Install Fleet-managed Elastic Agents
editInstall Fleet-managed Elastic Agents
editThese steps assume you’re running a fresh installation. If Elastic Agent is already running on your system, and you want to upgrade to a new version, see Upgrade Elastic Agents.
If you’re a new user, instead of following the steps described here, read our quick start guides:
Prerequisites
edit- Fleet is currently only available to users with the superuser role.
- A Fleet Server must be running in a location accessible to the Elastic Agent. See Fleet Server.
- To use Fleet, Elastic Agents must have a direct network connection to Fleet Server and Elasticsearch.
-
An internet connection is required for Kibana to download integration packages
from the Elastic Package Registry. Make sure the Kibana server can connect to
https://epr.elastic.coon port443. - You must have an enrollment token generated by Fleet. Don’t have a Fleet enrollment key? Read Fleet enrollment tokens to learn how to get one from Fleet.
- You must have the host and IP where Fleet Server is running. Not sure where it’s running? Look at the Fleet settings in Kibana.
- If you’re running Elastic Agent 7.9 or earlier, stop the agent and manually remove it from your host.
Installation steps
editYou can install only a single Elastic Agent per host.
To install an Elastic Agent and enroll it in Fleet:
-
On the machine where you’ll run Elastic Agent, download and extract the installation package.
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/elastic-agent/elastic-agent-7.17.29-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz tar xzvf elastic-agent-7.17.29-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/elastic-agent/elastic-agent-7.17.29-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar xzvf elastic-agent-7.17.29-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
# PowerShell 5.0+ wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/elastic-agent/elastic-agent-7.17.29-windows-x86_64.zip -OutFile elastic-agent-7.17.29-windows-x86_64.zip Expand-Archive .\elastic-agent-7.17.29-windows-x86_64.zip
Or manually:
- Download the Elastic Agent Windows zip file from the download page.
- Extract the contents of the zip file.
To simplify upgrading to future versions of Elastic Agent, we recommended that you use the tarball distribution instead of the DEB distribution.
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/elastic-agent/elastic-agent-7.17.29-amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i elastic-agent-7.17.29-amd64.deb
To simplify upgrading to future versions of Elastic Agent, we recommended that you use the tarball distribution instead of the RPM distribution.
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/elastic-agent/elastic-agent-7.17.29-x86_64.rpm sudo rpm -vi elastic-agent-7.17.29-x86_64.rpm
See the download page for other installation options.
