Getting started with infrastructure monitoring
editGetting started with infrastructure monitoringedit
To get started with infrastructure monitoring, you need:
- An Elasticsearch cluster and Kibana (version 6.5 or later) with a basic license
- Appropriate Beats shippers (version 6.5 or later) installed and enabled on each system you want to monitor
If your data uses nonstandard fields, you may also need to modify some default configuration settings.
Get Elasticsearch and Kibanaedit
To get started, you can use our hosted Elasticsearch Service on Elastic Cloud (recommended for new users), or you can install Elasticsearch and Kibana locally.
Use our hosted serviceedit
The hosted Elasticsearch Service is available on both AWS and GCP. Try out the Elasticsearch Service for free.
Install Elasticsearch and Kibana locallyedit
Alternatively, you can install Elasticsearch and Kibana locally. Follow the instructions to install Elasticsearch, and to install and start Kibana.
Install Beats shippersedit
To start collecting metrics and log data, you need to install and configure the following Beats shippers:
- Metricbeat for metrics
- Filebeat for log data
You can install and configure Beats shippers for most kinds of data directly from Kibana, or you can install Beats yourself.
Install Beats from Kibanaedit
To install Beats from Kibana, on the machine where you want to collect the data, open a Kibana browser window. In the Add Data to Kibana section, click Add metric data or Add log data. Now follow the instructions for the type of data you want to collect. The instructions walk you through the steps required to download, install and configure the appropriate Beats modules for your data.
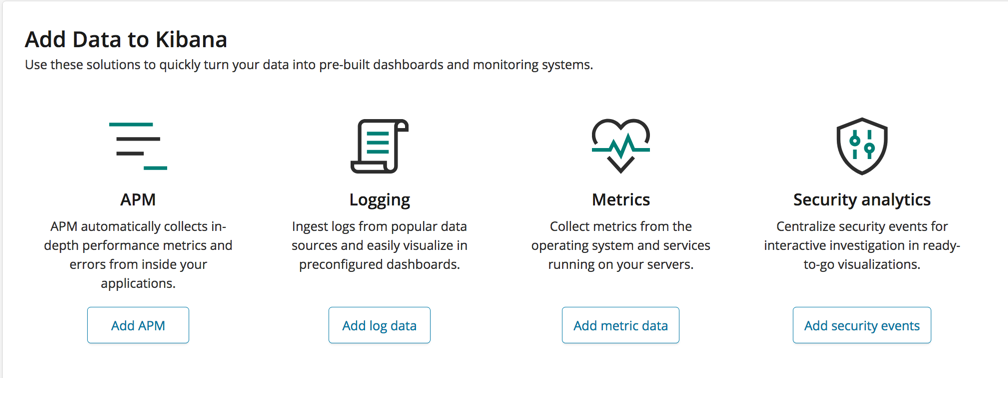
Install Beats yourselfedit
If your data source doesn’t have a Beats module, or if you want to install Beats the old fashioned way:
- For metrics data, follow the instructions in Metricbeat getting started and enable modules for the metrics you want to collect.
- For logs data, follow the instructions in Filebeat modules quick start and enable modules for the logs you want to collect. If there is no module for the logs you want to collect, see the Filebeat getting started to learn how to configure inputs.
Enable modulesedit
However you install Beats, you need to enable the appropriate modules in Filebeat and Metricbeat to populate the Infrastructure and Logs views with data.
To populate the Hosts view in the Infrastructure app and add logs, enable:
-
Metricbeat
systemmodule (enabled by default) -
Filebeat
systemmodule -
Other Filebeat modules needed for your environment, such as
apache2,redis, and so on -
Metricbeat
add_host_metadataprocessor (enabled by default) -
Metricbeat
add_cloud_metadataprocessor (enabled by default)
To populate the Docker view in the Infrastructure app and add logs, enable:
To populate the Kubernetes view in the Infrastructure app and add logs, enable:
Configure your data sourcesedit
If your metrics data or logs data has non-standard fields, you may need to modify some configuration settings in Kibana to change the default behaviors, such as the index pattern used to query the data, and the timestamp field used for sorting. For more information, see Infrastructure UI Settings and Logs UI Settings.
More about container monitoringedit
If you’re monitoring Docker containers or Kubernetes pods, you can use autodiscover to automatically change the configuration settings in response to changes in your containers. This ensures you don’t stop collecting data when your container configuration changes. To learn how to do this, see: