Over 90% of C-suite execs have already invested in or plan to invest in generative AI (GenAI) to deliver better customer and employee experiences. But 95% of enterprise AI projects fail,1 two times the rate of other IT projects.2 So, how do you build generative AI applications that are scalable, meet your business needs today, and deliver lasting value into the future when the odds seem stacked against you?
We have created and refined the process that we used to build Support Assistant, our generative AI experience for support engineers and customers, and ElasticGPT, our GenAI employee assistant app, and believe these steps are universally applicable. Here is what went into creating our successful GenAI apps.
1. Define clear objectives and KPIs
The first step is to define the business problem you’re solving. Before you touch models, vendors, or architectures, anchor the effort in a single, measurable business outcome. Validate the problem with real users and operational data, not assumptions. The goal is to prioritize GenAI investments by expected outcomes.
Here’s what the process looked like for our work on Support Assistant:
- Define the problem: The current customer support model couldn’t scale to meet the demand of our growing customer base. Support engineers struggled to quickly find relevant answers from 300,000+ documents, often leading to longer response times.
- Determine the ideal outcome and KPIs: We wanted the solution to provide users — both customers and support engineers — with real-time answers. With some customers self-serving, engineers could focus on more complex cases. Our KPIs were:
- 23% decrease in mean time to first response (MTFR) to customers
- 7% reduction in volume of assisted support cases
- $1.7 million cost avoidance from hard case deflections
Apply AI within workflows: We wanted to make sure this solution is accessible within existing workflows, so we decided to host the experience where customers and employees already spend their time: the Elastic Support Hub and Engineer View, our custom support interface.
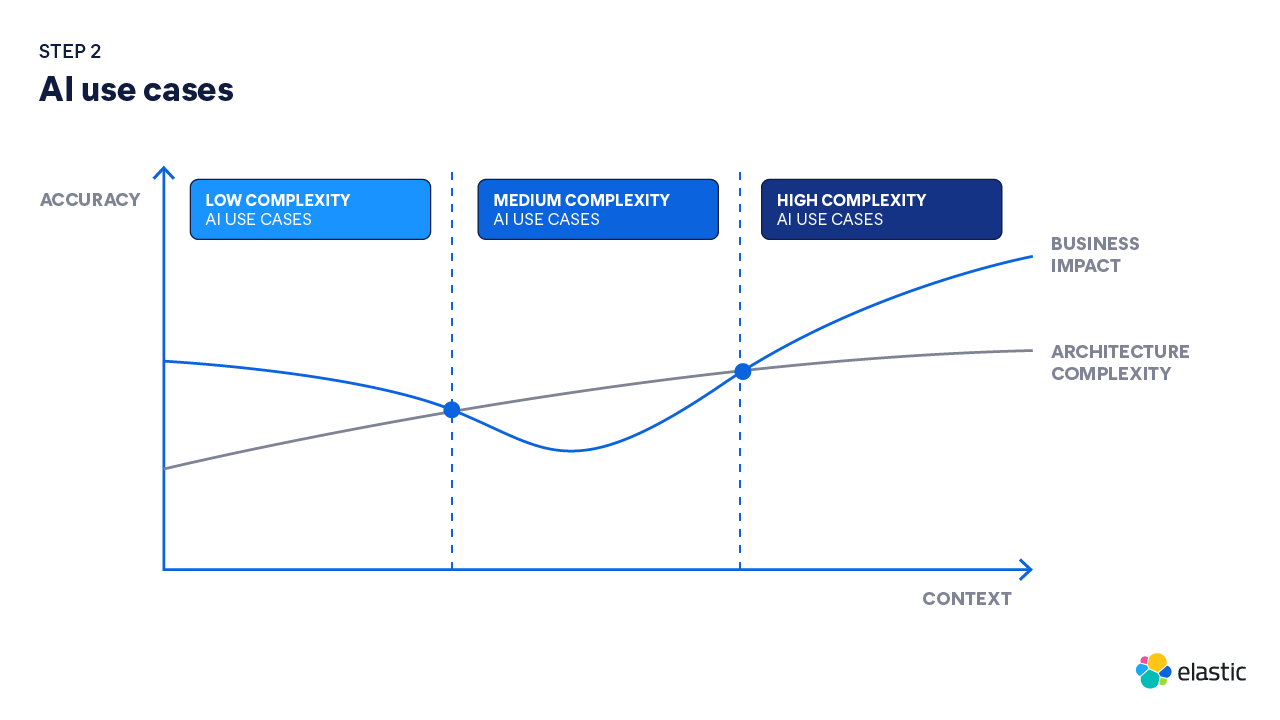
2. Balance business impact with technical complexity
With goals and KPIs established, next consider what resources and time you and your teams will be able to devote to this initiative. Depending on the level of business impact you're looking to drive, you'll need different levels of tech expertise, business process changes, and resource investment.
