Top 5 SIEM considerations of 2021 and how Elastic Security solves them
Security information and event management (SIEM) systems are centralized logging platforms that enable security teams to analyze event data in real time for early detection of targeted cyber attacks and data breaches. A SIEM is used as a tool to collect, store, investigate, and report on log data for threat detection, incident response, forensics, and regulatory compliance.
SIEM has continuously evolved since its early days of adoption. SIEM software today needs to support big data and provide credible risk assessments and forensics capabilities to piece together events after an incident has occurred. Security analysts have long needed to adapt to changing threats, environments, and perimeters. The ability to integrate with new technologies and increase flexibility in order to detect rapid threat changes has given rise to new expectations and demands on modern SIEM software.
In addition to SIEM, Elastic Security is used for leading security use cases such as endpoint security, threat hunting, and cloud monitoring. Here are today’s top five considerations that security teams expect out of their SIEM, and how Elastic Security for SIEM can satisfy each:
1. Stronger cloud integrations and monitoring capabilities
All major cloud services now provide in-depth analysis on the complete cloud infrastructure and application data. Most organizations require such deep-level analytical logs. After all, the more information teams have, the better they are able to protect their company infrastructure and data. Integration with in-depth cloud data is one of the key metrics to be strengthened with a centralized log management process.
Elastic integrates with a wide range of data sources from major cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud applications through data modules. This includes, but is not limited to, security-relevant cloud datasets such as metrics, traffic from virtual networks, cloud storage, application logs, audit trails, streaming services, containerized environments, and serverless functions. These modules are also built in with sample dashboards for rich visualizations and quick analysis of data.
2. Data protection
Most security teams will use SIEM as their front line detection and analyzing tool. With such large sets of data at hand, data protections — the process of safeguarding important information from corruption, compromise, or loss — play a major role.
Authentication, data segregation, encryption, and authorization are top security practices to safeguard data from breach. The importance of data protection increases as the amount of data created and stored continues to grow at unprecedented rates. Key pieces of information that are commonly stored by businesses need to be protected. This is to prevent that data from being misused by third parties for fraud, such as phishing scams and identity theft.
Data protection in the Elastic Stack
Elastic offers free security features to ensure your data stored in Elasticsearch indices is secure and protected from unauthorized users and unintentional modification.
Authentication
This is the one of the critical steps to protect data flowing through Elasticsearch, Kibana, Beats, and Logstash .
With the Elastic Stack, you can integrate with a number of industry-standard identity management systems. User authentication provides built-in realms such as native, LDAP, active_directory, PKI, file, SAML, and OIDC.
Use options like certificates, Kerberos, and SAML — or build a custom realm that supports your home-grown identity management system.
Authorization
Kibana Spaces: Segregate Kibana features and access to those features into multiple spaces within a single Kibana instance.
Role-based access control (RBAC): Control which users and roles can access each space, including the specific Kibana features and apps within it.
Encryption
Protect sensitive data, credit card numbers, email addresses, and accounts across your clusters and clients. With SSL/TLS encryption, you can secure node-to-node, HTTP, and transport client traffic across your Elastic Stack. Encrypt data at rest with filesystem encryption on the actual host running Elasticsearch.
3. Integration with security ecosystems
Security analytics have long needed to rapidly adapt to changing threats. Threat detection, investigation, and response are more involved than ever. SIEMs that have basic workflow automation have managed to maintain efficiency up to now, but as companies experience growth, additional capabilities are required.
Modern security analytics is much more than just SIEM. Effective analytics include close integration with a security ecosystem within the organization. Analysts need to be able to create custom analytics, integrate with threat intelligence platforms, correlate across different data types and sets, and orchestrate with third-party platforms using APIs.
Elastic's rich API-driven capabilities augment and orchestrate security data and detections by integrating security detections with notifications and third-party systems via webhooks.
Elastic's unified protection combines log analysis (SIEM) with endpoint security, threat hunting, cloud monitoring, and other leading security use cases to equip analysts to successfully prevent, detect, and respond to threats at speed and scale.
4. Advanced analytics
The increasing complexity of attacks is driving the need for advanced analytics beyond the log aggregation of traditional SIEM solutions. Advanced analytical features enhance the threat hunting capabilities within security operations and reduce the mean time to detect sophisticated attacks.
