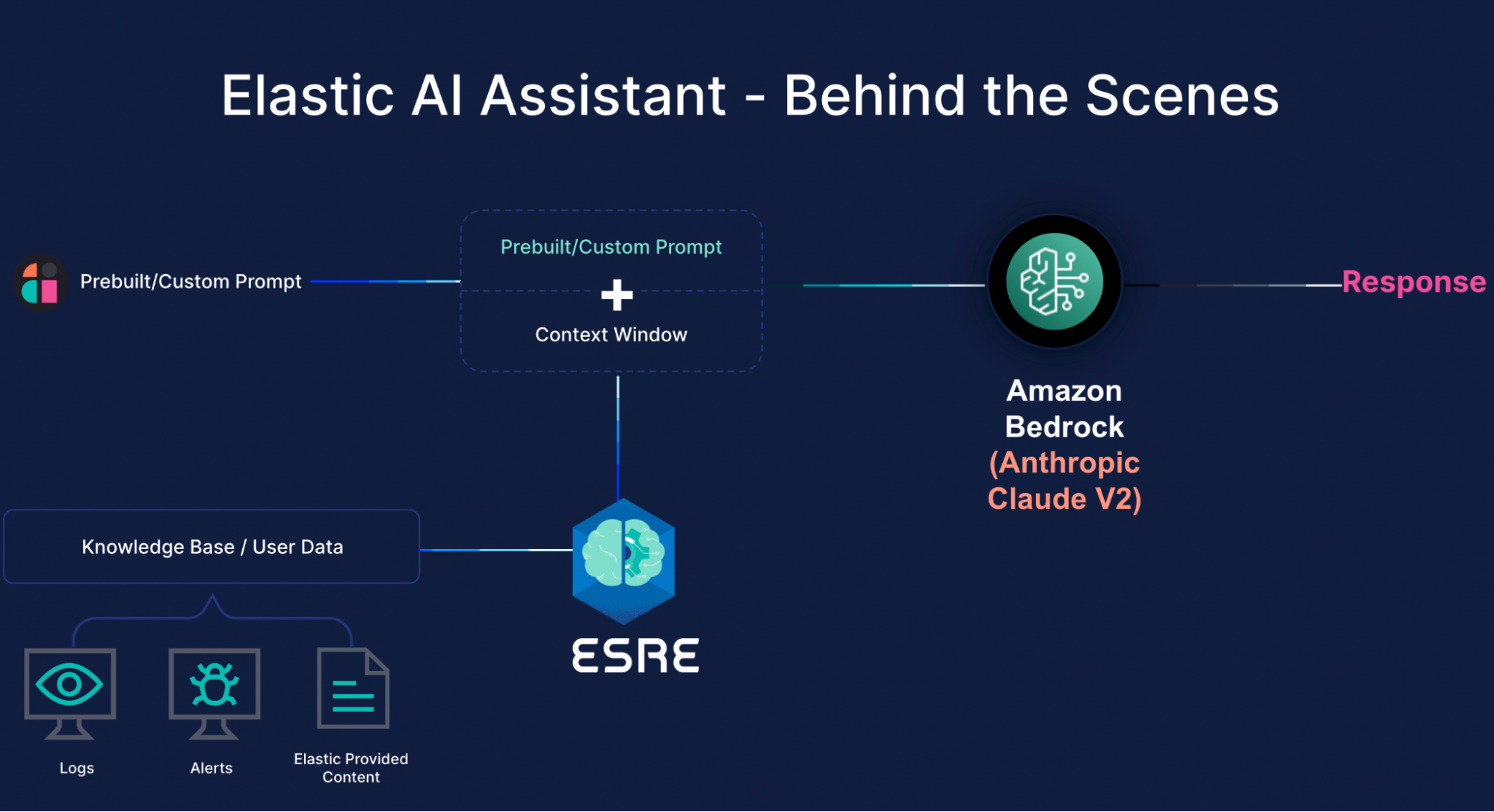
This seamless integration of Elastic, Amazon Bedrock Anthropic, and the generative AI app ensures an efficient and contextualized workflow for security analysts, enabling them to obtain pertinent information effectively.
How to set up the AI Assistant for Security with Amazon Bedrock
Next, we’ll take you through the process to get all of this set up.
Prerequisites
Create an account on Elastic Cloud by following the steps provided.
- Log in to your Elastic Cloud on AWS deployment.

Step by step to access Elastic AI Assistant for Security
Within Kibana®, navigate to the Security solution from the navigation menu.