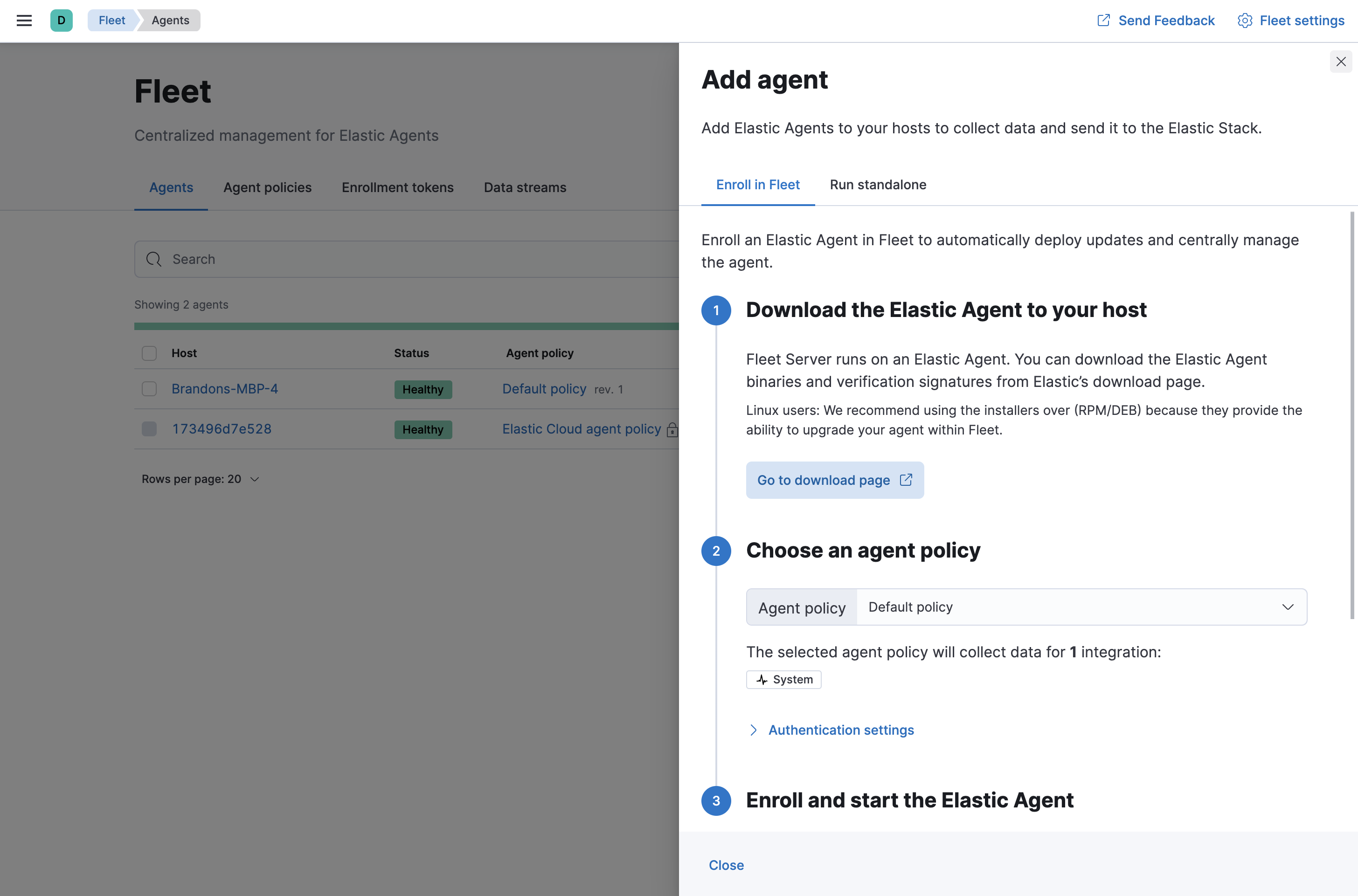
- On the Agents tab in Fleet, click Add agent.
-
Under Enroll in Fleet, follow the in-product installation steps (skip the download step if you’ve already done it).
See the download page for other installation options.
Notes:
- Use the default agent policy to get started quickly. This policy includes a system integration for collecting logs and metrics from the host system. You can change the policy later.
-
On macOS, Linux (tar package), and Windows, run the
installcommand to install Elastic Agent as a managed service, enroll it in Fleet, and start the service. The DEB and RPM packages include a service unit for Linux systems with systemd, so use theenrollcommand instead ofinstall.You must run this command as the root user because some integrations require root privileges to collect sensitive data.
You must run this command as the root user because some integrations require root privileges to collect sensitive data.
Open a PowerShell prompt as an Administrator (right-click the PowerShell icon and select Run As Administrator).
From the PowerShell prompt, change to the directory where you installed Elastic Agent, and run:
You must run this command as the root user because some integrations require root privileges to collect sensitive data.
sudo elastic-agent enroll --url=<fleet_server_url> --enrollment-token=<enrollment_token> sudo systemctl enable elastic-agent sudo systemctl start elastic-agent
fleet_server_urlis the host and IP where Fleet Server is running, andenrollment_tokenis the enrollment token acquired from Fleet. Not sure where Fleet Server is running? Look at the Fleet settings in Kibana.The DEB package includes a service unit for Linux systems with systemd. On these systems, you can manage Elastic Agent by using the usual systemd commands. If you don’t have systemd, run
sudo service elastic-agent start.You must run this command as the root user because some integrations require root privileges to collect sensitive data.
sudo elastic-agent enroll --url=<fleet_server_url> --enrollment-token=<enrollment_token> sudo systemctl enable elastic-agent sudo systemctl start elastic-agent
fleet_server_urlis the host and IP where Fleet Server is running, andenrollment_tokenis the enrollment token acquired from Fleet.The RPM package includes a service unit for Linux systems with systemd. On these systems, you can manage Elastic Agent by using the usual systemd commands. If you don’t have systemd, run
sudo service elastic-agent start.If you see an "x509: certificate signed by unknown authority" error, you might be trying to enroll in a Fleet Server that uses self-signed certs. To fix this problem in a non-production environment, pass the
--insecureflag. For more information, refer to the troubleshooting guide.Refer to Installation layout for the location of installed Elastic Agent files.