Elastic Security fulfills advanced analytics needs with layered analysis such as:
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection is an important tool for detecting rare events that may have great significance but are hard to find. Elastic’s machine learning automates the analysis of time series data by creating accurate baselines of normal behavior in the data and identifying anomalous patterns. It can automatically understand the data pattern over the cycle and will be able to detect any deviation/anomalies from normal activity.
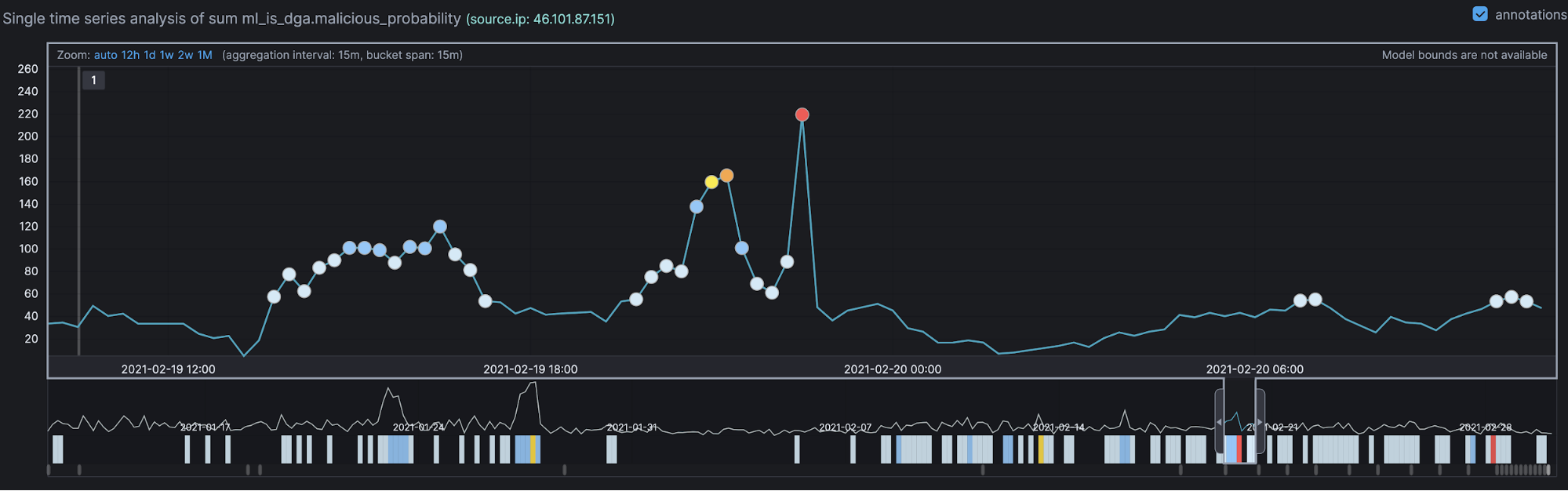
Detection engine rule types
Elastic Security provides different ways to address different threat detection use cases.
Custom query
Security operations look for particular conditional logic in order to detect suspicious events.
This query-based rule searches the defined indices and creates an alert when a document matches the rule’s query.
Threshold rules
Certain conditional logic might need to be expanded with the number of times the event has occurred. A lower number of occurrences on certain events might be normal, but the same event with a higher occurrence is suspicious. Threshold rules search the defined indices and create a detection alert when the field’s value meets the threshold number during a single execution.
Machine learning
Machine learning rules are used for creating alerts when an anomaly is triggered by an Elastic machine learning job.
Event correlation
Correlation rules are used for detecting potential threats through relationships between multiple events. Elastic’s Event Query Language (EQL) is a query language for event-based time series data that allows you to express relationships between events. EQL provides searches and detections for multiple related events that are chained together with a sequence of event queries.
Detection with third party data (threat intels)
As a powerful search engine, Elasticsearch provides various ways to enrich data with threat intel feeds, while the Elastic Security detection engine helps users detect alerts with threat indicator matching. Dynamic or static indicators (threat intels) can be streamed into a dedicated index and create an alert using detection rules when the indicator of compromise (IOC) matches with relevant data fields.
Prebuilt detections
Elastic provides a continuously growing library of out-of-the-box detection rules to address different threat use cases. Elastic detections further provide users the ability to define and create their own detection rules to match environmental use cases.
