Build area charts with Kibana
Area charts are line charts with the area below the line filled in with a certain color or texture. Area charts work with numeric metrics over the horizontal axis (typically time) and are ideal to display quantitative values over an interval or time period, to show trends for time series like traffic, CPU, revenue, or error rates.
You can create area charts in Kibana using Lens.
Before you start, make sure you have data indexed into Elasticsearch or install sample data. By default, Lens uses data views to access your Elasticsearch data. Data views are created automatically in most cases when you ingest data. You can also create one manually to select just the data that you want. Alternatively, you can use the ES|QL query mode to query your Elasticsearch data directly.
To build an area chart:
-
Access Lens
Lens is Kibana's main visualization editor. You can access it:
- From a dashboard: On the Dashboards page, open or create the dashboard where you want to add an area chart, then add a new visualization.
- From the Visualize library page by creating a new visualization.
-
Set the visualization to Area
New visualizations often start as Bar charts.
Using the Visualization type dropdown, select Area.
-
Define the data to show
- Select the data view that contains your data.
- Drag a time field to the Horizontal axis and a numeric field to the Vertical axis. Kibana automatically selects an appropriate aggregation function compatible with the selected field.
Optionally:
- Add more numeric fields to create additional series, or drag a categorical field to the Breakdown settings to segment your data by a categorical field, and create multiple areas within the same chart.
- You can click the Add layer icon to integrate additional visualizations, annotations, or a reference line.
The chart preview updates to show filled areas plotted over time. Each area represents a series, with the filled region emphasizing the volume of data.
-
Customize the chart to follow best practices
Tweak the appearance of the chart to your needs. Consider the following best practices:
- Choose the right stack mode
- Use Stacked to show contribution to a whole, Percentage for normalized representation of values, or Unstacked when absolute trends matter more than composition. For a practical use case, check how to show composition with stacked and 100% stacked areas.
- Handle gaps and noise
- For sparse data, configure Missing values and Line interpolation to avoid misleading gaps or sharp edges. Check the Visualization appearance options.
- Use color purposefully
- Apply colors to highlight important data or patterns. Avoid using too many colors that might distract from the data. You can also assign consistent colors to key categories.
- Label clearly
- Provide a descriptive title and axis labels that clearly communicate what the chart shows. For example, mention the metric being visualized ("Average Response Time") and reference the time period when relevant ("Dec 8-16, 2025").
Refer to Area chart settings to find all configuration options for your area chart.
-
Save the chart
- If you accessed Lens from a dashboard, select Save and return to save the visualization and add it to that dashboard, or select Save to library to add the visualization to the Visualize library and reuse it later.
- If you accessed Lens from the Visualize library, select Save. A menu opens and lets you add the visualization to a dashboard and to the Visualize library.
Use stacking to show how categories contribute to a total over time.
Create an area chart with a time-based Horizontal axis.
Break down the series by a categorical field, for example,
agent.keyword,response.keyword. You can set the area chart stack mode to:Stacked — Show cumulative totals and category contributions.
Percentage (100%) — Normalizes each timestamp to 100% to emphasize shares rather than magnitudes.
Optionally, in the Breakdown settings, you can set Rank by to specify the dimension the top values are ranked by.
In Area charts, you can enable time shift to compare different periods and identify deltas.
