Osquery
editOsquery
editOsquery is an open source tool that lets you query operating systems like a database, providing you with visibility into your infrastructure and operating systems. Using basic SQL commands, you can ask questions about devices, such as servers, Docker containers, and computers running Linux, macOS, or Windows. The extensive schema helps with a variety of use cases, including vulnerability detection, compliance monitoring, incident investigations, and more.
With Osquery in Kibana, you can:
- Run live queries for one or more agents
- Schedule query packs to capture changes to OS state over time
- View a history of past queries and their results
- Save queries and build a library of queries for specific use cases
Osquery in Kibana is powered by the Osquery Manager integration. For information on how to set up Osquery Manager, refer to Manage the integration.
Required privileges
editTo use Osquery Manager, you must be assigned to a role with the following privileges:
-
Readprivileges for thelogs-osquery_manager.result*index. -
Kibana privileges for Osquery Manager. The
Allprivilege enables you to run, schedule, and save queries.Readenables you to view live and scheduled query results, but you cannot run live queries or edit.
Run live queries
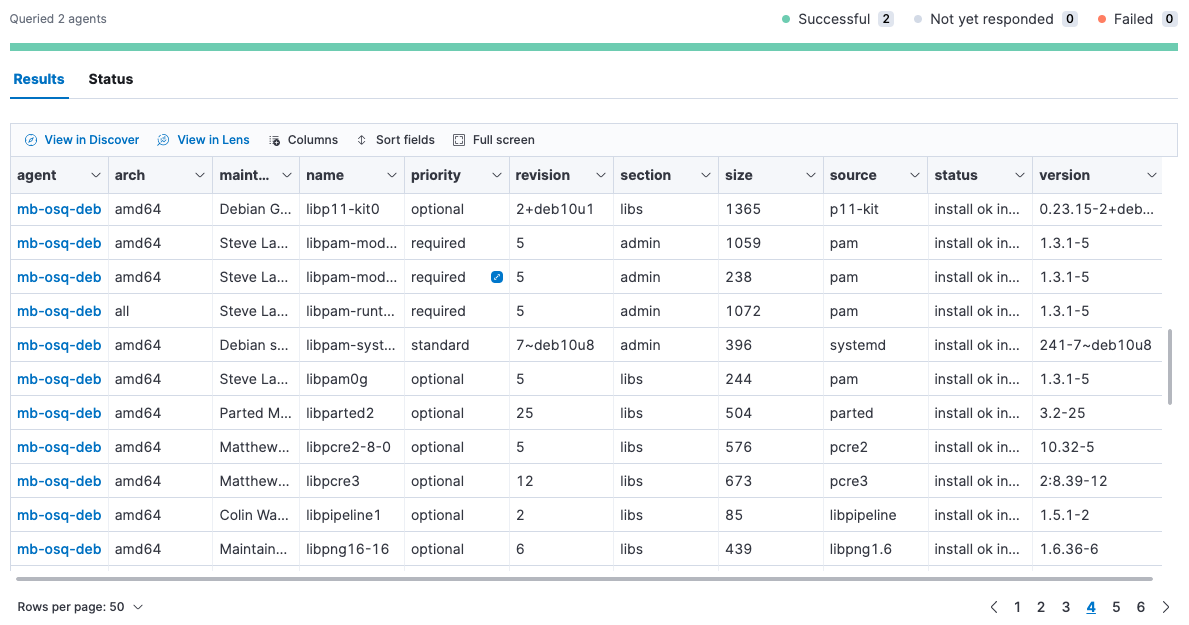
editTo inspect hosts, run a query against one or more agents or policies, then view the results.
- Open the main menu, and then click Osquery.
- In the Live queries view, click New live query.
- Select one or more agents or groups to query. Start typing in the search field, and you’ll get suggestions for agents by name, ID, platform, and policy.
-
Enter a query or select a query from your saved queries.
