API keys
editAPI keysedit
This documentation refers to configuring the standalone (legacy) APM Server. This method of running APM Server will be deprecated and removed in a future release. Please consider upgrading to Fleet and the APM integration. If you’ve already upgraded, see API keys.
API keys are sent as plain-text, so they only provide security when used in combination with SSL/TLS. They are not applicable for agents running on clients, like the RUM agent, as there is no way to prevent them from being publicly exposed.
Configure API keys to authorize requests to the APM Server.
To enable API key authorization, set apm-server.auth.api_key.enabled to true.
There are multiple, unique privileges you can assign to each API key. API keys can have one or more of these privileges:
-
Agent configuration (
config_agent:read): Required for agents to read Agent configuration remotely. -
Ingest (
event:write): Required for ingesting Agent events. -
Sourcemap (
sourcemap:write): Required for uploading sourcemaps.
To secure the communication between APM Agents and the APM Server with API keys, make sure SSL/TLS is enabled, then complete these steps:
Enable and configure API keysedit
API keys are disabled by default. Enable and configure this feature in the apm-server.auth.api_key
section of the apm-server.yml configuration file.
At a minimum, you must enable API keys,
and should set a limit on the number of unique API keys that APM Server allows per minute.
Here’s an example apm-server.auth.api_key config using 50 unique API keys:
|
Enables API keys |
|
|
Restricts the number of unique API keys that Elasticsearch allows each minute. This value should be the number of unique API keys configured in your monitored services. |
All other configuration options are described in API key configuration options.
Create an API key user in Kibanaedit
API keys can only have the same or lower access rights than the user that creates them. Instead of using a superuser account to create API keys, you can create a role with the minimum required privileges.
The user creating an APM agent API key must have at least the manage_own_api_key cluster privilege
and the APM application-level privileges that it wishes to grant.
The example below uses the Kibana role management API
to create a role named apm_agent_key_role.
POST /_security/role/apm_agent_key_role
{
"cluster": ["manage_own_api_key"],
"applications": [{
"application": "apm",
"privileges": ["event:write", "config_agent:read"],
"resources": ["*"]