To identify the level of investment, start by determining how much data will be required for this GenAI app to produce relevant answers. Large language models (LLMs) need context (your data) to retrieve, synthesize, and structure accurate answers. The more context you need, the bigger the investment. Additionally, if you’re looking to embed it within a specific application, that may require additional architecture investments. Consider these use cases and their requirements:
- Low complexity use cases can provide immediate impact and don’t typically require complex architecture, as you might only be pulling from a few data sources and systems. For example, a GenAI chatbot could help teams quickly find answers to common IT-related questions. This use case only requires access to your IT knowledge base and doesn’t require a complex architecture to deploy. It’s easy to quantify business impact; just look for a decrease in IT tickets.
- Medium complexity use cases aim to apply GenAI to workflows to reclaim user time. For example, applying GenAI to a customer support process can deliver self-service experiences that minimize case volume and recoup time required from the support team to solve customer problems. This leads to cost efficiencies across the function. Initiatives like this require a higher level of tech effort as it involves pulling context from disparate data sources (CRM data, issue resolutions, defects, cases, knowledge documentation, educational content, etc.), a robust architecture that connects all systems, and investment into change management of business processes. Although this is more resource-intensive upfront, in the long term, this type of use case will deliver greater business impact than a low complexity use case and can serve as a foundational architecture for even more complex GenAI use cases in the future.
- High complexity use cases drive new revenue streams. These types of initiatives use AI to help your organization create new products and services that deliver new revenue streams. Often, these types of use cases require access to a wealth of proprietary data and sophisticated architectures. This means it will have a longer time-to-value. For example, a pharmaceutical company could use AI and its proprietary data to discover new, previously unknown material compounds, or an investment bank could develop a new financial planning application that analyzes historical data and market trends to generate personalized investment strategies for its customers.
Our Support Assistant was a medium-complexity use case. It enhances the entire support workflow with insights from proprietary data via retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and integrates into engineer and customer workflows. It demanded moderate technical and organizational effort and had a longer time-to-value than simple copilots. However, it delivers outsized, durable return on investment (ROI) through case deflection, faster responses, increased engineer capacity, and compounding knowledge creation.
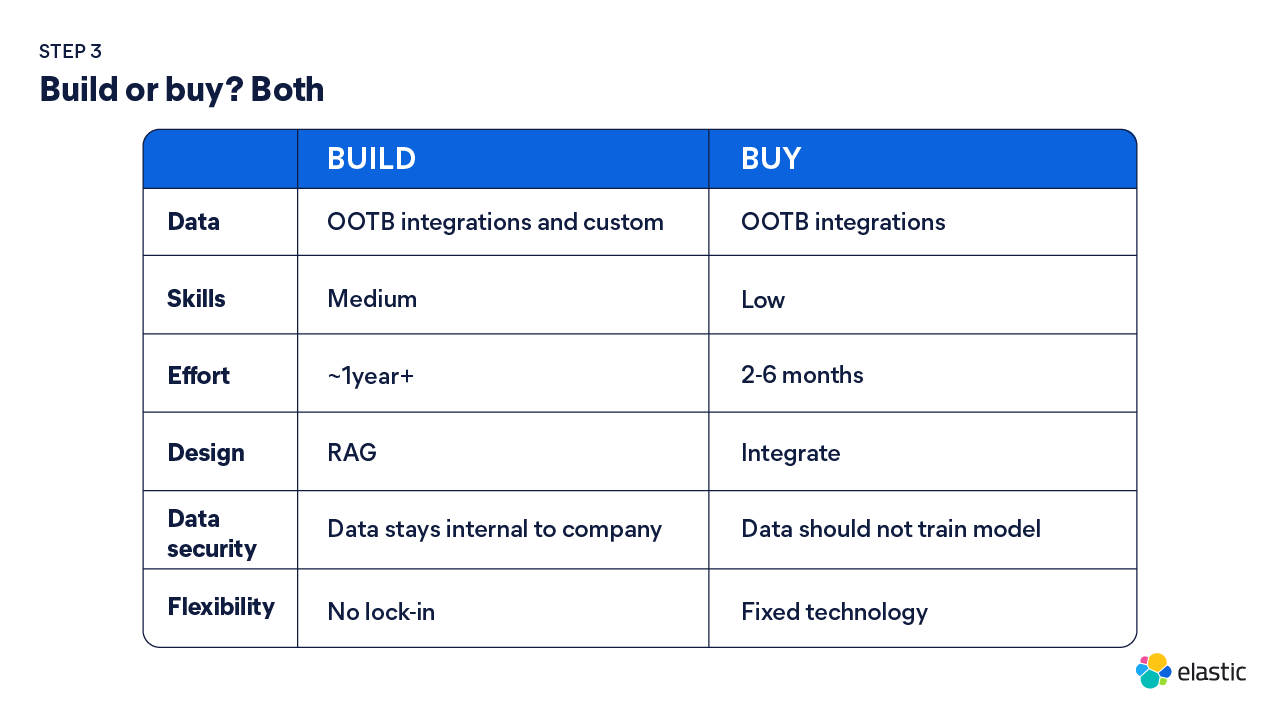
3. Build or buy? Both