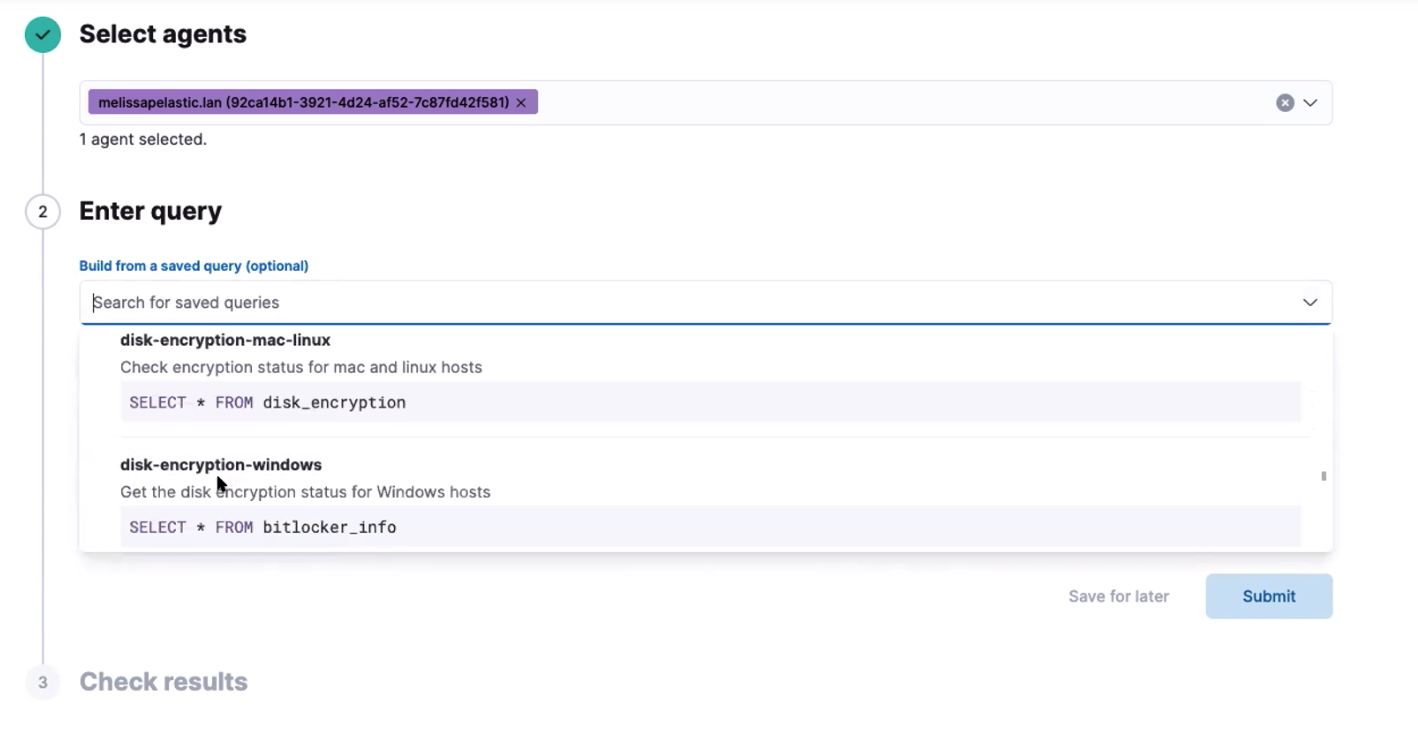
- (Optional) Expand the Advanced section to view or set mapped ECS fields included in the results from the live query.
- Click Submit.
- Review the results in a table, or navigate to Discover to dive deeper into the response, or to the drag-and-drop Lens editor to create visualizations.
- To view more information about the request, such as failures, open the Status tab.
- To save the query for future use, click Save for later and define the ID, description, and other details.
View or rerun previous live queries
editFrom the Live queries history section on the Live queries tab:
Schedule queries with packs
editCreate packs to organize sets of queries. For example, you might create one pack that checks for IT compliance-type issues, and another pack that monitors for evidence of malware. You can schedule packs to run for one or more agent policies. When scheduled, queries in the pack are run at the set intervals for all agents in those policies. Scheduling packs is optional.
- Open the Packs tab.
- Click Add pack to create a new pack, or click the name of an existing pack, then Edit to add queries to an existing pack.
-
Provide the following fields:
- The name of the pack.
- A short description of the pack.
- The agent policies where this pack should run. If no agent policies are set, then the pack is not scheduled.
-
Add queries to schedule:
- To add a query to the pack, click Add query, and then either add a saved query or enter a new query. Each query must include a unique query ID and the interval at which it should run. Optionally, set the minimum Osquery version and platform, or map ECS fields. When you add a saved query to a pack, this adds a copy of the query. A connection is not maintained between saved queries and packs.