}]
}
Assign the newly created apm_agent_key_role role to any user that wishes to create APM agent API keys.
Create an API keyedit
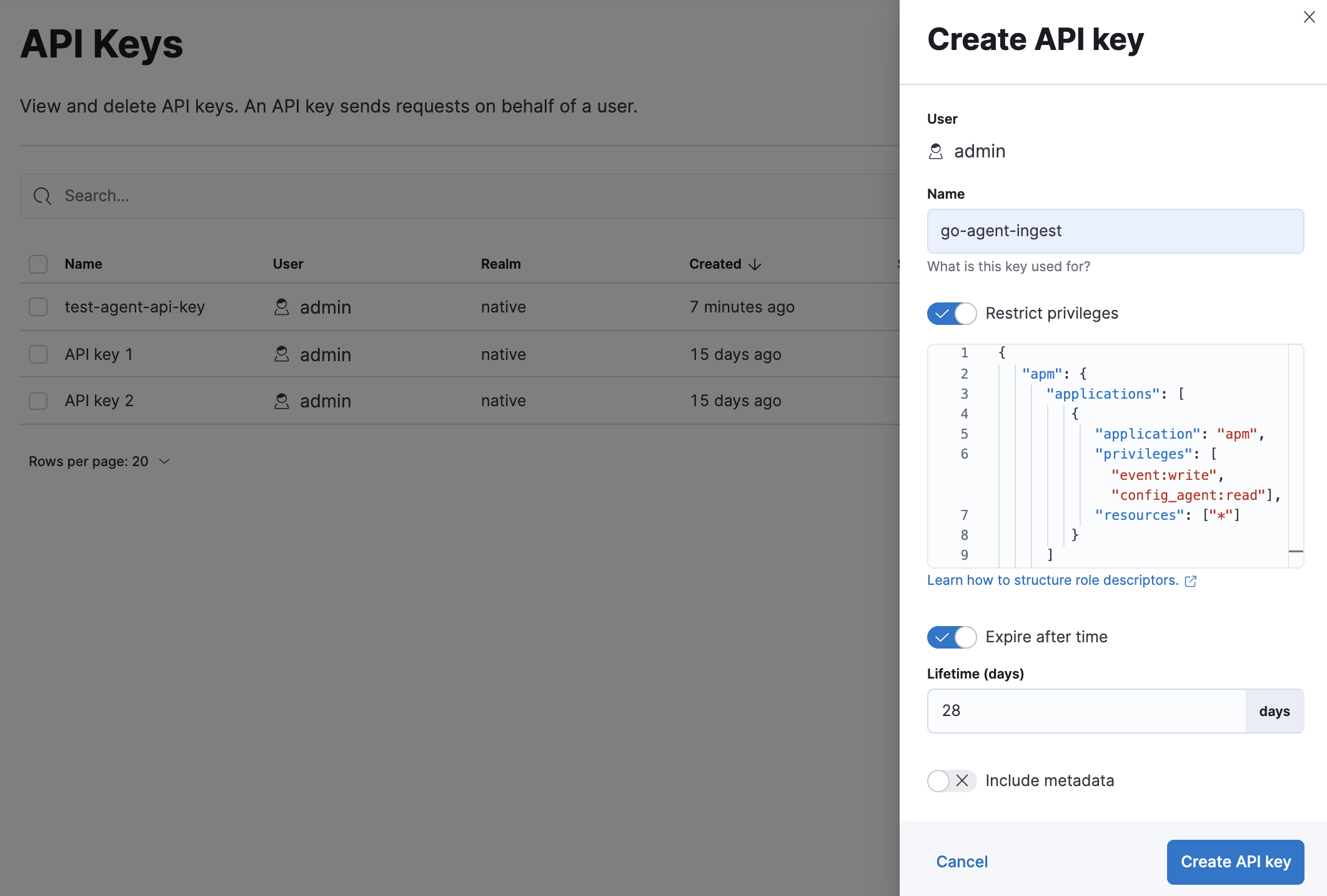
Using a superuser account, or a user with the role created in the previous step, open Kibana, navigate to Stack Management > API keys and click Create API key.
Enter a name for your API key and select Restrict privileges. In the role descriptors box, copy and paste the following JSON. This example creates an API key with privileges for ingesting APM events, reading agent central configuration, uploading a sourcemap:
{
"apm": {
"applications": [
{
"application": "apm",
"privileges": ["sourcemap:write", "event:write", "config_agent:read"],
"resources": ["*"]
}
]
}
}
|
This example adds all three API privileges to the new API key. Privileges are described above. Remove any privileges that you do not need. |
To set an expiration date for the API key, select Expire after time and input the lifetime of the API key in days.
Click Create API key and then copy the Base64 encoded API key. You will need this for the next step, and you will not be able to view it again.
Set the API key in your APM agentsedit
You can now apply your newly created API keys in the configuration of each of your APM agents. See the relevant agent documentation for additional information:
Alternate API key creation methodsedit
API keys can also be created and validated outside of Kibana:
APM Server API key workflowedit
APM Server provides a command line interface for creating, retrieving, invalidating, and verifying API keys. Keys created using this method can only be used for communication with APM Server.
apikey subcommandsedit
-
create -
Create an API Key with the specified privilege(s). No required flags.
The user requesting to create an API Key needs to have APM privileges used by the APM Server. A superuser, by default, has these privileges. For other users, you can create them. See create an API key user for required privileges.
-
info -
Query API Key(s).
--idor--namerequired. -
invalidate -
Invalidate API Key(s).
--idor--namerequired. -
verify -
Check if a credentials string has the given privilege(s).
--credentialsrequired.
Privilegesedit
If privileges are not specified at creation time, the created key will have all privileges.
-
--agent-configgrants theconfig_agent:readprivilege -
--ingestgrants theevent:writeprivilege -
--sourcemapgrants thesourcemap:writeprivilege
Create an API keyedit
Create an API key with the create subcommand.
