Analyze and compare hosts on the Hosts page
editAnalyze and compare hosts on the Hosts page
editThe Hosts page provides a metrics-driven view of your entire infrastructure backed by an easy-to-use interface called Lens. On the Hosts page, you can view health and performance metrics to help you quickly:
- Analyze and compare hosts without having to build new dashboards.
- Troubleshoot and resolve issues quickly.
- Filter and search the data to focus on the hosts you care about the most.
To access the Hosts page, go to Observability → Infrastructure, and then click Hosts. If the view is not enabled, click Enable host view to begin exploring.
If there are no metrics to display, Kibana prompts you to add a metrics integration. Click Add a metrics integration to get started.
If you want to add more data in the future, click Add data from any page in the Infrastructure UI. To learn more about adding observability data, refer to Send data to Elasticsearch.
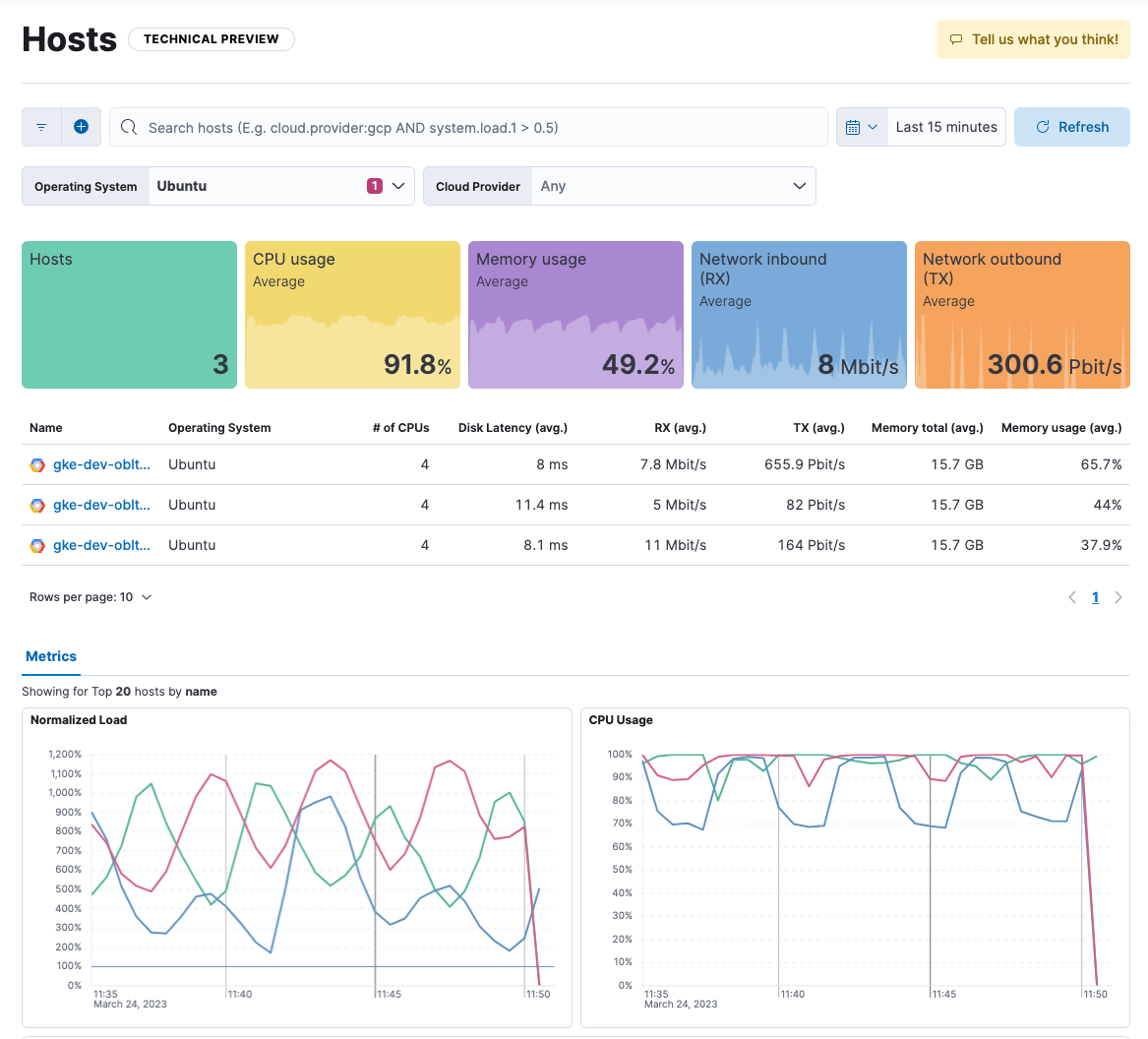
The Hosts page provides a few different ways to view host metrics:
- Overview tiles show the number of hosts returned by your search plus averages of key metrics, including CPU usage, memory usage, and throughput.
- The host list shows all the hosts returned by your search with a breakdown of metrics for each host. You may need to page through the list or change the number of rows displayed on each page to see all of your hosts.
- Each host name is an active link to an overview page with additional metrics about the host, such as CPU usage, load, memory usage, and network traffic.
- The Metrics view shows metrics trending over time for the top 20 hosts, including normalized load, CPU usage, memory usage, network inbound, network outbound, disk read IOPS, and disk write IOPS. Place your cursor over a line to view metrics at a specific point in time.
Filter the Hosts view
editThe Hosts page provides several mechanisms for filtering the data on the page:
- Enter a search query to show metrics that match your search criteria. For example, to see metrics for all hosts running on linux, enter `host.os.type : "linux". Otherwise you’ll see metrics for all your monitored hosts.
