Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools in Elastic Agent Builder
Agent Builder MCP tools enable calling a remote MCP server's tools in your agent chat. When your agent calls an MCP tool, it executes the associated tool on the MCP server and returns its result.
To use external MCP tools, you first need to set up an MCP connector. This interface enables Agent Builder MCP tools to communicate with a remote MCP server.
You can import MCP tools individually or in bulk.
Once you've set up an MCP connector, click "New tool" on the Tools landing page and select the MCP tool type.
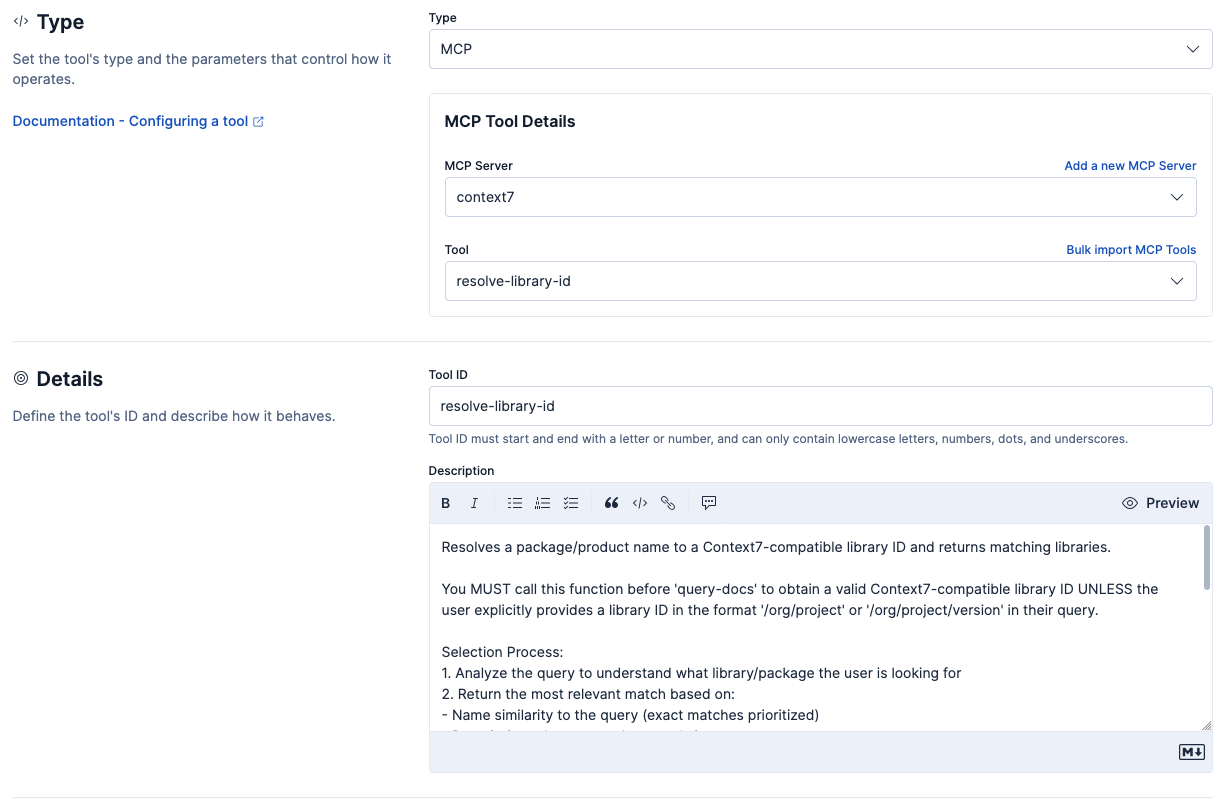
Individual MCP tools have the following configuration settings:
- MCP Server
- The MCP connector to interface with.
- Tool
- The specific tool on MCP server to create an Agent Builder MCP tool for.
Once a tool is selected, the Tool ID and Description fields automatically populate with the tool name and description provided by the MCP server.
To import multiple tools at once, go to the Tools landing page and select Bulk import MCP tools from the "Manage MCP" dropdown.
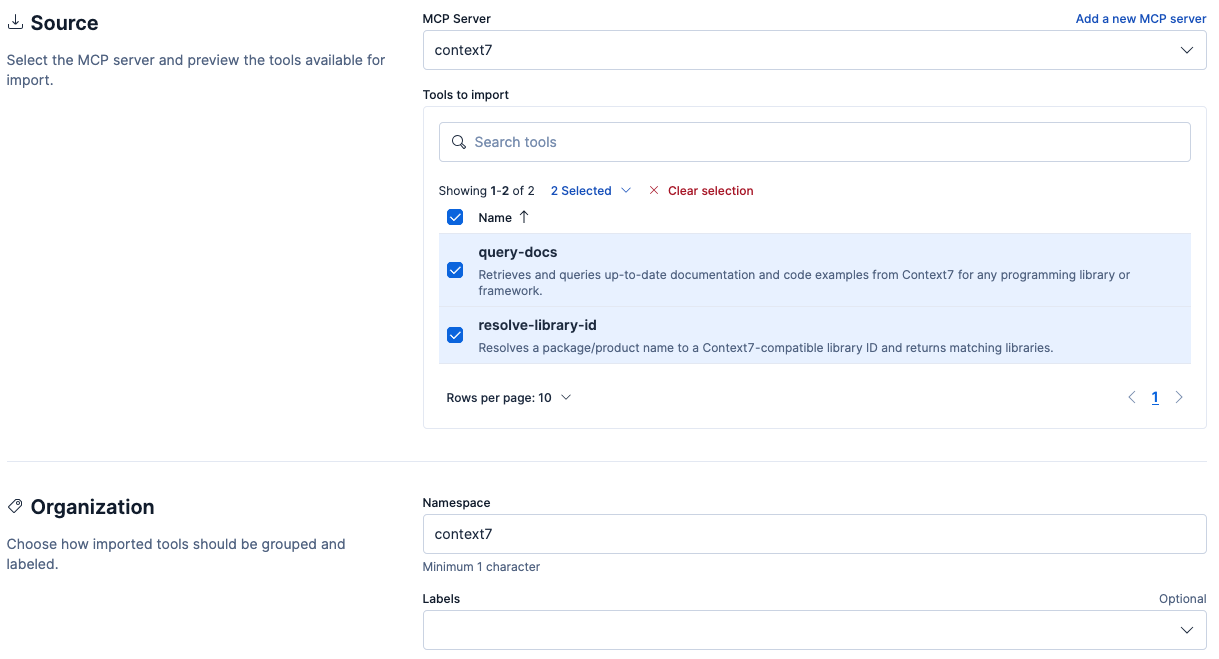
Configure the following fields:
- MCP Server
- The MCP connector to interface with.
- Tools to import
- The specific tools from the MCP server to import.
- Namespace
- A string to prepend to the tool name to aid in searching and organization. A namespace must start with a letter and contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens.
After clicking Import tools, Agent Builder creates an MCP tool for each selection.
Each tool's ID is generated as namespace.tool-name (for example, context7.resolve-library-id), and descriptions are populated automatically from the MCP server.
When an agent calls an MCP tool:
- Agent Builder retrieves the tool's input schema from the MCP connector.
- Agent Builder calls the MCP server tool with the required parameters.
- The MCP server returns the result directly to the LLM with no post-processing.
- The LLM interprets the result for the user.
MCP tools have built-in health monitoring. Tools that are unhealthy display an icon next to their IDs in the Tools landing page.
An MCP tool is marked "unhealthy" when:


