Kubernetes security posture management
editKubernetes security posture management
editThe Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM) integration allows you to monitor how your Kubernetes clusters' configuration measures up to security benchmarks.
To set up the integration, you’ll need to first add it to an Elastic Agent policy, then deploy the KSPM DaemonSet to the Kubernetes clusters you want to monitor.
Set up a KSPM integration
editTo install the integration:
- Go to Dashboards → Cloud Posture.
- Click Add a CIS integration.
- Click Add Kubernetes Security Posture Management.
- Name your integration.
- Select whether to use the CIS or EKS Benchmarks — use CIS unless you’re deploying on EKS.
- Select the Elastic Agent policy where you want to add the integration.
-
Click Save and continue, then Add agent to your hosts. The Add agent wizard appears and provides a DaemonSet manifest
.yamlfile with pre-populated configuration information, such as theFleet IDand`Fleet URL`.
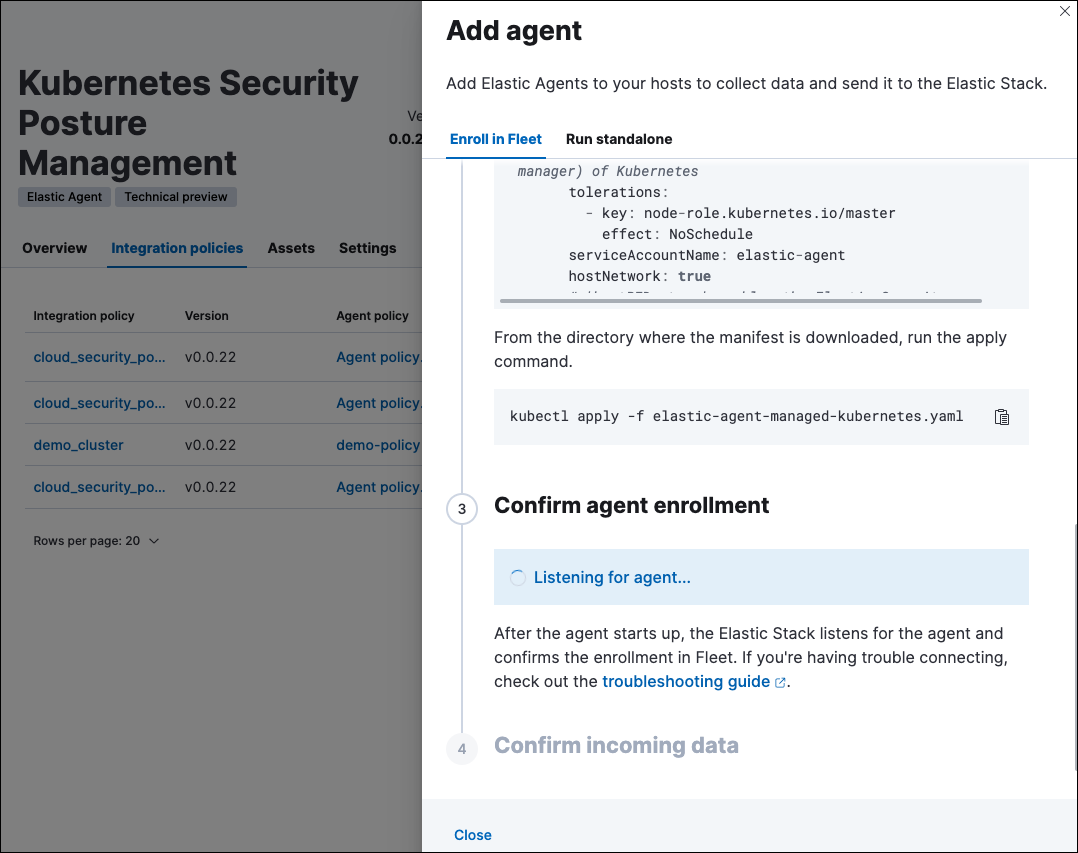
The Add agent wizard helps you deploy a DaemonSet on the Kubernetes clusters you wish to monitor. To do this, for each cluster:
- Download the manifest and make any necessary revisions to its configuration to suit the needs of your environment.
-
Apply the manifest using the
kubectl apply -fcommand. For example:kubectl apply -f elastic-agent-managed-kubernetes.yaml
After about a minute, an “Agent enrollment confirmed” message appears, followed by “Incoming data confirmed." You can then click View assets to see where the newly-collected configuration information appears throughout Kibana, including the Findings page and the Cloud Posture dashboard.
Findings page
edit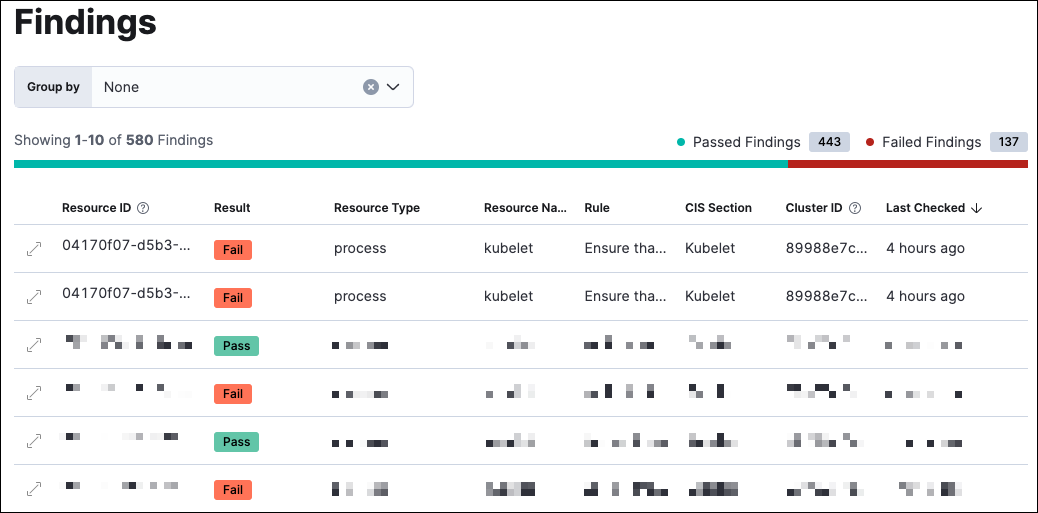
The Findings page shows how the configuration of your Kubernetes clusters measures up to the standards defined on the CSP Benchmarks page.
Findings are organized by the resource IDs of the associated Kubernetes infrastructure and include data about the infrastructure and benchmark rules. Each finding’s result (which can be pass or fail) indicates whether a particular part of your Kubernetes infrastructure meets an active CSP benchmark rule.
You can filter table data by entering queries into the KQL search bar.