-
Select additional criteria to filter the view:
- In the Operating System list, select one or more operating systems and include (or exclude) metrics for those hosts.
- In the Cloud Provider list, select one or more cloud cloud providers to include (or exclude) metrics for the selected cloud providers.
- Change the date range in the Time Picker, or click and drag on a visualization to change the date range.
- In the visualizations under Metrics, click a point on a line and apply filters to set other visualizations on the page to the same time and/or host.
To learn more about filtering data in Kibana, refer to Kibana concepts.
Limitation on filtering by service names
You may see queries where either the expected hosts are not returned, or where returned hosts do not return metrics. This may happen when your filter returns events that do not contain all of the fields and/or values specified within your search.
For example, if you search for service.name : myservice, you will return all hosts where there are events
containing both service.name : myservice and where host.name exists.
You may find that some metrics show as 0 when there are no events which contain both
host.name and service.name : myservice and the metric you are looking for — like system.memory.actual.used.pct for Memory Usage.
You can configure which indices you are searching in the Settings page.
Open in Lens
editMetrics visualizations are powered by Lens, meaning you can continue your analysis in Lens if you require more flexibility. Under Metrics, hover your cursor over a visualization, then click the ellipsis icon in the upper-right corner to open the visualization in Lens.
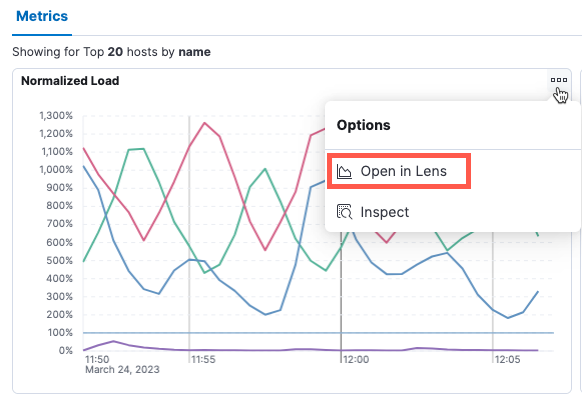
In Lens, you can examine all the fields and formulas used to create the visualization, make modifications to the visualization, and save your changes.
For more information about using Lens, refer to the Kibana documentation about Lens.
Inspect and download metrics
editFrom the Hosts page, you can access a text-based view of the data underlying your metrics visualizations and optionally download the data to a comma-separated (CSV) file.
Under Metrics, hover your cursor over a visualization, then in the upper-right corner, click the ellipsis icon to inspect the data.
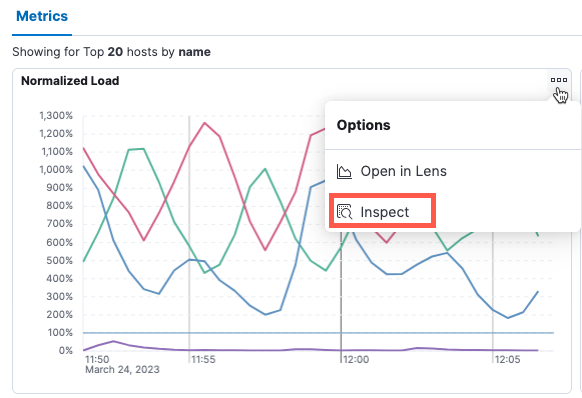
In the flyout, click Download CSV to download formatted or raw data to a CSV file.
Notice that you can change the view to View: Requests to explore the request used to fetch the data and the response returned from Elasticsearch. You can click links to further inspect and analyze the request in the Dev Console or Search Profiler.
Fields used to populate the Hosts page
editThe Hosts page displays metrics from indices that match the index patterns
specified on the Settings page. For example, the default patterns are
metrics-* and metricbeat-*.
The following sections describe the fields used to populate the Hosts page with data.
Metrics
edit| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
# of CPUs |
Number of CPU cores Field Calculation: count(system.cpu.cores) |
CPU Usage |
Percentage of CPU time spent in states other than Idle and IOWait, normalized by the number of CPU cores. This includes both time spent on user space and kernel space. 100% means all CPUs of the host are busy. Field Calculation: |
Disk Latency |
Time spent to service disk requests. Field Calculation: |
Disk Read IOPS |
Average number of bytes read from the device per second. Field Calculation: |
Disk Write IOPS |
Average number of bytes written from the device per second. Field Calculation: |
Memory Total |
Total available memory. Field Calculation: |
Memory Usage |
Percentage of main memory usage excluding page cache. This includes resident memory for all processes plus memory used by the kernel structures and code apart from the page cache. A high level indicates a situation of memory saturation for the host. For example, 100% means the main memory is entirely filled with memory that can’t be reclaimed, except by swapping out. Field Calculation: |
Network Inbound (RX) |
Number of bytes which have been received per second on the public interfaces of the hosts. Field Calculation: |
Network Outbound (TX) |
Number of bytes which have been sent per second on the public interfaces of the hosts. Field Calculation: |
Normalized Load |
1 minute load average normalized by the number of CPU cores. Load average gives an indication of the number of threads that are runnable (either busy running on CPU, waiting to run or waiting for a blocking IO operation to complete). 100% means the 1 minute load average is equal to the number of CPU cores of the host. For example, with a 32 CPU cores host, if 1 min load average is 32, the value reported here is 100%. If 1 min load average is 48, the value reported here is 150%. Field Calculation: |
Fields
edit| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of host. Field Calculation: |
Operating System |
Operating System of host. Field Calculation: |
Cloud Provider |
Cloud Provider host is running on. Field Calculation: |