Add symbols for native frames
To see function names and line numbers in traces of applications written in programming languages that compile to native code (C, C++, Rust, Go, etc.), you need to push symbols to the cluster using the symbtool CLI utility.
Click the appropriate link for your system to download the symbtool binary:
The symbtool binary currently requires a Linux machine.
Before using the symbtool binary, create an Elasticsearch API token. Pass this token using the -t or --api-key argument.
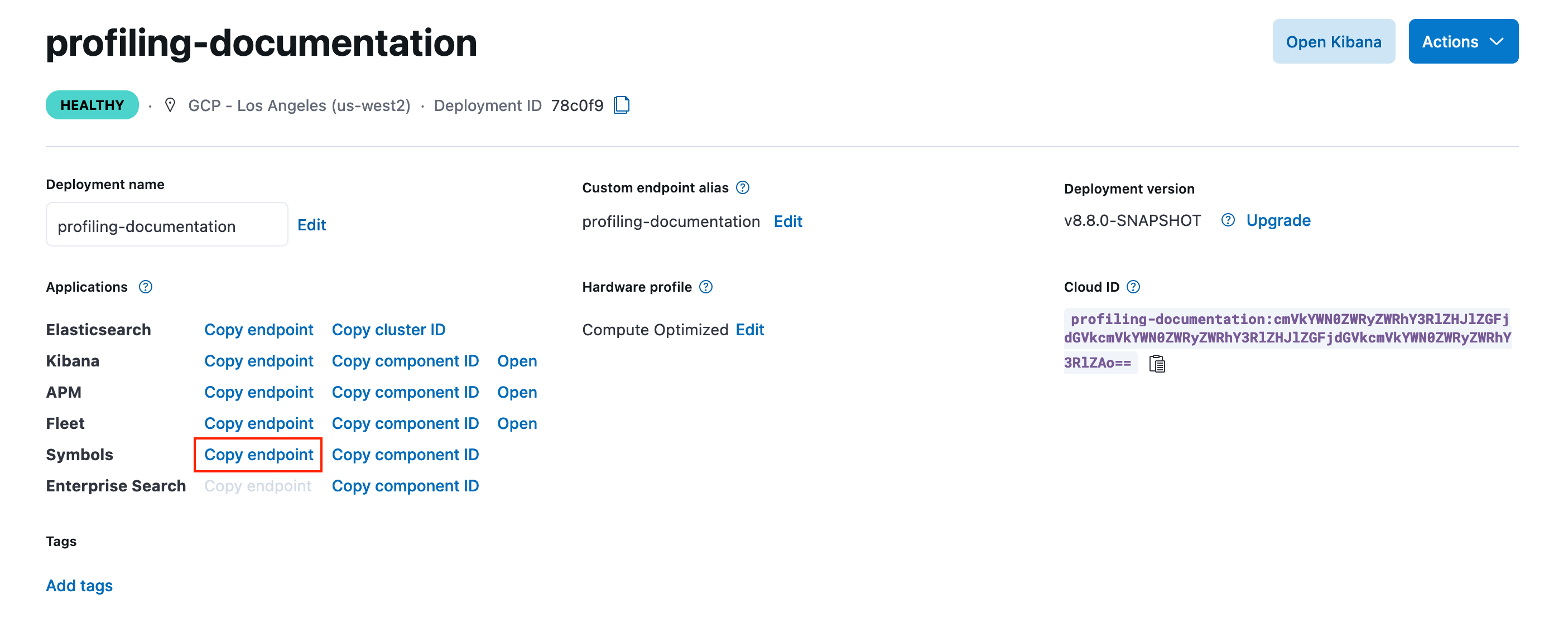
You also need to copy the Symbols endpoint from the deployment overview page. Pass this URL using the -u or --url argument.
C/C++ applications must be built with debug symbols (-g) for symbolization to work. Rust applications must be built with debug = 1 (or higher). Go binaries will not require any special compiler flags and come with debug information by default. The debug info doesn’t have to be deployed to production, but it does have to be present temporarily to push it to the Elastic cluster.
If you don’t mind deploying your applications with debug symbols, run:
./symbtool push-symbols executable -e ./my-app -u <symbolizer url> -t <API token>
If you don’t want debug symbols in production, copy the executable and strip the copy. You can then use the -d argument to instruct the tool to read the symbols from the original unstripped binary while still calculating the file ID from the final stripped binary. After the symbols have been pushed, you can remove the unstripped binary:
cp ./my-app ./my-stripped-app
strip ./my-stripped-app
./symbtool push-symbols executable -e ./my-stripped-app -d ./my-app -u <symbolizer url> -t <API token>
rm ./my-app
Pushing debug information and then stripping the binary later does not work. The executable passed using the -e argument is used to calculate the file ID that associates stack traces with their symbols and stripping the binary later changes that ID.
Elastic hosts a public service with symbol information for all packages in the repositories for various popular Linux distributions. Applications installed from these repositories are automatically symbolized without any action required on the user’s side.
Elastic supports the following Linux distributions:
- Alpine Linux
- Amazon Linux
- Debian
- Fedora
- Ubuntu