In every organization, IT teams have invested in SaaS applications that address a specific use case while offering a system of record. These applications offer prebuilt workflows and a way to enforce reliability, security, and transparency. SaaS tools will always have their place in your architecture (e.g., Salesforce, Seismic, Adobe) as they are well-suited for workflows. These SaaS solutions deliver AI features that may enable productivity gains but can be limited by:
- Lack of context: To deliver accurate outputs and answers, AI requires context that spans your entire organization. Although these tools have a single source of truth for those given workflows and use cases, the data stored within them is disconnected from enterprise sources that can provide AI with additional information that would deliver more relevant insights.
- Lack of insights: Many SaaS solutions with AI features fail to deliver actionable insights about the AI model. They do not capture telemetry on AI features to track user sentiment, satisfaction, engagement, or accuracy of responses, like LLM observability could when included in an app that you built. So, although your team may be using AI within a given workflow tool and you may see that the feature is providing an uplift to productivity, you can’t see what users are asking and how the experience could be better suited to their needs. This limited oversight can delay efforts to mature your AI solution to deliver even more impact.
- Lack of customization: Often, AI features within these SaaS applications are limited by customization constraints and are embedded within predefined task-specific workflows. This makes it impossible to tune AI features to your teams’ needs.
To build one tech stack that enables faster innovation for multiple LOBs, it’s essential to buy open SaaS applications that can integrate into a larger AI ecosystem. GenAI delivers the most value when it’s fitted within your business context. By integrating data and SaaS tools across your organization, you can build custom GenAI solutions that are orchestrated within a larger enterprise architecture to augment your AI solutions from data and context across various SaaS applications, delivering relevant answers and a seamless experience.
Real-world use case
Discover how we built a scalable GenAI app that transforms the customer support experience
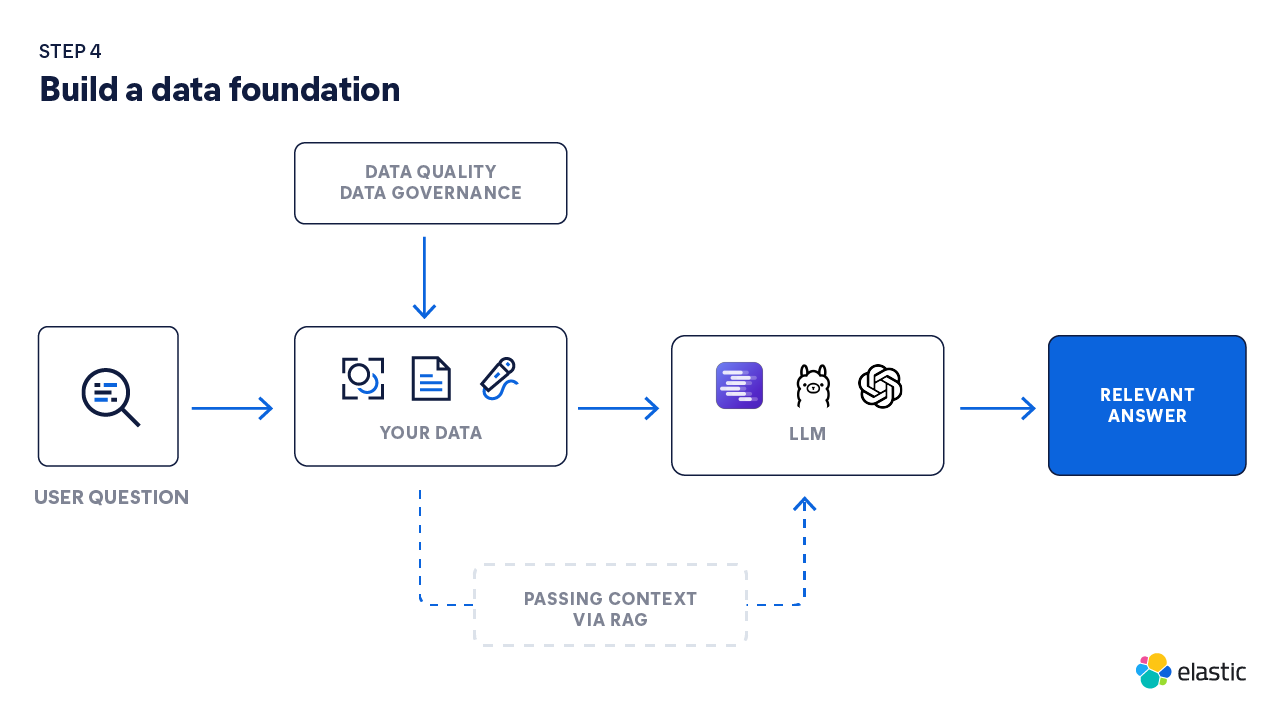
4. Build a data foundation
One of the most crucial components of your GenAI app is your data foundation. This consists of data integration techniques, your datastore, the quality of your data, and how you keep it all secure.
- Data quality: The quality of your data is critical to building a GenAI app that delivers relevant answers. Based on your use case, ensure you’re choosing data sources — unstructured, structured, semi-structured — that will produce accurate, high-quality answers. This may include further cleaning data before ingestion and leveraging a standard schema for field mapping and normalization. AI can also be used to automate data onboarding to your relevant datastore, further reducing data pipeline engineering efforts.