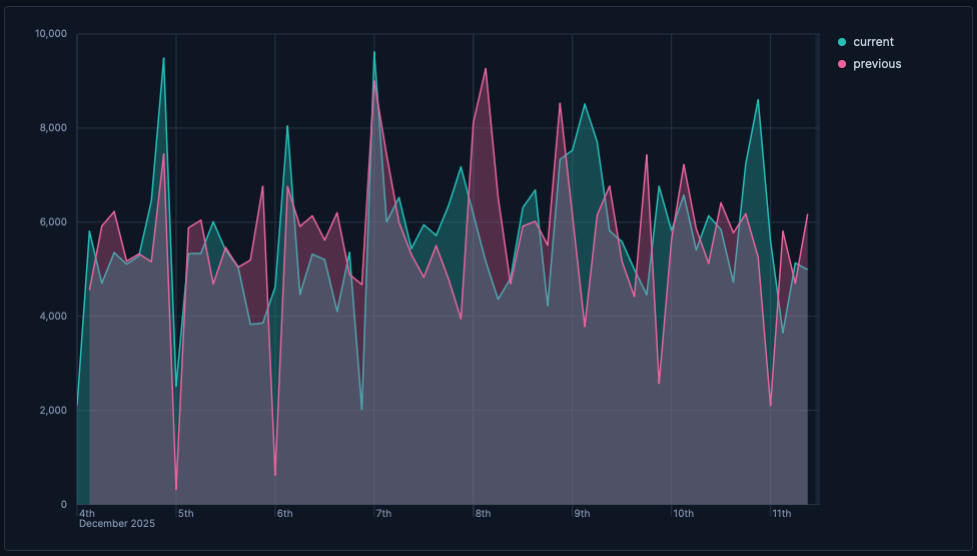
- Create an area chart with a time-based Horizontal axis and your main metric on Vertical axis, for example:
bytes. - Duplicate the layer:
-
Select Duplicate layer from the visualization editor. -
Open the contextual menu of the visualization editor and select Duplicate layer.
-
- From the duplicated layer settings, select the field defined as vertical axis to open its details. Expand its Advanced options and set Time shift to
1wor to the time value of your choice. Check Compare differences over time for more details. - Optionally, customize the appearance of the layer to adjust how it looks on the chart. When you duplicate a layer, Kibana automatically assigns a different Series color to the new layer. You can for example change this color, or adjust the layer's name and axis position. This name is used for the chart's legend.
You can also compute the relative change using a formula, for example:
(average(bytes) - average(bytes, shift='1w')) / average(bytes, shift='1w')
Customize your area chart to match the information you need and how you want it displayed.
- Data
-
- Functions:
- Top values: Create separate areas for the most common values in a field.
- Field: Select the field to group by. You can add up to 4 fields. When multiple fields are selected, each area represents a unique combination of values across those fields. You can reorder the fields by dragging them to change their priority.
- Number of values: How many top values to display.
- Rank by: Specifies the dimension the top values are ranked by. Available options:
- Count of records: Rank by the number of documents containing each value. This is the default when a metric is defined.
- Alphabetical: Rank by the term key alphabetically. This is the default when no metric is defined.
- Rarity: Find terms that appear in very few documents, using a rare terms aggregation. You can configure the Max doc count to set the maximum number of documents a term can appear in to be considered rare (default: 1, max: 100). Only available for non-numeric fields and single-field terms.
- Significance: Find statistically unusual terms compared to the overall data set, using a significant terms aggregation. Only available for
keywordfields and single-field terms. - Custom: Define a custom metric aggregation to rank by (for example, rank by the sum of a numeric field rather than by count).
- Rank direction: Ascending or descending order. Disabled when Rank by is set to Rarity or Significance.
Advanced settingsSeveral advanced options allow you to refine the behavior of the breakdown:
- Include documents without the selected field: Off by default.
- Group remaining values as "Other": On by default.
- Enable accuracy mode: This option improves results for high-cardinality data, but increases the load on the Elasticsearch cluster.
- Include values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always show a tile for.
- Exclude values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always exclude from the displayed tiles.
- Date histogram: Group data points into time-based buckets (for example, hourly, daily, weekly).
- Field: Select the date field to use for the time-based grouping.
Include empty rows: This option is on by default. Turn it off to exclude empty rows from the data.
Bind to global time picker: Associate the selected field to the Lens or dashboard main time selector.
Minimum interval: Define the time interval for aggregating the data. For example,
30s,20m,24h,2d,1w,1MDrop partial intervals: Exclude incomplete intervals from the data. This option is off by default.
- Intervals: Create numeric ranges for continuous data. You can define the interval granularity or specify custom ranges.
- Field: Select the numeric field to create intervals from.
- Filters: Allow you to segment your data based on specific conditions, creating separate areas for each filter.
- Top values: Create separate areas for the most common values in a field.
- Functions:
- Appearance
- Name: By default, the chart uses the function or formula as title. It's a best practice to customize this with a meaningful title.
- Data
-
To represent the metrics or values you want to visualize, you can use quick functions like Average, Count, Percentile, Counter rate, or create custom calculations with formulas. Refer to Lens > Use formulas to perform math for examples.