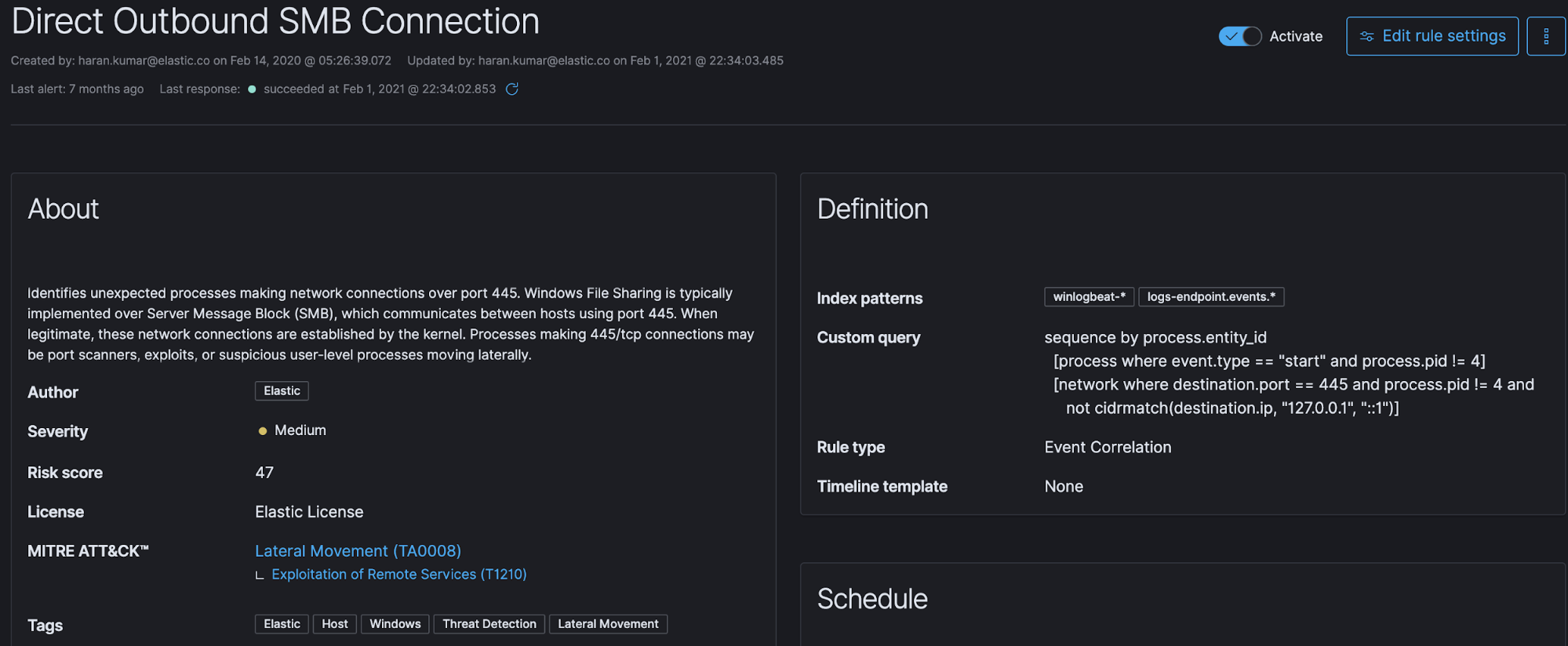
Detection mechanism based on a standardized cybersecurity framework
Over recent years, the MITRE ATT&CK® framework has become the de facto threat detection framework, based on models of how attackers operate. Elastic adopts the MITRE ATT&CK framework across built-in detection use cases. Such standardized cybersecurity frameworks help analysts better understand and track gaps in their environment to detect attacks before they progress.