-
To upload queries from a
.confquery pack, drag the pack to the drop zone under the query table. To explore the community packs that Osquery publishes, click Example packs.
- Click Save pack. The queries run when the policy receives the update.
View status of scheduled packs
edit- Open the Packs tab.
-
Click a pack name to view the status.
Details include the last time each query ran, how many results were returned, and the number of agents the query ran against. If there are errors, expand the row to view the details, including an option to view more information in the Logs.
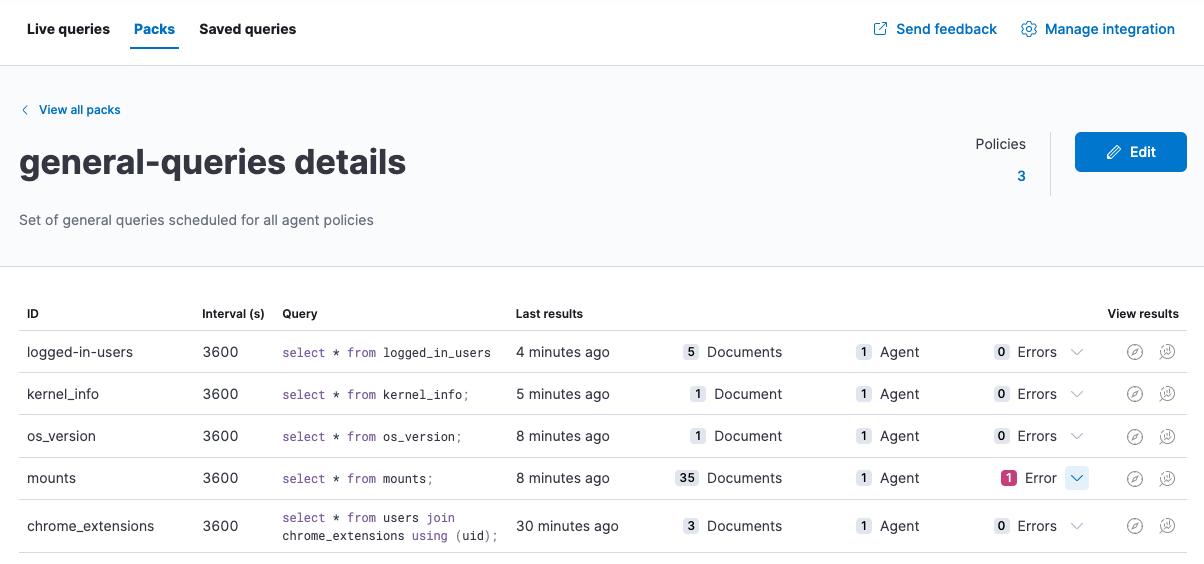
- View scheduled query results in Discover or the drag-and-drop Lens editor.
Prebuilt Elastic packs
editThe Osquery Manager integration includes a set of prebuilt Osquery packs that you can optionally load. Once added, you can then activate and schedule the packs.
You can modify the scheduled agent policies for a prebuilt pack, but you cannot edit queries in the pack. To edit the queries, you must first create a copy of the pack.
For information about the prebuilt packs that are available, refer to Prebuilt packs reference.
Load and activate prebuilt Elastic packs
edit-
Go to Packs, and then click Load Elastic prebuilt packs.
This option is only available if new or updated prebuilt packs are available.
-
For each pack that you want to schedule:
- Enable the option to make the pack Active.
- Click the pack name, then Edit.
- Update the Scheduled agent policies to specify the policies where this pack should run.
- Click Update pack.
Copy prebuilt Elastic packs
editTo modify queries in prebuilt packs, you must first make a copy of the pack.
- Go to Stack Management → Saved Objects.
- Search for the Osquery packs you want to modify by name.
- Select the checkboxes of the packs to export.
- Click Export x objects.
- Click Import.
- Select the import option Create new objects with random IDs, then click Import to import the pack. This creates a copy of the pack that you can edit.
Save queries
editYou can save queries in two ways:
- After running a live query, click the Save for later link.
- From the Saved queries tab, click the Add saved query button.
Once you save a query, you can only edit it from the Saved queries tab.
To add or edit saved queries from the Saved queries tab:
- Go to Saved queries, and then click Add saved query or the edit icon.
-
Provide the following fields:
- The unique identifier.