Within Security, launch the Assistant by clicking on the button in the toolbar, using the keyboard shortcut (cmd/ctrl and ;) or any of the contextual “chat” buttons in the Alert or event flyouts, Data quality dashboard, or timeline tab.

After launching the Assistant, you’ll be prompted to add your first connector.
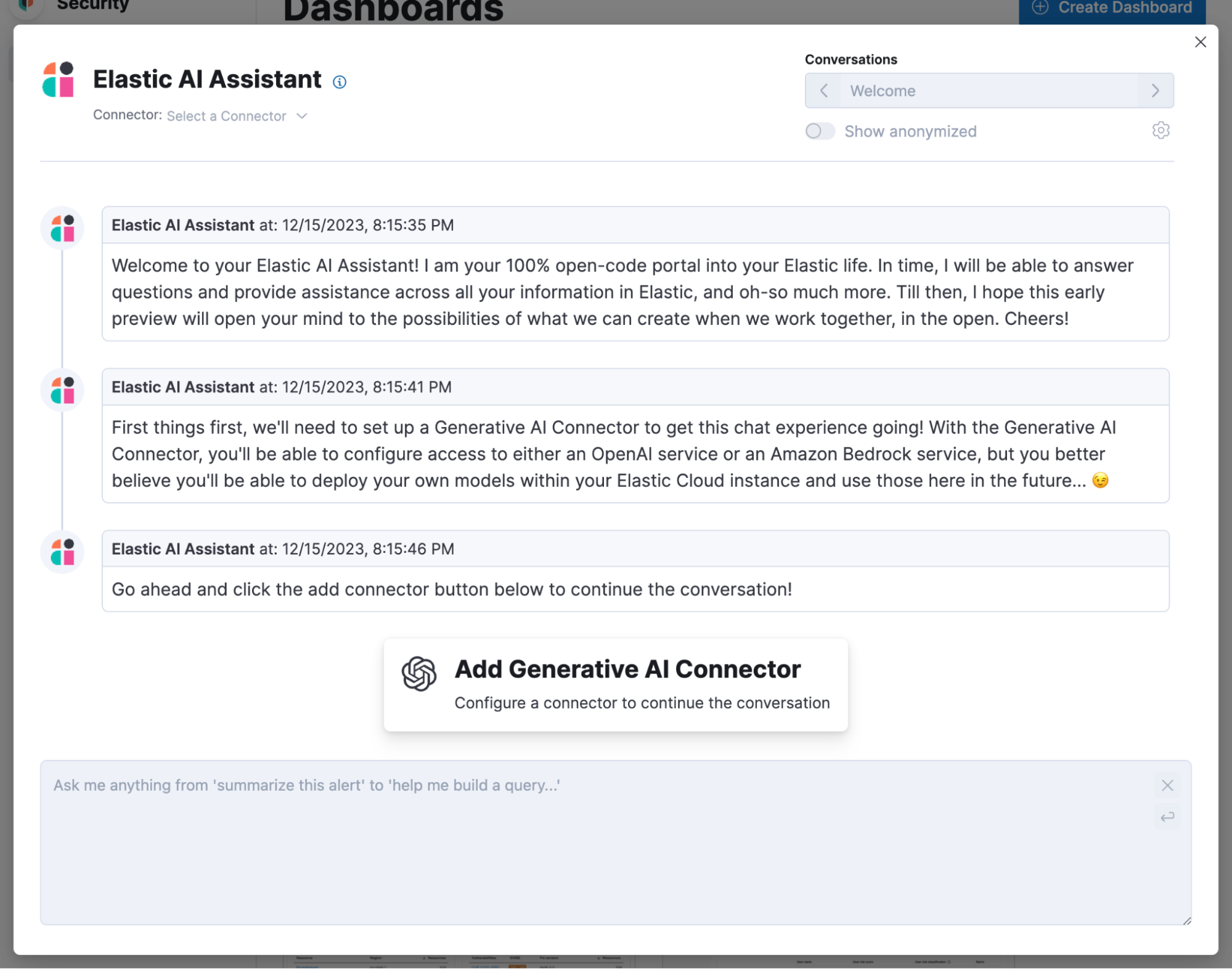
To add an Amazon Bedrock connector, select the option from the pop-up.

Assuming you’ve already set up Amazon Bedrock in your preferred region, enter the connector settings when prompted and click Save. You may set up multiple connectors for different regions should you wish.