Advanced settingsDepending on the data you defined, you can use the following options to apply additional filtering:
- Filter by: Specify a query.
- Time shift: Compare current data with historical data by shifting the time frame of your metrics.
- Appearance
-
Configure series-level options, including:
- Name: Customize the series label.
- Value format: Control how numeric values are displayed on your vertical axis and in tooltips.
- Series color: Determine the color of your data series in the visualization.
- Axis side: Determine which side of the chart the vertical axis appears on.
You can split your data by a categorical field to create multiple stacked or overlapping areas. You can specify the following options:
- Data
-
- Functions:
- Top values: Create separate areas for the most common values in a field.
- Field: Select the field to group by. You can add up to 4 fields. When multiple fields are selected, each area represents a unique combination of values across those fields. You can reorder the fields by dragging them to change their priority.
- Number of values: How many top values to display.
- Rank by: Specifies the dimension the top values are ranked by. Available options:
- Count of records: Rank by the number of documents containing each value. This is the default when a metric is defined.
- Alphabetical: Rank by the term key alphabetically. This is the default when no metric is defined.
- Rarity: Find terms that appear in very few documents, using a rare terms aggregation. You can configure the Max doc count to set the maximum number of documents a term can appear in to be considered rare (default: 1, max: 100). Only available for non-numeric fields and single-field terms.
- Significance: Find statistically unusual terms compared to the overall data set, using a significant terms aggregation. Only available for
keywordfields and single-field terms. - Custom: Define a custom metric aggregation to rank by (for example, rank by the sum of a numeric field rather than by count).
- Rank direction: Ascending or descending order. Disabled when Rank by is set to Rarity or Significance.
Advanced settingsSeveral advanced options allow you to refine the behavior of the breakdown:
- Include documents without the selected field: Off by default.
- Group remaining values as "Other": On by default.
- Enable accuracy mode: This option improves results for high-cardinality data, but increases the load on the Elasticsearch cluster.
- Include values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always show a tile for.
- Exclude values: Values from the breakdown dimension to always exclude from the displayed tiles.
- Date histogram: Group data points into time-based buckets (for example, hourly, daily, weekly).
- Field: Select the date field to use for the time-based grouping.
Include empty rows: This option is on by default. Turn it off to exclude empty rows from the data.
Bind to global time picker: Associate the selected field to the Lens or dashboard main time selector.
Minimum interval: Define the time interval for aggregating the data. For example,
30s,20m,24h,2d,1w,1MDrop partial intervals: Exclude incomplete intervals from the data. This option is off by default.
- Intervals: Create numeric ranges for continuous data. You can define the interval granularity or specify custom ranges.
- Field: Select the numeric field to create intervals from.
- Filters: Create separate colored areas based on filter conditions.
- Top values: Create separate areas for the most common values in a field.
- Functions:
- Appearance
-
Allow you to customize how your breakdown data is displayed in line charts, including:
- Name: It's a best practice to customize this with a meaningful title.
- Color mapping: Determine how colors are assigned to your breakdown series.
When creating or editing a visualization, you can adjust the following settings.
Style
Adjust the visual appearance of your area chart to control how the data series are labeled and displayed alongside your chart. Click to open the Style panel.
- Appearance
- Allow you to customize the overall chart appearance:
Area fill opacity: Control how transparent or opaque the colored area beneath the data line appears. The opacity value ranges from 0 to 1.
Point visibility: Show or hide data points. Set to Auto by default: Points are visible unless the distance between them is too short.
Line interpolation: Choose how to interpolate the line between data points from the available options: Straight (default), Smooth, and Step.
Missing values: Choose between Hide, Zero, Linear, Last, and Next. This option controls how gaps in data appear on the chart. By default, gaps are hidden. Missing values include empty buckets and metrics: Buckets without documents or metrics that returned
nulldue to their operation and data content.NoteYou can only use this option when the Include empty rows option of the chart is enabled or when a metric produces a null bucket. For example, if a moving average finds empty buckets.
- Hide: Don't show gaps in data.
- Zero: Fill gaps by connecting starting and ending data points to zero.
- Linear: Fill gaps by connecting related starting and ending data points together with a direct line.