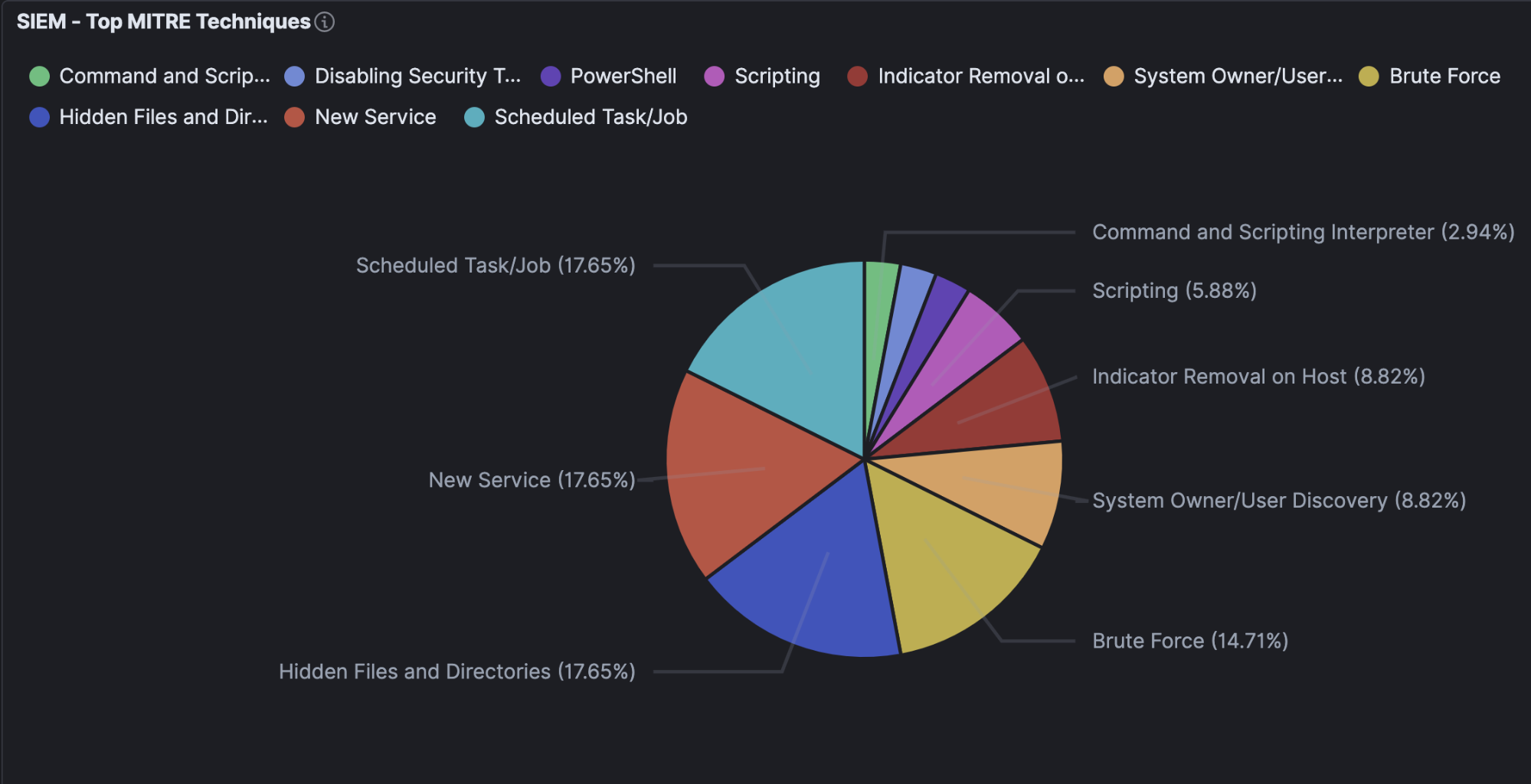
Example of a visualization created on Top SIEM alerts mapped with MITRE techniques:
Flexible delivery models
Analyst-driven security solutions need to adopt different and flexible delivery models, including on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid deployments. Such flexible deployment and log management ability provides adaptability to infrastructure needs.
From platform deployment to data integration, Elastic provides flexibility in the way the logs and log platforms are managed:
- Elastic Cloud and enterprise-grade, service-oriented architecture with Elastic Cloud Enterprise (ECE) lets you scale each service separately, with different reliability and performance requirements.
- Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK), built on the Kubernetes Operator pattern, extends Kubernetes orchestration capabilities to support the setup and management of Elasticsearch and Kibana on Kubernetes.
- And, of course, native on-prem deployment and subscription to Elasticsearch Service from your preferred marketplace brings Elastic to your preferred deployment method.
Wrapping up
These top five considerations provide us with strong insight into how SIEM is evolving beyond being merely a log monitoring tool. There will always be continuous changes in both the security threat landscape and the way enterprise systems address challenges, and we at Elastic will continue to be there to help security teams take those changes head on.
It’s easy to get started with Elastic Security — we offer Quick Start training to set you up for success. Start your free 14-day trial (no credit card required) or download our products, free, for your on-prem deployment.
Check out the SIEM Overview Guide to learn more.