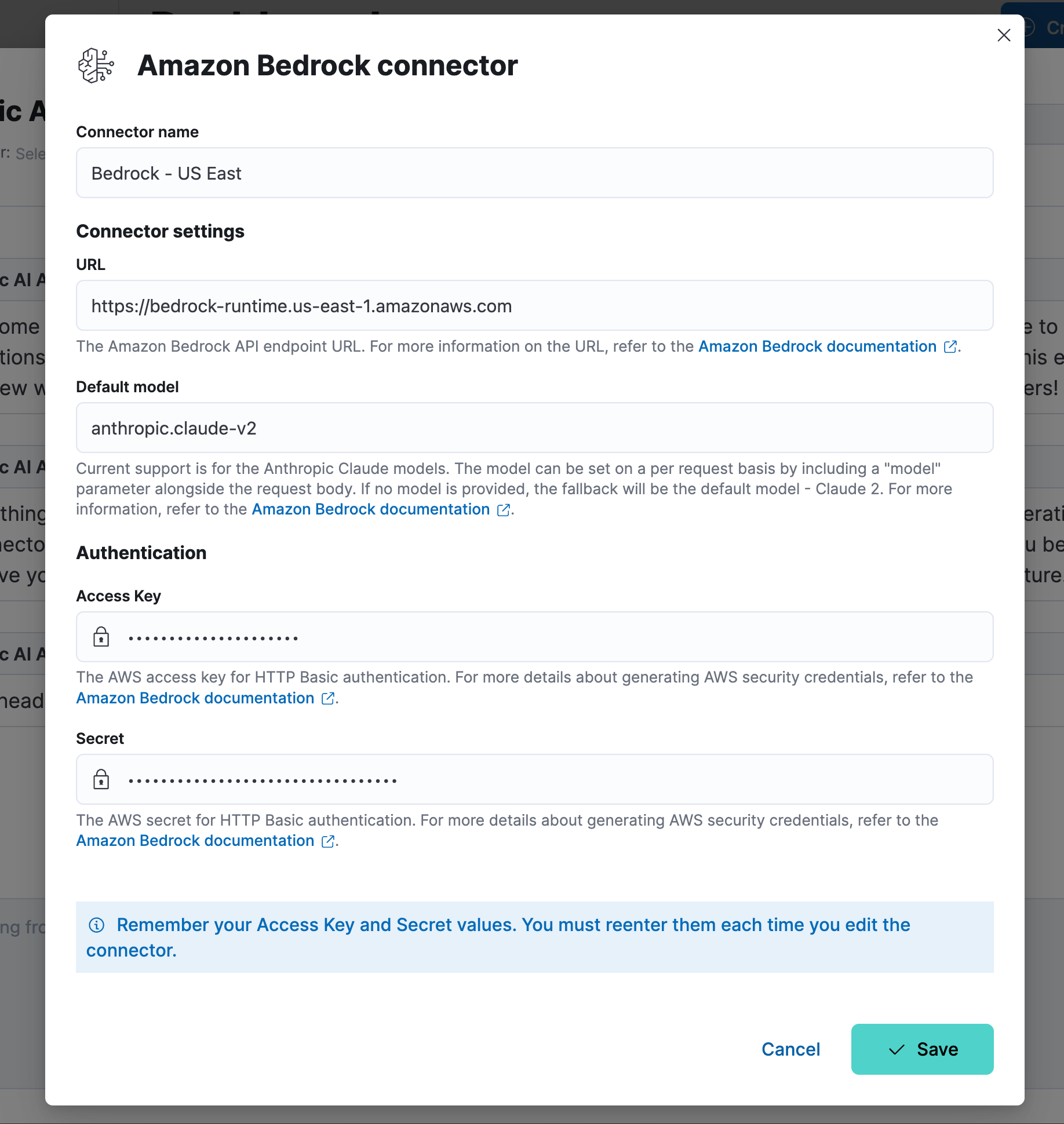
Once complete, you can start to use the Elastic AI Assistant. Below you’ll find a couple of examples of the Assistant in action.
Assistance during alert triage and investigation:
Assistance with query generation:
You’re all set to begin exploring this powerful combination of solutions!
Taking SecOps to the next level
The Elastic AI Assistant is a superb complement to any Security Operations team. Coupled with Anthropic’s Claude model via Amazon Bedrock, organizations that avail of AWS services can get started with the Assistant in a matter of minutes, elevating a security team’s posture and eliminating mundane tasks.
Learn more about the AI Assistant or watch an end-to-end demo.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.
In this blog post, we may have used or referred to third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch, ESRE, Elasticsearch Relevance Engine and associated marks are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of their respective owners.