Elastic Enterprise Search 8.5: Machine learning for intuitive search experiences

The latest release of Elastic Enterprise Search introduces a suite of new features and capabilities for building world-class search experiences for your mission-critical applications, websites, online stores, or anything in-between:
- Configurable machine learning (ML) and ingestion pipelines helps customers enrich their documents with natural language processing (NLP). Users can much more quickly and easily create and manage tasks like identifying user sentiment in support requests, utilizing named-entity recognition (NER) at query time to filter search results, answering questions programmatically with vector similarity, and preparing data for analysis by reducing whitespace. All of this happens with a few clicks in the Enterprise Search UI, no complexity required.
- Thanks to Elastic’s new native connectors for Enterprise Search, customers using MongoDB and MySQL can now leverage the full power of the Elastic Stack. These connectors enable best-in-class search experiences with the data within and allow customers to leverage Elasticsearch’s speed and flexibility to free up resources. With Elastic Cloud in the mix, customers can also offload business-critical data and operational responsibility to Elastic.
- Brand new in 8.5, Python support for the Enterprise Search connector framework enables customers to customize existing Python native connectors, like the MySQL connector mentioned above, to suit their business needs or use cases.
With this release, building search experiences for your ecommerce retail site, enhancing your employees’ ability to access relevant HR documentation, or building a custom application to quickly draw analytic insights can draw on the power of using the trained model of your choice.
In addition to these new features, Enterprise Search 8.5 also brings the generally available (GA) releases of App Search support for Elasticsearch-backed engines and hybrid ranking for vector similarity, significantly expanding Enterprise Search’s feature set to any Elasticsearch index.
New ML and ingestion pipeline management tools for search-optimized Elasticsearch indices
Enterprise Search 8.5 introduces pipeline management tools for search-optimized indices, enabling deep customization and ML-powered enrichment of incoming data:
- Apply machine learning models at ingest-time, opening an entire world of ML possibilities — sentiment analysis, NLP, NER, language detection, and more.
- Content extraction, enabled by default, generates documents from popular file formats, like PDFs and Microsoft Word.
- Reduce whitespace for incoming documents, whether you’re preparing data for further analysis or cleaning up the output of an ML model.
- Build custom ingest pipelines to augment incoming data to suit your needs or hook into your existing ETL workflows.
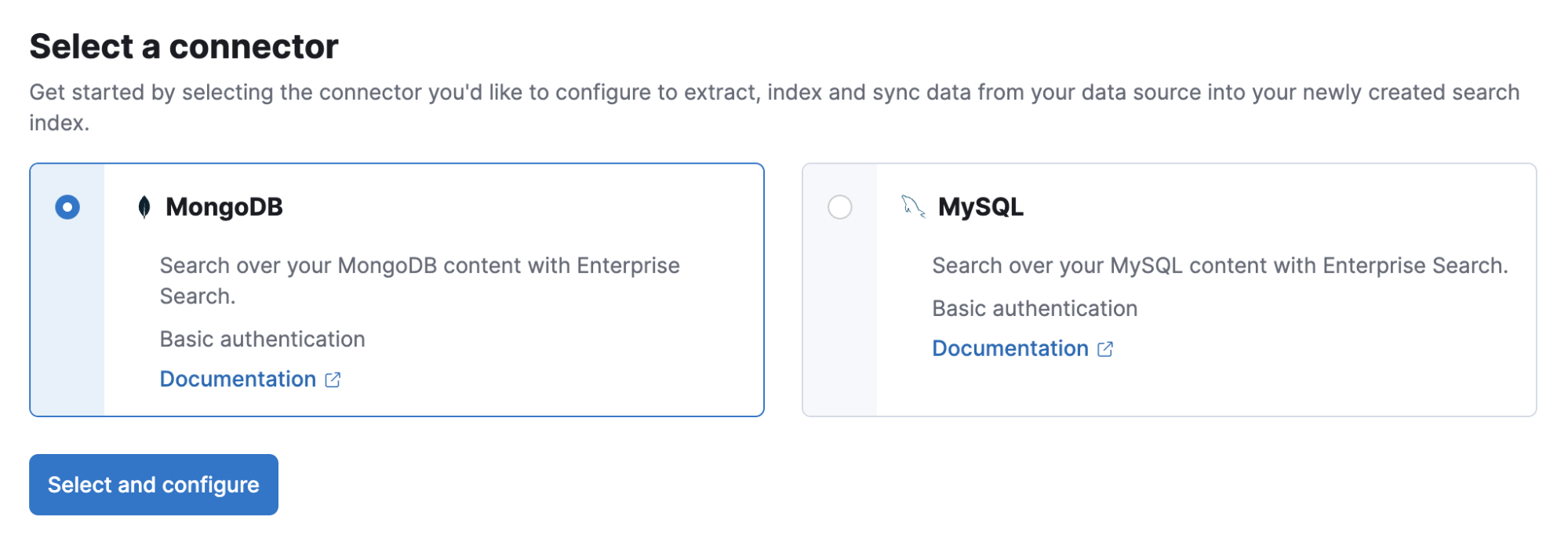
Native connectors for MongoDB and MySQL
In 8.5, Elastic is excited to debut the first native connectors for search-optimized indices, MongoDB and MySQL, as a technical preview. These new native connectors allow you to quickly offload your operational databases to Elasticsearch, opening the data within to all the benefits of the Elastic Stack and Elastic Cloud. Build world-class, relevant, and intuitive search experiences, leverage the Elastic Stack’s deep machine learning capabilities, or simply use Elasticsearch as a speed layer for critical use cases.
