Configuring map data
editConfiguring map data
editDepending on your Kibana setup, to display and interact with data on the map you might need to:
To see source and destination connections lines on the map, you must
configure source.geo and dest.geo ECS fields for your indices.
Add geoIP data
editIf you are not using Beats to ship your data, add the relevant index patterns to Kibana (Management → Index patterns) and the SIEM app (Management → Advanced settings → SIEM default index). When the ECS source.geo.location and destination.geo.location fields are mapped, network data is displayed on the map.
If you use Beats, configure a geoIP processor to add data to the relevant fields:
-
Define an ingest node pipeline that uses one or more
geoIPprocessors to add location information to events. For example, use the Console in Kibana to create the following pipeline:PUT _ingest/pipeline/geoip-info { "description": "Add geoip info", "processors": [ { "geoip": { "field": "client.ip", "target_field": "client.geo", "ignore_missing": true } }, { "geoip": { "field": "source.ip", "target_field": "source.geo", "ignore_missing": true } }, { "geoip": { "field": "destination.ip", "target_field": "destination.geo", "ignore_missing": true } }, { "geoip": { "field": "server.ip", "target_field": "server.geo", "ignore_missing": true } }, { "geoip": { "field": "host.ip", "target_field": "host.geo", "ignore_missing": true } } ] }In this example, the pipeline ID is
geoip-info.fieldspecifies the field that contains the IP address to use for the geographical lookup, andtarget_fieldis the field that will hold the geographical information."ignore_missing": trueconfigures the pipeline to continue processing when it encounters an event that doesn’t have the specified field. -
In your Beats configuration files, add the pipeline to the
output.elasticsearchtag:The value of this field must be the same as the ingest pipeline name in step 1 (
geoip-infoin this example).
Map your internal network
editIf you want to add your network’s internal IP addresses to the map, define geo
location fields under the processors tag in the Beats configuration files
on your hosts:
processors:
- add_host_metadata:
- add_cloud_metadata: ~
- add_fields:
when.network.source.ip: <private/IP address>
fields:
source.geo.location:
lat: <latitude coordinate>
lon: <longitude coordinate>
target: ''
- add_fields:
when.network.destination.ip: <private/IP address>
fields:
destination.geo.location:
lat: <latitude coordinate>
lon: <longitude coordinate>
target: ''
|
For the IP address, you can use either You can also enrich your data with other host fields. |
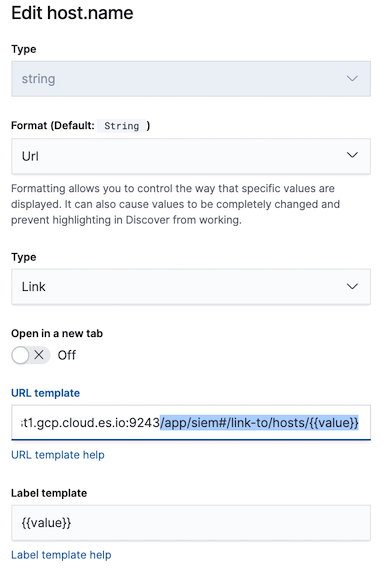
Define map field links
editTo jump from the map to specific Host and IP Details pages, format these fields in all SIEM indices as URL links:
-
host.name -
source.ip -
destination.ip- Go to Management → Index Patterns.
- Select the relevant index pattern.
-
Edit the the index’s
host.namefield. -
Repeat step 3 for the
source.ipanddestination.ipindex fields, using the following Url template:<KibanaURL>/app/siem#/network/ip/{{value}}