- Last: Fill gaps between data points with a horizontal or vertical line that uses the last ending point value, when available, to determine its position.
- Next: Fill gaps between data points with a horizontal or vertical line that uses the next starting point value, when available, to determine its position.
End values: If you've chosen to show missing values, you can also decide to extend data series to the edge of the chart. By default, end values are hidden.
- Hide: Don't extend series to the edge of the chart.
- Zero: Extend series as zero to the edge of the chart.
- Nearest: Extend series with their first or last value to the edge of the chart.
Show as dotted line: If you've chosen to show missing values, you can turn on this option to show gaps as a dotted line.
- Left axis
- Allow you to customize the Y-axis appearance.
- Axis Title. Show, hide or add a custom title.
- Gridlines. Show or hide gridlines.
- Tick labels. Show or hide tick labels.
- Orientation. Choose the tick labels orientation.
- Axis scale. Choose an axis scale type. Options include: Linear (default), Logarithmic, and Square root.
- Bounds. Use Bounds to set the minimum and maximum values for the Y-axis. Options include: Full, Data, and Custom
- Round to nice value. Axis labels can be rounded to more readable numbers.
- Bottom axis
- Allow you to customize the bottom axis appearance:
- Axis Title. Show, hide or add a custom title.
- Gridlines. Show/hide gridlines.
- Tick labels. Show/hide tick labels.
- Show partial data markers: indicate data points where Data collection is incomplete (the time bucket is still open and actively collecting events), or data may change (the values represented might increase as more data arrives).
- Show current time marker: Add a vertical line on your chart that represents the current time.
Legend
You can customize the way the legend is displayed and the data it shows. Click to open the Legend panel.
With the Visibility, Position, and Width options, you can adjust the way the legend appears in or next to the visualization.