The following example creates an API key with a name of java-001,
and gives the "agent configuration" and "ingest" privileges.
apm-server apikey create --ingest --agent-config --name java-001
The response will look similar to this:
Name ........... java-001 Expiration ..... never Id ............. qT4tz28B1g59zC3uAXfW API Key ........ rH55zKd5QT6wvs3UbbkxOA (won't be shown again) Credentials .... cVQ0dHoyOEIxZzU5ekMzdUFYZlc6ckg1NXpLZDVRVDZ3dnMzVWJia3hPQQ== (won't be shown again)
You should always verify the privileges of an API key after creating it.
Verification can be done using the verify subcommand.
The following example verifies that the java-001 API key has the "agent configuration" and "ingest" privileges.
apm-server apikey verify --agent-config --ingest --credentials cVQ0dHoyOEIxZzU5ekMzdUFYZlc6ckg1NXpLZDVRVDZ3dnMzVWJia3hPQQ==
If the API key has the requested privileges, the response will look similar to this:
Authorized for privilege "event:write"...: Yes Authorized for privilege "config_agent:read"...: Yes
To invalidate an API key, use the invalidate subcommand.
Due to Elasticsearch caching, there may be a delay between when this subcommand is executed and when it takes effect.
The following example invalidates the java-001 API key.
apm-server apikey invalidate --name java-001
The response will look similar to this:
Invalidated keys ... qT4tz28B1g59zC3uAXfW Error count ........ 0
A full list of apikey subcommands and flags is available in the API key command reference.
Elasticsearch API key workflowedit
It is also possible to create API keys using the Elasticsearch create API key API.
This example creates an API key named java-002:
POST /_security/api_key
{
"name": "java-002",
"expiration": "1d",
"role_descriptors": {
"apm": {
"applications": [
{
"application": "apm",
"privileges": ["sourcemap:write", "event:write", "config_agent:read"],
"resources": ["*"]
}
]
}
}
}
The response will look similar to this:
{
"id" : "GnrUT3QB7yZbSNxKET6d",
"name" : "java-002",
"expiration" : 1599153532262,
"api_key" : "RhHKisTmQ1aPCHC_TPwOvw"
}
The credential string, which is what agents use to communicate with APM Server,
is a base64 encoded representation of the API key’s id:api_key.
It can be created like this:
echo -n GnrUT3QB7yZbSNxKET6d:RhHKisTmQ1aPCHC_TPwOvw | base64
You can verify your API key has been base64-encoded correctly with the Authenticate API:
curl -H "Authorization: ApiKey R0gzRWIzUUI3eVpiU054S3pYSy06bXQyQWl4TlZUeEcyUjd4cUZDS0NlUQ==" localhost:9200/_security/_authenticate
If the API key has been encoded correctly, you’ll see a response similar to the following:
{
"username":"1325298603",
"roles":[],
"full_name":null,
"email":null,
"metadata":{
"saml_nameid_format":"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient",
"saml(http://saml.elastic-cloud.com/attributes/principal)":[
"1325298603"
],
"saml_roles":[
"superuser"
],
"saml_principal":[
"1325298603"
],
"saml_nameid":"_7b0ab93bbdbc21d825edf7dca9879bd8d44c0be2",
"saml(http://saml.elastic-cloud.com/attributes/roles)":[
"superuser"
]
},
"enabled":true,
"authentication_realm":{
"name":"_es_api_key",
"type":"_es_api_key"
},
"lookup_realm":{
"name":"_es_api_key",
"type":"_es_api_key"
}
}
You can then use the APM Server CLI to verify that the API key has the requested privileges:
apm-server apikey verify --credentials R25yVVQzUUI3eVpiU054S0VUNmQ6UmhIS2lzVG1RMWFQQ0hDX1RQd092dw==
If the API key has the requested privileges, the response will look similar to this:
Authorized for privilege "config_agent:read"...: Yes Authorized for privilege "event:write"...: Yes Authorized for privilege "sourcemap:write"...: Yes
API key configuration optionsedit
auth.api_key.* configuration optionsedit
You can specify the following options in the apm-server.auth.api_key.* section of the
apm-server.yml configuration file.
