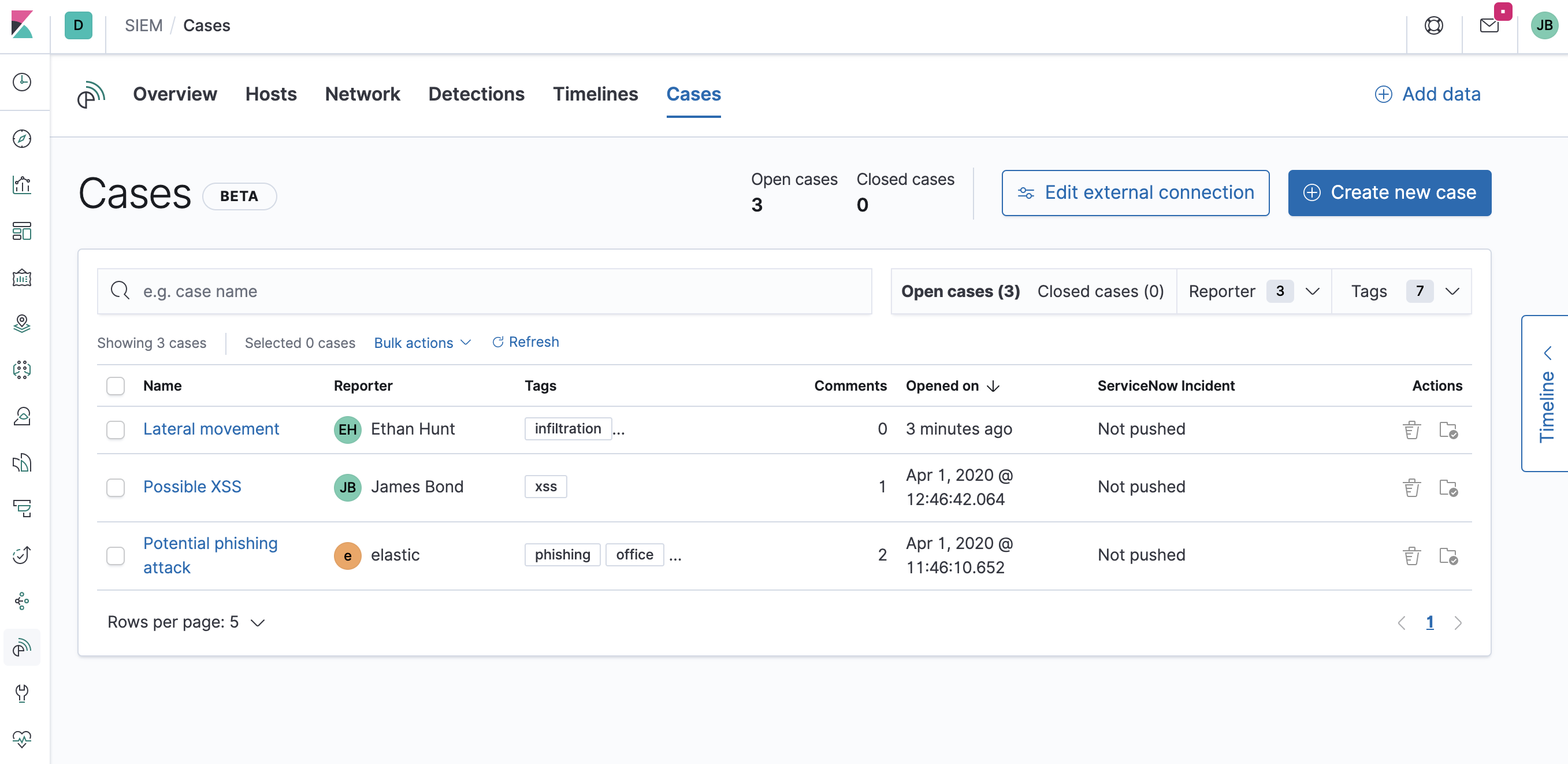
Cases (beta)
editCases (beta)edit
This functionality is in beta and is subject to change. The design and code is less mature than official GA features and is being provided as-is with no warranties. Beta features are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
Cases are used to open and track security issues directly in the SIEM app.
All cases list the original reporter and all users who contribute to a case
(participants). Comments support Markdown syntax, and allow linking to saved
Timelines. Additionally, you can send cases to external
systems from within the SIEM app (currently ServiceNow). Configuring external connections
describes how to set this up.
You can create and manage cases via the UI or the Cases API.
To send cases to ServiceNow, you need the appropriate license.
To make sure you can view and open cases, see Cases prerequisites.
Open a new caseedit
Open a new case to keep track of security issues and share their details with colleagues.
- Go to SIEM → Cases → Create new case.
-
Give the case a name, and add a description and any relevant tags.