Because Elastic Agent is installed as an auto-starting service, it will restart automatically if the system is rebooted.
To confirm that Elastic Agent is installed and running, go to the Agents tab in Fleet. Notice that the Default policy is assigned to the agent.
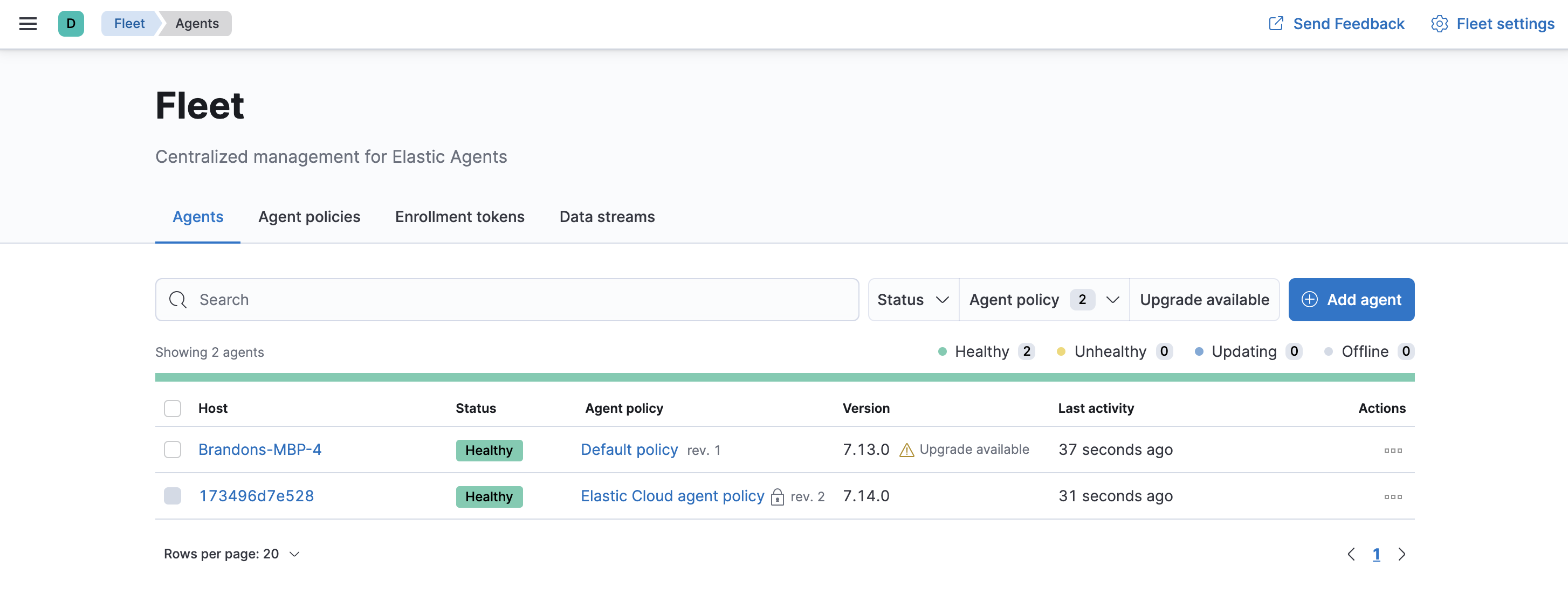
If the status hangs at Enrolling, make sure the elastic-agent process
is running.
If you run into problems:
- Check the Elastic Agent logs. If you use the default policy, agent logs and metrics are collected automatically unless you change the default settings. For more information, refer to View Elastic Agent logs in Fleet.
- Refer to the troubleshooting guide.
For information about managing Elastic Agent in Fleet, refer to Centrally manage Elastic Agents in Fleet.