Elastic Infrastructure 7.2.0 released
We are pleased to announce a new release of Elastic Infrastructure, version 7.2.0. The Elastic Infrastructure application, available on the Elasticsearch Service and included with the default distribution of Elastic Stack, lets you visualize and drill into your infrastructure metrics via a purpose-built user interface, and now includes the Metrics Explorer.
Exploring metrics in the Infrastructure app
The biggest update to the Infrastructure app in Kibana for 7.2 is the addition of the Metrics explorer. The Metrics explorer lets you quickly build time-series based visualizations based on your metrics, charting them against related metrics, and breaking them down per the field of your choice. That's not all, though- you can send the visualizations off to the Visualizer, where you can enhance, annotate, and save your them for reuse on your own custom dashboards.
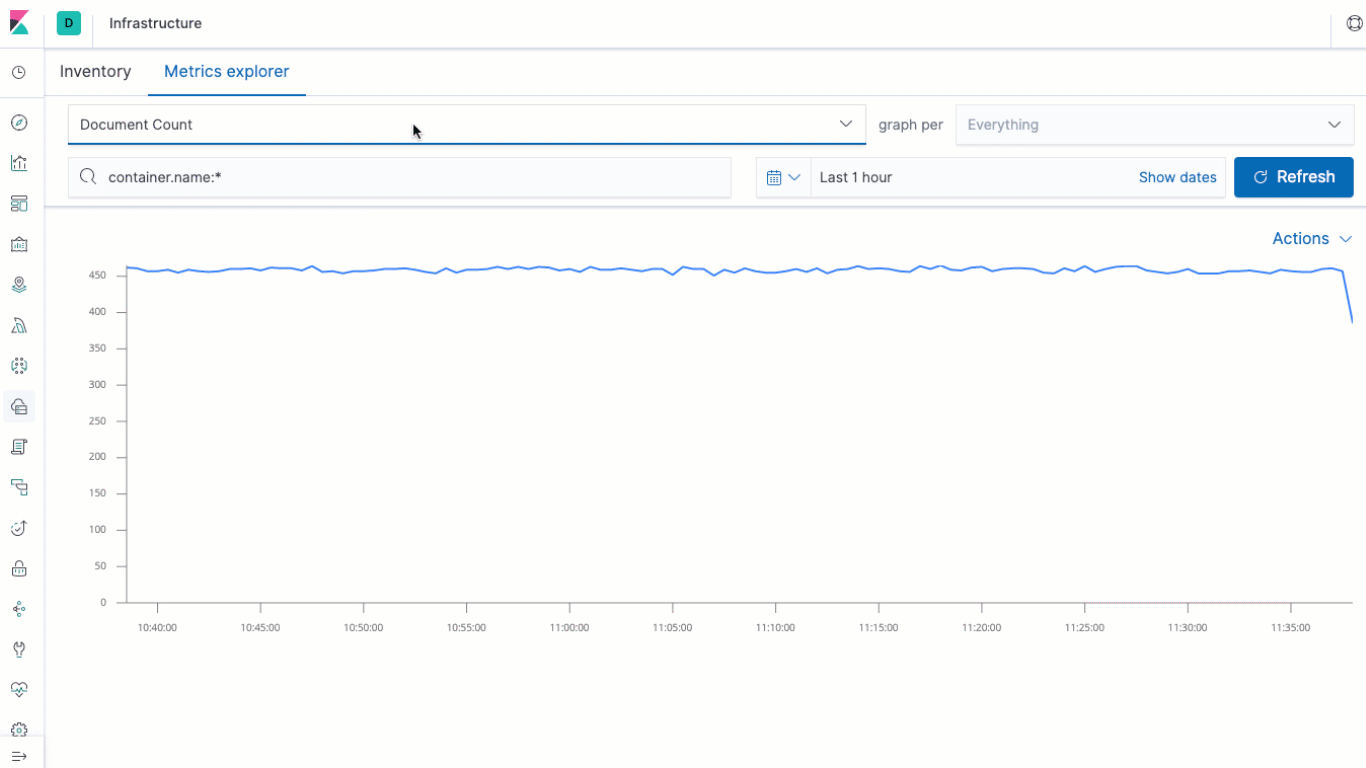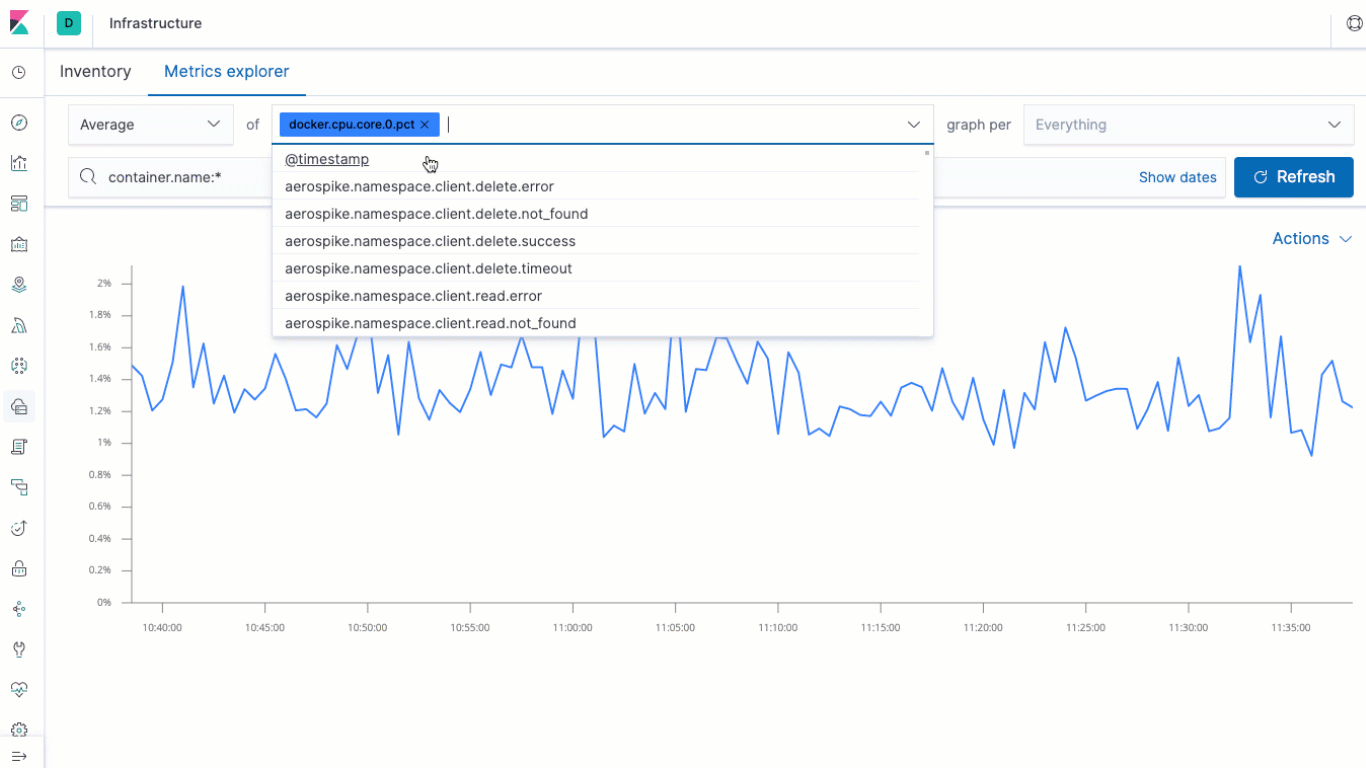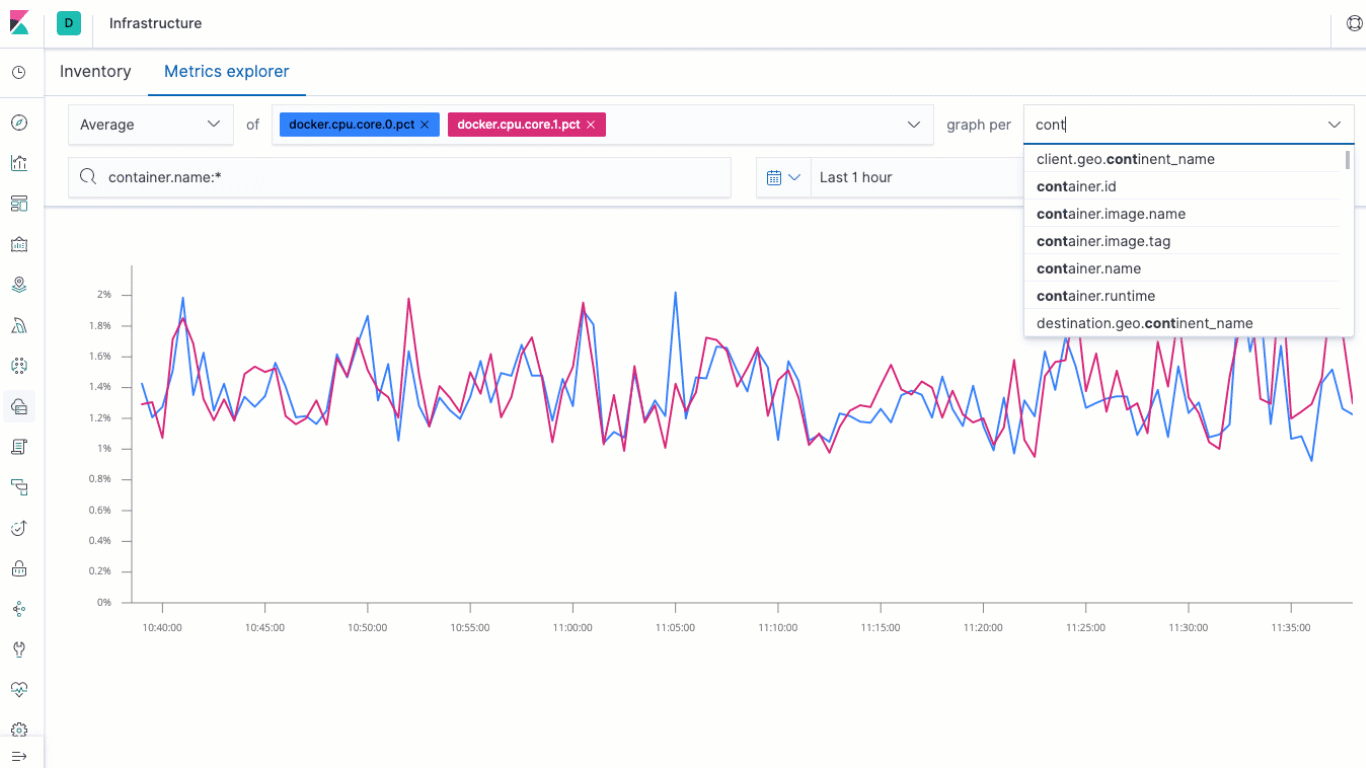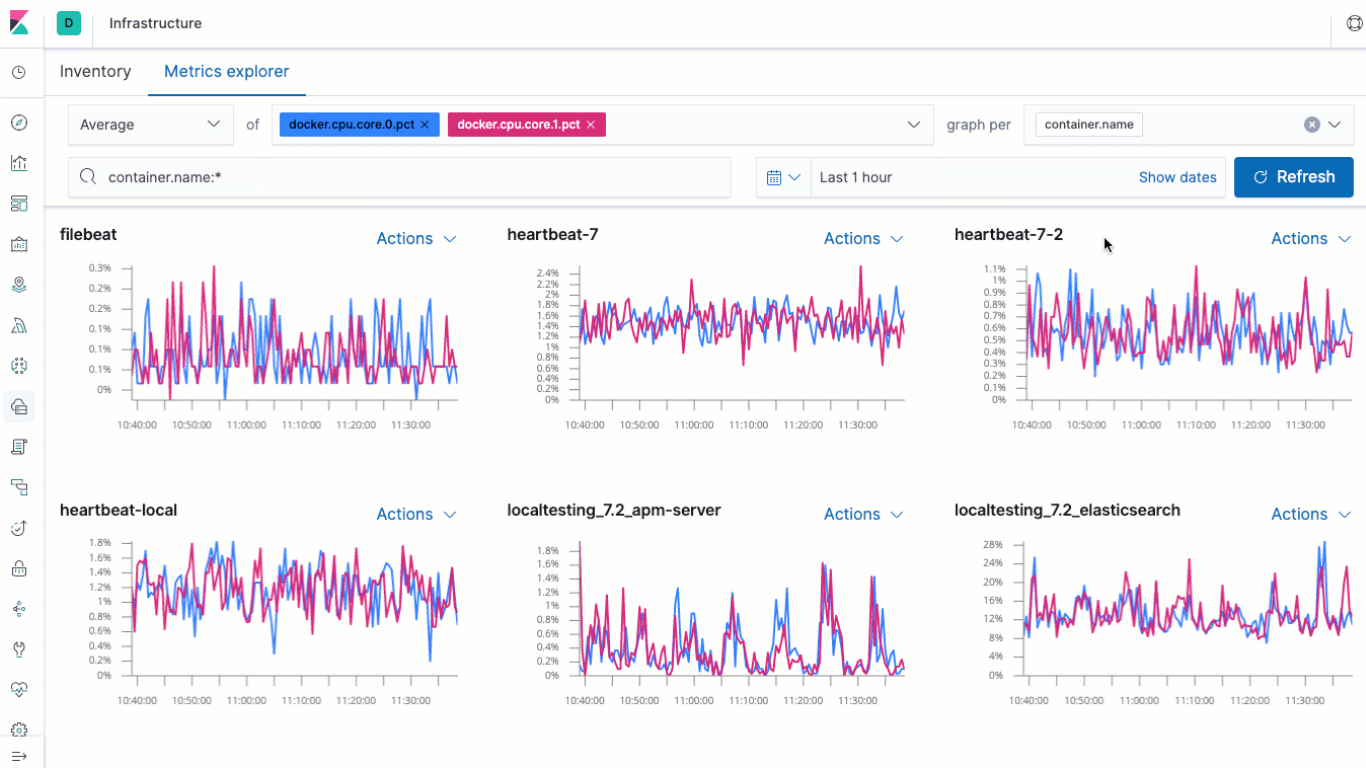
We've also made some tweaks to the layout of the Inventory view of the Infrastructure app, making the header a bit more compact to give you more real estate for your infrastructure metrics, while at the same time increasing accessibility and keyboard navigation capabilities throughout the entire Infrastructure application.
New modules
Release 7.2 brings with it a new module for CoreDNS metrics (beta). The CoreDNS module provides one metricset, stats, adding to our already robust tools for monitoring Kubernetes and container deployments. The CoreDNS module for Metricbeat captures statistics on dns requests and responses, sizes, cache hits and misses, and request duration information.
In addition to the CoreDNS module, a module fo Hashicorp's Consul was made available as a beta release. The Consul module includes the agent metricset, with metrics covering the overall health of the local server cluster, allocations, garbage collection stats, and memory information.
How to get it
You can access the Elastic Infrastructure application on the Elasticsearch Service on Elastic Cloud by creating a new cluster, or upgrading an existing cluster the day of release, or you can download it as part of the default distribution of the Elastic Stack.