- Vector database: To understand the context and meaning of data, a robust vector database serves as the key datastore and retrieval mechanism for building GenAI applications that deliver relevant answers to user queries. By storing vector embeddings, your architecture can retrieve the most relevant context through precise semantic matches and pass it to LLMs to deliver grounded responses. Some of the best vector databases enable teams to work efficiently with large, evolving datasets by offering data compression.
- Security: To ensure that data is protected, GenAI development teams should define role and attribute-based access controls to only authorize relevant users to access specific data that is available within the application. For example, a manager might have access to more company data than an individual contributor. Additionally, data encryption is crucial when transferring data to LLMs to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. By implementing security measures, organizations can meet compliance requirements and maintain governance over data.
5. Architect a solution
Now it’s time to determine what will be a part of your solution. You’ll have your data foundation from above, and you’ll also need to take into account:
- Step 1: Infrastructure and architecture: Scalable development environments should be deployed on cloud infrastructure to leverage features such as auto-scaling and CPU/GPU acceleration, ensuring efficient resource management as demand fluctuates. All major cloud service providers and vector databases offer integrations to many enterprise data sources, system integrations, and AI/ML models. A durable AI architecture is what allows teams to move from simple, low-complexity AI use cases to highly complex agentic workflows.
- Step 2: Data ingestion: Here is where you will connect mission-critical source systems via managed integrations. Effective ingestion will normalize data into a common schema to eliminate reconciliation friction downstream. This includes defining your data ingestion frequency (batch processing, real-time processing, etc.), relevant maintenance requirements, and data cleaning and standardization.
- Step 3: Retrieval augmented generation (RAG): LLMs are pretrained on vast amounts of publicly available data, so by using RAG, your teams can ensure the answers from your GenAI app are grounded with your own trusted, unstructured data — without retraining models or copying everything into the LLM. The app retrieves the most relevant data (from wikis, tickets, contracts, logs, and more) from your systems in real time and feeds them to the model to generate accurate, context-aware responses. RAG improves answer quality, reduces hallucinations, and tightens governance by keeping data in approved stores with access controls and audit.
- Step 4: AI/ML integrations: To build a RAG architecture, you can use RAG development frameworks such as Hugging Face, LlamaIndex, and more. To quickly build a GenAI application, ensure you’re choosing a platform and cloud provider that offers integrations to frameworks and preferred LLMs to speed up development. Using ML models, teams can further tune relevance to pass the most accurate context to LLMs, enhancing answer accuracy and user experience.