- A brief description.
- The SQL query.
- The ECS fields to populate when the query is run. These fields are also copied in when you add this query to a pack.
-
The defaults to set when you add the query to a pack.
- The frequency to run the query.
- The minimum version of Osquery required to run the query.
- The operating system required to run the query. For information about supported platforms per table, refer to the Osquery schema.
-
Click Test configuration to test the query and any mapped fields:
-
From the Test query panel, select agents or groups to test the query, then click Submit to run a live query. Result columns with the
 icon are mapped. Hover over the icon to see the mapped ECS field.
icon are mapped. Hover over the icon to see the mapped ECS field.
-
From the Test query panel, select agents or groups to test the query, then click Submit to run a live query. Result columns with the
- Click Save or Update.
Map result fields to ECS
editWhen you save queries or add queries to a pack, you can optionally map Osquery results or static values to fields in
the Elastic Common Schema (ECS).
This standardizes your Osquery data for use across detections, machine learning,
and any other areas that rely on ECS-compliant data.
When the query is run, the results include the original osquery.<fields>
and the mapped ECS fields. For example, if you update a query to map osquery.name to user.name, the query results include both fields.
-
Edit saved queries or queries in a pack to map fields:
- For Saved queries: Open the Saved queries tab, and then click the edit icon for the query that you want to map.
- For packs: Open the Packs tab, edit a pack, and then click the edit icon for the query that you want to map.
- In the ECS mapping section, select an ECS field to map.
-
In the Value column, use the dropdown on the left to choose what type of value to map to the ECS field:
- Osquery value: Select an Osquery field. The fields available are based on the SQL query entered, and only include fields that the query returns. When the query runs, the ECS field is set dynamically to the value of the Osquery field selected.
-
Static value: Enter a static value. When the query runs, the ECS field is set to the value entered. For example, static fields can be used to apply
tagsor your preferredevent.categoryto the query results.
- Map more fields, as needed. To remove any mapped rows, click the delete icon.
- Save your changes.
- Some ECS fields are restricted and cannot be mapped. These are not available in the ECS dropdown.
- Some ECS fields are restricted to a set of allowed values, like event.category. Use the ECS Field Reference for help when mapping fields.
- Osquery date fields have a variety of data types (including integer, text, or bigint). When mapping an Osquery date field to an ECS date field, you might need to use SQL operators in the query to get an Elasticsearch-compatible date type.
Extended tables for Kubernetes queries
editIn addition to the Osquery schema, the Elastic-provided version of Osquery also includes the following tables to support Kubernetes containers. These can be queried with live or scheduled queries.
-
host_users -
host_groups -
host_processes
When querying these tables, the expectation is that the /etc/passwd, /etc/group, and /proc are available in the container under /hostfs as:
/hostfs/etc/passwd, /hostfs/etc/group, and /hostfs/proc. For information about the fields available in these tables, see the
exported fields reference.
Osquery status
editA query can have the following status:
Successful |
The query successfully completed. |
Failed |
The query encountered a problem, such as an issue with the query or the agent was disconnected, and might have failed. |
Not yet responded |
The query has not been sent to the agent. |
Expired |
The action request timed out. The agent may be offline. |
If an agent is offline, the request status remains pending as Kibana retries the request. By default, a query request times out after five minutes. The time out applies to the time it takes to deliver the action request to an agent to run a query. If the action completes after the timeout period, the results are still returned.
Osquery results
editWhen you run live or scheduled queries, the results are automatically stored in an Elasticsearch index, so that you can search, analyze, and visualize this data in Kibana. For a list of the Osquery fields that can be returned in query results, refer to exported fields. Query results can also include ECS fields, if the query has a defined ECS mapping.
Osquery responses include the following information:
-
Everything prefaced with
osquery.is part of the query response. These fields are not mapped to ECS by default. -
Results include some ECS fields by default, such as
host.*andagent.*, which provide information about the host that was queried. -
For live queries, the
action_data.queryis the query that was sent. -
For scheduled queries in a pack, the
action_idhas the formatpack_<pack-name>_<query-ID>. You can use this information to look up the query that was run. - By default, all query results are snapshot logs that represent a point in time with a set of results, with no differentials.
-
Osquery data is stored in the
logs-osquery_manager.result-<namespace>datastream, and the result row data is under theosqueryproperty in the document.