Understanding the CISO: Role, skills, and security impact

In the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, the chief information security officer, or CISO, is responsible for ensuring the organization's data is secure.
CISOs ensure that proper security strategies, policies, and technologies are working to meet their goals of mitigating risk, maintaining regulatory compliance, and upholding customer trust. A CISO helps align security initiatives with business goals, enabling growth while minimizing disruptions and vulnerabilities.
But what is it like being a CISO? Stepping into this leadership role means effectively communicating and handling the security challenges and vulnerabilities of the entire organization. This is no easy task. This article will help you understand the role of a CISO and what it takes to become one.
What is a CISO?
The primary role of a chief information security officer is to develop, implement, and enforce security policies and procedures for an organization or business. The CISO also oversees the implementation of security technologies and employee training programs to prevent data breaches and system compromises.
CISOs integrate cybersecurity into the organization’s strategic planning and daily operations. They help build an internal culture of security awareness, reducing the likelihood of costly breaches and ensuring that the business remains compliant and resilient in a constantly changing threat landscape.
Why it’s important to have a CISO
Having a CISO is essential for protecting an organization’s digital assets, reputation, and operational resilience.
As the executive leader of cybersecurity, a CISO’s first priority is auditing and assessing the organization’s current security posture. A CISO will identify gaps and priorities by reviewing existing policies, systems, risks, and team capabilities. This foundational understanding helps the CISO to develop a tailored, risk-based security roadmap aligned with business goals.
Skills and experiences needed for CISOs
Chief information security officers need a unique blend of “in the trenches” cybersecurity experience, technical expertise, leadership ability, and strategic thinking. CISOs face growing security challenges and must have deep knowledge of cybersecurity, risk management, regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, NIST, SOC2), and effective threat detection and response practices.
Beyond their technical skills, a CISO needs to display leadership skills for managing security teams, budgets, and resources. Strong communication skills are essential for CISOs, as they are frequently called upon to translate complex security issues to nontechnical stakeholders. A successful CISO is also adept at building and leading cross-functional teams that can stay ahead of emerging threats.