- Step 5: LLM observability and application performance monitoring (APM): To gain business insights into the user experience, performance, and response accuracy of your GenAI app, invest in observability solutions. LLM observability will provide visibility that allows you to further fine-tune experiences and maintain uptime. Using application performance monitoring, you can gain valuable insights into technology performance and system health, enabling your DevOps team to detect issues, identify anomalies, debug more efficiently, and resolve incidents. With signals such as model performance, conversation quality, and user activity, you can optimize models and context to further enhance the accuracy of responses while tracking costs.
6. Establish governance
It will be necessary to have guardrails, processes, and safeguards in place to ensure your AI models are safe, compliant, and ethical. You’ll need to consider:
- New data sources: Ensure new data is of high quality, accurate, and lawful to use. Set standards for data provenance, validation, and freshness before any new data source is connected. Classify data sensitivity (public, internal, confidential, regulated) and enforce least-privilege access. As you add more data to your environment, continue to implement and enforce data security, including field and document-level security as well as role and attribute-based access controls. For Support Assistant, we continue to enhance the experience by adding new data sources to provide additional context for our support engineers, enabling them to further personalize customer interactions. We leverage role-based access controls to prohibit customers from accessing the same answers.
- Compliance
- Regulatory compliance: Consider how you will comply with GDPR and other compliance regulations to protect personally identifiable information (PII). Set up a process to continuously audit your app to ensure its compliance with AI laws and regulations.
- Internal governance: Establish policies for data access, retention, and use (including what data can and can’t be used for training or fine‑tuning), and enforce them with role-based access controls, approval workflows, and audit trails. Create an incident response playbook for AI-specific failures (data leakage, harmful content, etc.).
Search AI Platform
Discover the platform that combines your private data with AI to build GenAI apps that deliver context-aware answers for any data-centric use case
7. Measure success and performance
Determine how your GenAI app has met your business goals that you set in step 1. If you can establish ROI for this AI use case, you will more likely be able to procure additional resources to expand and evolve it as your business scales. You’ll look at:
- User adoption: Determine the adoption and satisfaction rates among your users. Most likely, the more contextually accurate the responses users get, the more they’ll adopt the solution. With Support Assistant, we used Elastic Observability to capture usage metrics. We saw 100% support engineer penetration, with 1 in 2 using it daily. This reduced reliance on senior engineers for onboarding and training and minimized our ramp time.
- Business impact: See how your solution has met its KPIs, like improved productivity, reduced costs, or contributed to better decision-making. For Support Assistant, we looked at MTFR, hard case deflections (where users explicitly abandon creating a support ticket after finding answers via Support Assistant), and soft case deflections (where users implicitly abandon creating a support ticket or looking through knowledge articles after finding answers via Support Assistant). Using these metrics, we could quantify how quickly we realized ROI. We saw:
- 23% decrease in mean-time-to-resolution (MTFR)
- 6x hard case deflections and 20x soft case deflections
- 4-month ROI
It’s important to look at these metrics consistently so you can make adjustments to the model, data, and user experience as needed.
8. Continuously improve and iterate
As with all new solutions, you and your teams will need to iterate to improve them and ensure they contribute business value. At this stage, you’ll look to:
- Add new data sources: First, ensure the data sources are high-quality and accurate to expand the knowledge base and breadth of information retrieval.
- Embed in workflows: Bring GenAI to the tools where employees work to drive adoption, like what we did with our own AI Assistant for security analysts to speed up their threat intelligence reporting process.
- Integrate agentic AI: As you advance your AI maturity, explore use cases for autonomous agents that further synergize information and actions from given context and tools to execute a sequence of events to achieve a specific goal.
Building scalable GenAI applications requires a strategic and methodical approach. By defining clear objectives, building a robust data foundation, and continuously measuring and improving, organizations can unlock the full potential of GenAI.
Elastic's Search AI Platform provides the comprehensive tools and capabilities needed to accelerate this journey. It helps enable businesses to create powerful, secure, and future-proof GenAI experiences that drive real business value. Our platform combines GenAI, RAG, and your proprietary data to create conversational search experiences to unlock relevant, accurate, domain-specific responses and actions. And with access to Elastic Observability, teams can take it one step further to monitor applications and ensure optimal LLM performance.
See how Docusign built a scalable and secure GenAI that helps its customers find documents in minutes, not hours.
Footnotes
- MIT, “The GenAI Divide: STATE OF AI IN BUSINESS 2025,” 2025.
- Rand, “The Root Causes of Failure for Artificial Intelligence Projects and How They Can Succeed” 2024.