Customers gravitate to MongoDB because, unlike traditional relational databases, it’s easy to scale with a single command for global distribution. At that juncture, their business needs also require industry leading search experiences that can keep up with that desired simplicity and scale. Elastic has been at the forefront of enabling developers to build best in class search for custom applications for decades. Pairing those capabilities with full stack observability, our new native connector, and our connector clients allow us to serve the needs of those growing businesses as they transition from on-premises deployments to cloud first with the same production level of quality each step of the way.
Build your Python connector by taking advantage of our Elastic managed connector framework
In 8.4, Elastic released the Enterprise Search connector framework with support for Ruby, which allowed developers to build connector clients to interface with content data sources not currently provided by Enterprise Search and ingest directly into search-optimized Elasticsearch indices. The underlying connector protocol has always been tech stack agnostic, but many Elastic customers may prefer to work in Python rather than Ruby.
In 8.5, Elastic is excited to announce a second connector framework repository with support for our Python users. Use these robust frameworks, now available as technical previews, to customize the existing library of Ruby connectors, like MongoDB, or Python connectors, like MySQL. As always, you can still build your own connectors using the language of your choice. The path to customizing a connector but promoting it to be an Elastic-managed native connector starts here.
Learn more about the Enterprise Search connector framework in Python.
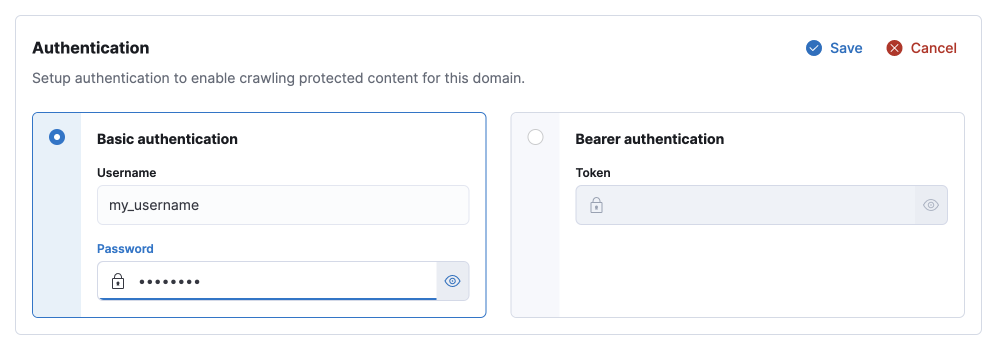
Manage authenticated crawls in the Web Crawler UI
In 8.4, Elastic introduced a web crawler for search-optimized indices, which included the ability to crawl private websites by passing login credentials as part of an API call. With today’s release of 8.5, that configuration has been elevated to the web crawler UI. Easily configure username and password or token-based authentication setups for private websites you’d like to crawl with a few clicks.
App Search support for Elasticsearch index-backed engines and hybrid ranking for vector similarity reach GA
In 8.4, Elastic released public betas of App Search support for Elasticsearch-backed engines and hybrid ranking for vector similarity. With 8.5, these features have now reached general availability.
Support for Elasticsearch index-backed engines introduces App Search’s relevance tuning, synonym management, curations, and analytics features to any Elasticsearch index, with no configuration required. This means less time spent fine-tuning your search system, with zero additional implementation effort or cost.
Hybrid ranking combines vector similarity with query scoring, so you can integrate vector search with your existing Elasticsearch scoring functions. Simply use the _search endpoint, provide a weight for each of the ranking methods, and get a result set ranked by a linear combination of the scores, no manual rescoring required. With this hybrid approach, result filtering is natively supported, making it highly pertinent for most real-world applications — from mission-critical app services to online stores, and everything in-between.
More Workplace Search connectors added to the mix
Bring more of the data you work with every day to Workplace Search with new native connectors for Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom, now available as public betas. Joining the rest of Workplace Search’s native connectors, these new additions allow customers to build engaging search experiences with federated data from multiple sources.
Learn more about the new Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom connectors.
Try it out
Existing Elastic Cloud customers can access many of these features directly from the Elastic Cloud console. If you’re new to Elastic Cloud, take a look at our Quick Start guides (bite-sized training videos to get you started quickly) or our free fundamentals training courses. You can always get started for free with a free 14-day trial of Elastic Cloud. Or download the self-managed version of the Elastic Stack for free.
Read about these capabilities and more in the Elastic Enterprise Search 8.5 release notes, and other Elastic Stack highlights in the Elastic 8.5 announcement post.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.