They apply to API key communication between the APM Server and APM Agents.
These settings are different from the API key settings used for Elasticsearch output and monitoring.
enablededit
Enable API key authorization by setting enabled to true.
By default, enabled is set to false, and API key support is disabled.
Not using Elastic APM agents?
When enabled, third-party APM agents must include a valid API key in the following format:
Authorization: ApiKey <token>. The key must be the base64 encoded representation of the API key’s id:name.
limitedit
Each unique API key triggers one request to Elasticsearch.
This setting restricts the number of unique API keys are allowed per minute.
The minimum value for this setting should be the number of API keys configured in your monitored services.
The default limit is 100.
auth.api_key.elasticsearch.* configuration optionsedit
All of the auth.api_key.elasticsearch.* configurations are optional.
If none are set, configuration settings from the apm-server.output section will be reused.
elasticsearch.hostsedit
API keys are fetched from Elasticsearch. This configuration needs to point to a secured Elasticsearch cluster that is able to serve API key requests.
elasticsearch.protocoledit
The name of the protocol Elasticsearch is reachable on.
The options are: http or https. The default is http.
If nothing is configured, configuration settings from the output section will be reused.
elasticsearch.pathedit
An optional HTTP path prefix that is prepended to the HTTP API calls.
If nothing is configured, configuration settings from the output section will be reused.
elasticsearch.proxy_urledit
The URL of the proxy to use when connecting to the Elasticsearch servers.
The value may be either a complete URL or a "host[:port]", in which case the "http"scheme is assumed.
If nothing is configured, configuration settings from the output section will be reused.
elasticsearch.timeoutedit
The http request timeout in seconds for the Elasticsearch request.
If nothing is configured, configuration settings from the output section will be reused.
auth.api_key.elasticsearch.ssl.* configuration optionsedit
SSL is off by default. Set elasticsearch.protocol to https if you want to enable https.
elasticsearch.ssl.enablededit
Enable custom SSL settings. Set to false to ignore custom SSL settings for secure communication.
elasticsearch.ssl.verification_modeedit
Configure SSL verification mode.
If none is configured, all server hosts and certificates will be accepted.
In this mode, SSL based connections are susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks.
Use only for testing. Default is full.
elasticsearch.ssl.supported_protocolsedit
List of supported/valid TLS versions. By default, all TLS versions from 1.0 to 1.2 are enabled.
elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authoritiesedit
List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications.
elasticsearch.ssl.certificateedit
The path to the certificate for SSL client authentication.
elasticsearch.ssl.keyedit
The client certificate key used for client authentication. This option is required if certificate is specified.
elasticsearch.ssl.key_passphraseedit
An optional passphrase used to decrypt an encrypted key stored in the configured key file. It is recommended to use the provided keystore instead of entering the passphrase in plain text.
elasticsearch.ssl.cipher_suitesedit
The list of cipher suites to use. The first entry has the highest priority. If this option is omitted, the Go crypto library’s default suites are used (recommended).
elasticsearch.ssl.curve_typesedit
The list of curve types for ECDHE (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman ephemeral key exchange).
elasticsearch.ssl.renegotiationedit
Configure what types of renegotiation are supported.
Valid options are never, once, and freely. Default is never.
-
never- Disables renegotiation. -
once- Allows a remote server to request renegotiation once per connection. -
freely- Allows a remote server to repeatedly request renegotiation.
api_key.* configuration optionsedit
Deprecated in 7.14.0.
Replaced by auth.api_key.*. See auth.api_key.* configuration options
In versions prior to 7.14.0, API Key authorization was known as apm-server.api_key. In 7.14.0 this was renamed apm-server.auth.api_key.
The old configuration will continue to work until 8.0.0, and the new configuration will take precedence.