The core responsibilities of a chief information security officer
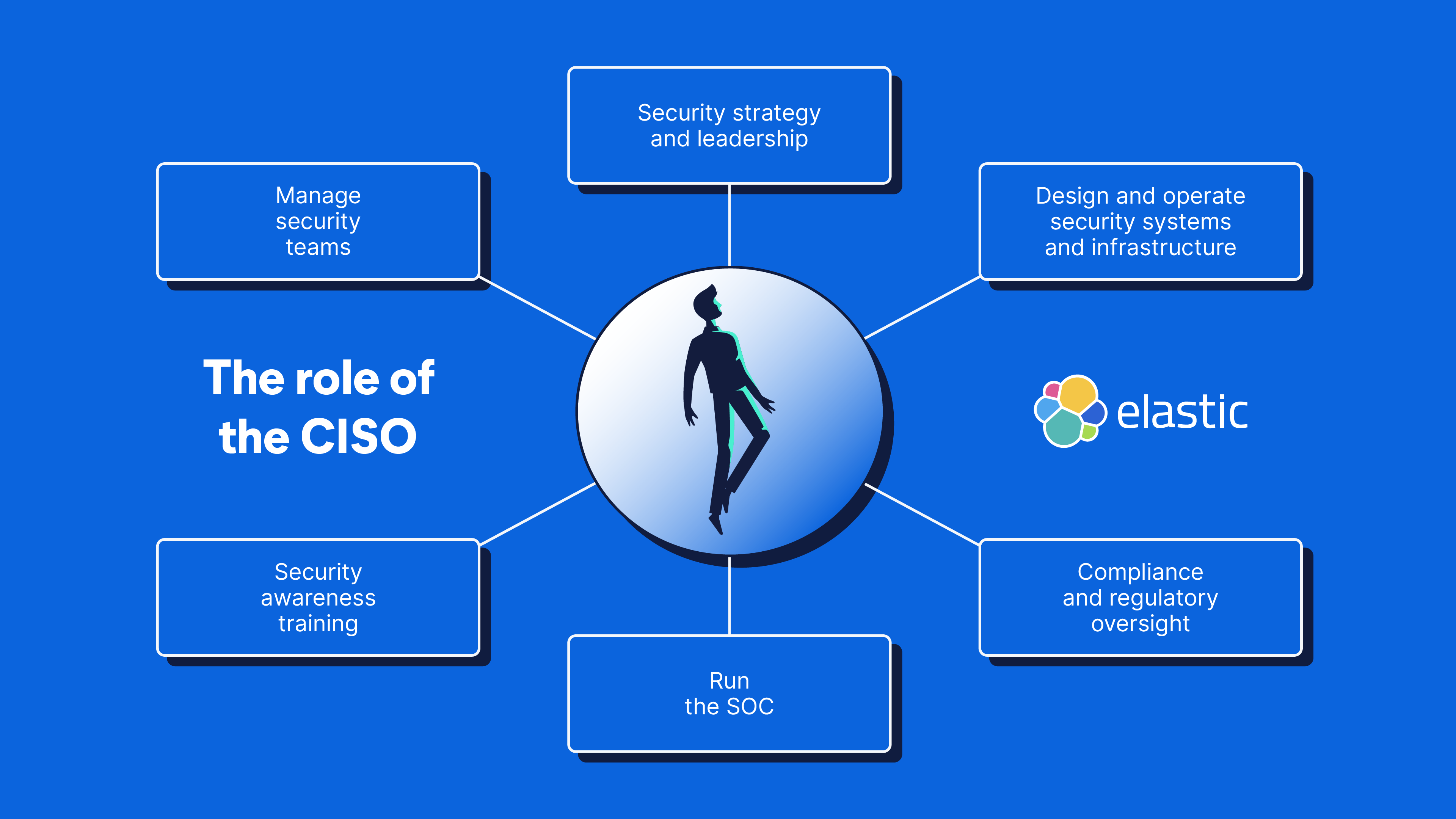
The chief information security officer leads the company-wide information security strategy, ensures the secure design and operation of systems and infrastructure, and equips their team to effectively manage cybersecurity risks.
CISOs need to balance a security-first mindset and smooth business operations. They must develop and enforce security policies while complying with relevant regulations and standards. Increasingly, CISOs must also consider customers’ security demands and concerns.
The CISO oversees the hiring, performance, and structure of security teams; directs the allocation of resources and budget to support security initiatives; and collaborates across departments like IT to embed security into the organization’s culture and decision-making processes.
The CISO is responsible for running an organization's security operations center (SOC) smoothly and effectively, which unifies and coordinates all cybersecurity processes, technologies, and operations. This role includes managing money as well as people — budgeting for technology or MSSP vendors, partners, CSPs, and more.
The core responsibilities of a CISO
| Responsibility | Description |
| Security strategy and leadership | Develop and implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy |
| Design and operate security systems and infrastructure | Develop and enforce security policies while complying with relevant regulations and standards |
| Compliance and regulatory oversight | Ensure adherence to GDPR, NIST, SOC2, and other compliance frameworks |
| Run the SOC | Unify and coordinates all cybersecurity processes |
| Security awareness training | Educate employees and leadership on cybersecurity best practices |
| Manage security teams | Hire security teams and manage their performance and structure |
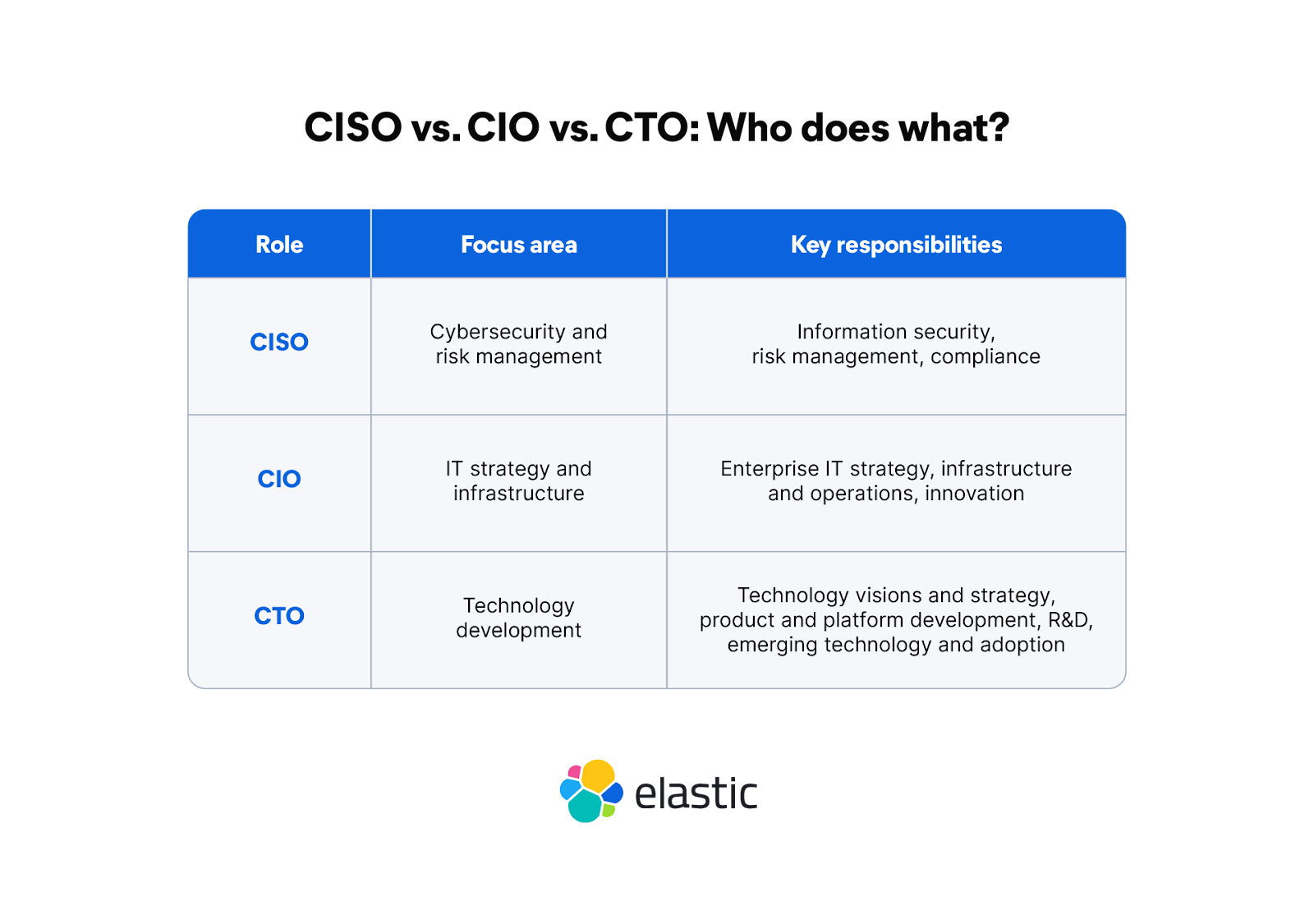
CISO vs. CIO vs. CTO
The chief information security officer role can vary for different businesses and may have some overlapping responsibilities with the chief information officer (CIO) or chief technology officer (CTO).
The CISO role might sit under or work across various departments, like IT, and may frequently collaborate with the CIO and CTO. Generally, the CISO focuses on cybersecurity and risk, the CIO focuses on IT strategy and infrastructure, and the CTO focuses on technology development. All three roles must coordinate to ensure that innovation and operational efficiency do not come at the expense of security or compliance.
Areas of overlap and collaboration between the CISO, CIO, and CTO include IT infrastructure and cloud strategy, data governance and privacy, and digital transformation and innovation. It is important to clearly define the role of a CISO within an organization.
CISO’s role in cybersecurity strategy and risk management
A CISO develops and implements cybersecurity strategies by understanding the organization’s assets, systems, and security threats. They create a risk management framework to identify an organization’s vulnerabilities and evaluate the potential impact of various threats. By working with others on the leadership team, CISOs prioritize risk mitigation efforts based on their most critical needs.
In addition to proactive risk management, CISOs create a plan for incident response and crisis management in the event of a cyber attack or security breach. The response plans will include ways to coordinate internal teams and external partners, as well as communication strategies to minimize damage and ensure rapid recovery.
Business continuity planning also falls within a CISO’s scope. If a cyber attack occurs, CISOs work to ensure critical operations can continue or resume quickly. Through regular testing, training, and refinement of response plans, the CISO helps build organizational resilience and ensures readiness for evolving threats, such as AI-powered cyber attacks.
Challenges CISOs face
CISOs face new types of cyber threats, including AI-powered cyber attacks and the risks that come with working with third-party vendors and vendor supply chains.
CISOs also face challenges inside their organizations. Immediate business needs and secure architecture don’t always align. A CISO may face challenges advocating for the funds needed to properly prepare an organization for the latest security challenges. It’s important for CISOs to clearly explain risks and countermeasures to business leaders.
The future of the CISO role
As organizations’ need for cybersecurity grows, so too does the role of the CISO. Successful CISOs will be able to anticipate and prepare for the newest threat trends while effectively communicating security needs across the organization.
How CISOs modernize their security posture with Elastic Security
Elastic Security helps CISOs modernize their security posture by empowering their security teams with a unified, scalable threat prevention, detection, investigation, and response platform.
Elastic enables real-time visibility across endpoints, environments, and network data, helping teams quickly detect anomalies and investigate incidents with powerful search, correlation, and analytics capabilities.
Explore more security resources for CISOs and security practitioners
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.
In this blog post, we may have used or referred to third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch, and associated marks are trademarks, logos, or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos, or registered trademarks of their respective owners.