In the
Descriptionarea, you can use Markdown syntax and insert a timeline link (click the icon in the top right corner of the area). - When ready, create the case.
- If external connections are configured, you can send the case to ServiceNow.
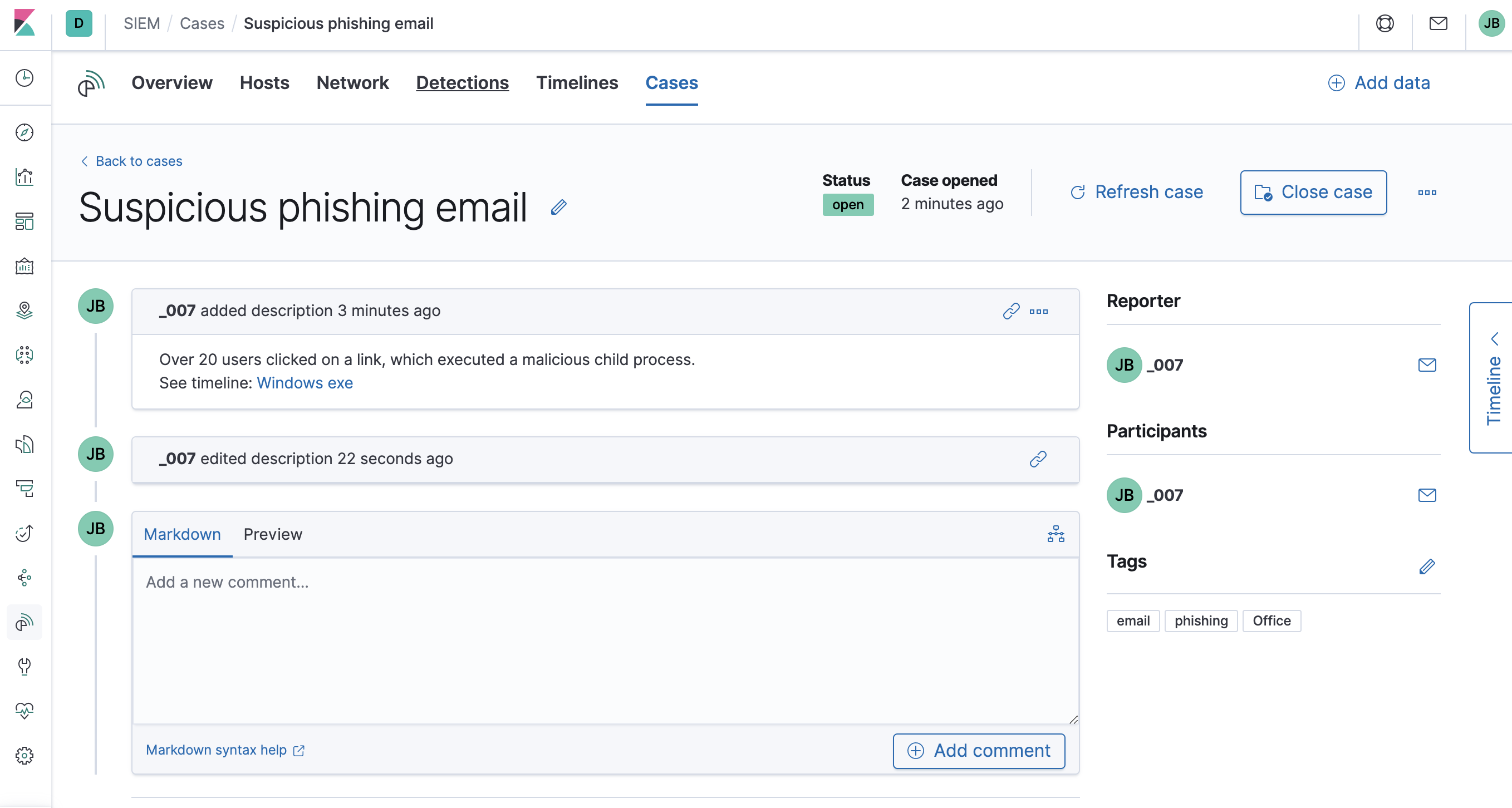
Manage existing casesedit
You can search existing cases, and filter them by tags, reporter, and status (open or closed).
To view a case, click on its name. You can then:
- Add a new comment.
- Edit existing comments and the case’s description.
- Send updates to ServiceNow (if external connections are configured).
- Close the case.
- Reopen a closed case.
- Edit tags.
- Refresh the case to retrieve the latest updates.
Cases prerequisitesedit
To view cases, you need the Kibana space Read privilege for the Saved Objects
Management feature. To create cases and add comments, you need the All Kibana
space privilege for the Saved Objects Management feature. For more information,
see Feature access based on user privileges.