- Statistics
- To make your legends as informative as possible, you can show some additional statistics. All statistics are computed based on the selected time range and the aggregated data points shown in the chart, rather than the original data coming from Elasticsearch. For example, if the metric plotted in the chart is Median(system.memory) and the time range is last 24 hours, when you show the Max statistic in the Legend, the value that shows corresponds to the Max[Median(system.memory)] for the last 24 hours.
- Average: Average value considering all data points in the chart.
- Median: Median value considering all data points in the chart.
- Minimum: Minimum value considering all data points in the chart.
- Maximum: Maximum value considering all data points in the chart.
- Range: Difference between min and max values.
- Last value: Last value considering all data points in the chart.
- Last non-null value: Last non-null value.
- Label truncation
- Keep your legend minimal in case of long labels that span over multiple lines. You can adjust the line limit.
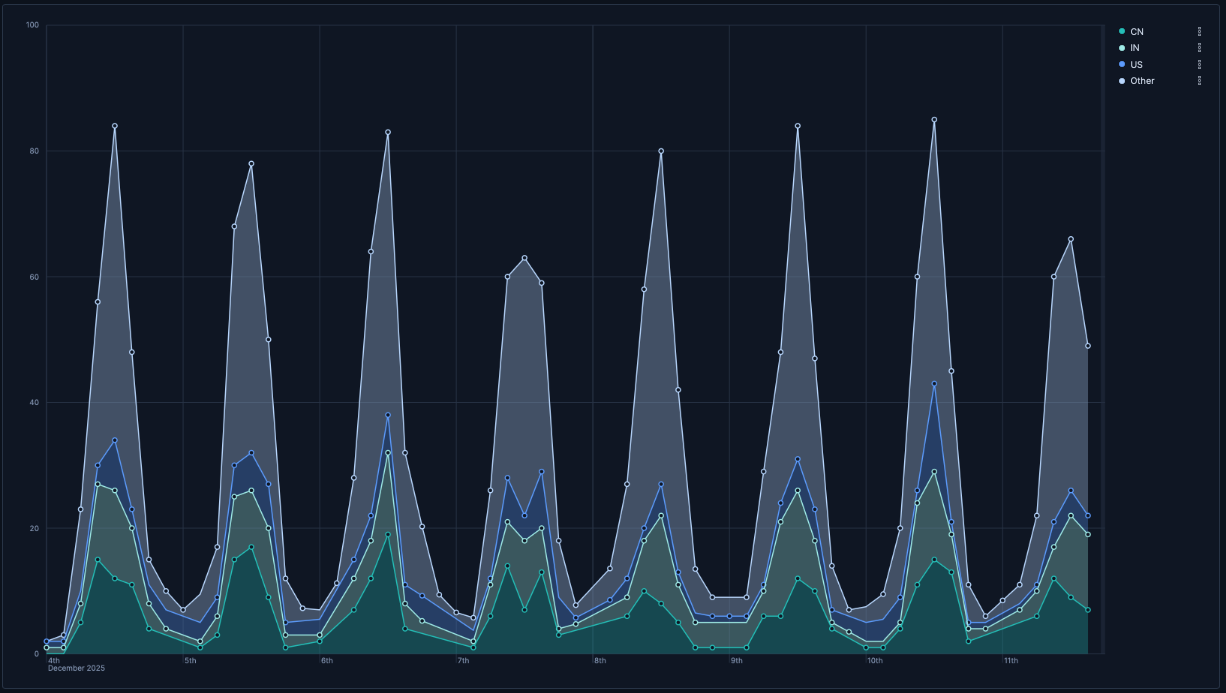
- Traffic by geographic region
-
Visualizing which geographic regions generate the most traffic:
- Horizontal axis:
@timestamp(Date histogram) - Vertical axis:
records - Breakdown:
geo.dest
- Horizontal axis:
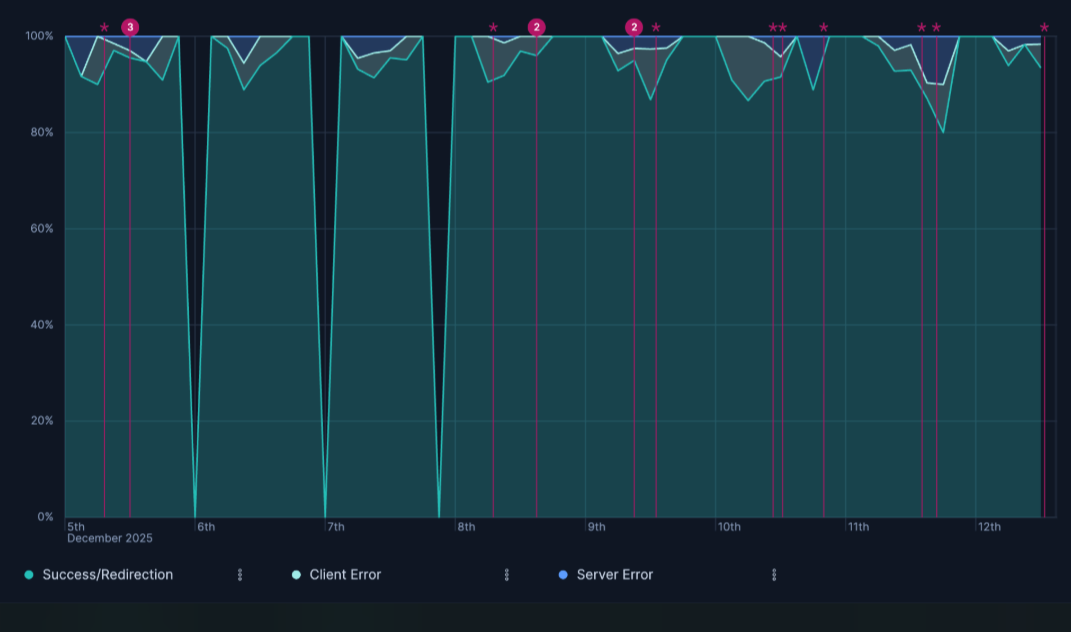
- Response code over time with annotations
- Visualizing HTTP response codes over time, highlighting the proportion of success, client error, and server error responses, with annotations for key events:
Horizontal axis:
@timestamp(Date histogram)Vertical axis:
Count of records- Breakdown:
- Success/Redirection
response.keyword >= 200 and response.keyword < 400 - Client Error
response.keyword >= 400 and response.keyword < 500 - Server Error
response.keyword >= 500
- Success/Redirection
- Stacking:
Percentageto show the distribution relative to the total count at each point in time.- Annotation Query:
tags:error AND tags:security
- Annotation Query:
- Breakdown: