Elastic Serverless Forwarder for AWS
editElastic Serverless Forwarder for AWS
editThe Elastic Serverless Forwarder is an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda function that ships logs from your AWS environment to Elastic.
Overview
editThe Elastic Serverless Forwarder can forward AWS data to cloud-hosted or self-managed Elastic environments. It supports the following inputs:
- Amazon S3 (via SQS event notifications)
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs subscription filters
- Amazon SQS message payload
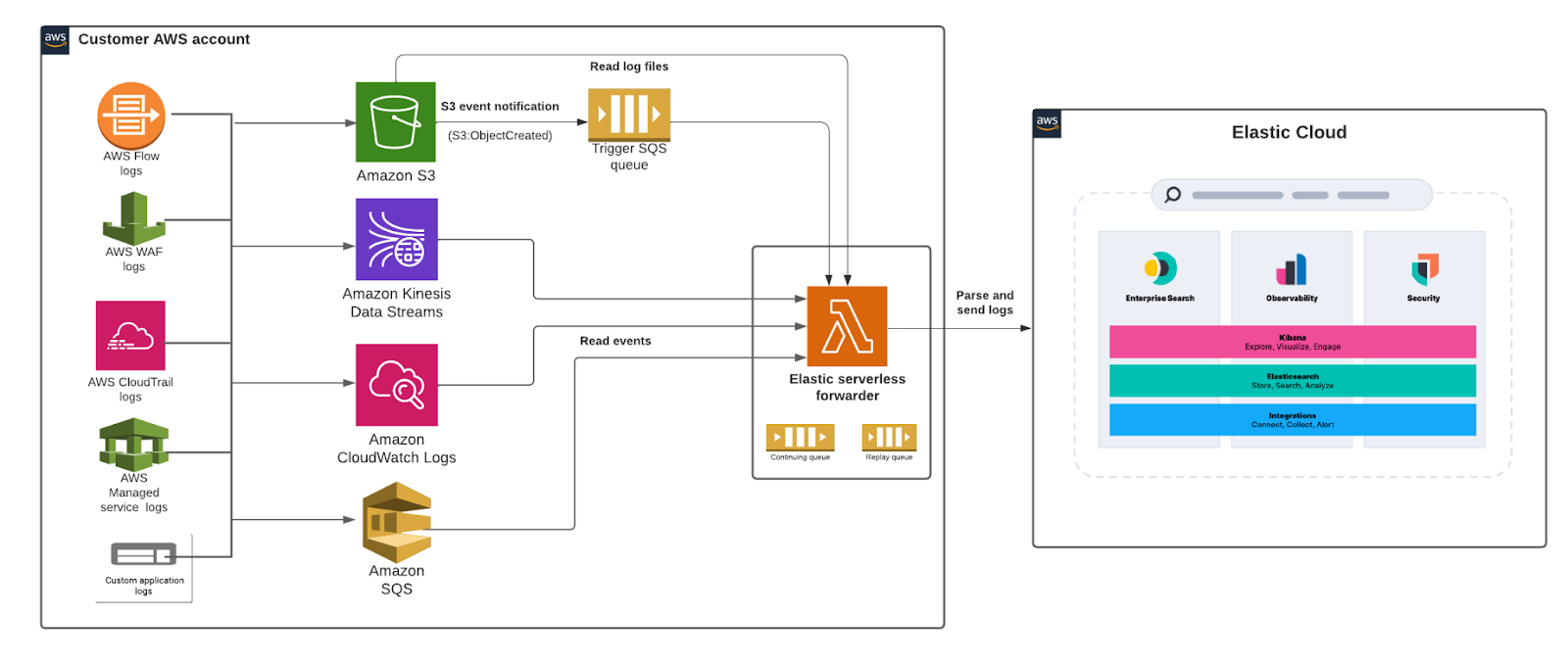
When you successfully deploy the forwarder, an SQS Continuing queue is automatically created in Lambda to ensure no data is lost. By default the forwarder runs for a maximum of 15 minutes so it’s possible that AWS may exit the function in the middle of processing event data. The forwarder handles this scenario by keeping track of the last offset processed. When the queue triggers a new function invocation, the forwarder will start where the last function run stopped.
The forwarder uses a Replay queue (also automatically created during deployment) to handle any ingestion-related exception or fail scenarios. Data in the replay queue is stored as individual events. Lambda keeps track of any failed events and writes them to a replay queue that can then be consumed by adding an additional SQS trigger via Lambda.
You can use the config.yaml file to configure the service for each input type, including information such as SQS queue ARN (Amazon Resource Number) and Elasticsearch connection details. You can create multiple input sections within the configuration file to map different inputs to specific log types.
The forwarder also supports writing directly to an index, alias, or custom data stream. This enables existing Elasticsearch users to re-use index templates, ingest pipelines, or dashboards that are already created and connected to other processes.
Inputs
editAmazon S3 (via SQS event notifications)
editThe forwarder can ingest logs contained in an Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket through a Simple Queue Service (SQS) notification (s3:ObjectCreated) and send them to Elastic. The SQS queue serves as a trigger for the forwarder. When a new log file is written to an S3 bucket and meets the user-defined criteria (including prefix/suffix), an SQS notification is generated that triggers the Lambda function.
You can set up separate SQS queues for each type of log (for example, aws.vpcflow, aws.cloudtrail, aws.waf). A single configuration file can have many input sections, pointing to different SQS queues that match specific log types. The es_datastream_name parameter in the config file is optional. The forwarder supports automatic routing of various AWS service logs to the corresponding data streams for further processing and storage in the Elasticsearch cluster. It supports automatic routing of aws.cloudtrail, aws.cloudwatch_logs, aws.elb_logs, aws.firewall_logs, aws.vpcflow, and aws.waf logs.
For other log types, you can optionally set the es_datastream_name value in the configuration file according to the naming convention of the Elasticsearch data stream and integration. If the es_datastream_name is not specified, and the log cannot be matched with any of the above AWS services, then the dataset will be set to generic and the namespace set to default, pointing to the data stream name logs-generic-default.
For more information on creating SQS event notifications for S3 buckets, read the AWS documentation.
You must set a visibility timeout of 910 seconds for any SQS queues you want to use as a trigger. This is 10 seconds greater than the Elastic Serverless Forwarder Lambda timeout.
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
editThe forwarder can ingest logs contained in the payload of a Kinesis Data Stream record and send them to Elastic. The Kinesis Data Stream serves as a trigger for the forwarder. When a new record gets written to a Kinesis Data Stream, it triggers the Lambda function.
You can set up separate Kinesis Data Streams for each type of log. The es_datastream_name parameter in the config file is mandatory. If this value is set to an Elasticsearch data stream, the type of log must be correctly defined with configuration parameters. A single configuration file can have many input sections, pointing to different data streams that match specific log types.
Amazon CloudWatch Logs subscription filters
editThe forwarder can ingest logs contained in the message payload of CloudWatch Logs events and send them to Elastic. The CloudWatch Logs service serves as a trigger for the forwarder. When a new event gets written to a CloudWatch Logs log stream, it triggers the Lambda function.
You can set up separate CloudWatch Logs groups for each type of log. The es_datastream_name parameter in the config file is mandatory. If this value is set to an Elasticsearch data stream, the type of log must be correctly defined with configuration parameters. A single configuration file can have many input sections, pointing to different CloudWatch Logs groups that match specific log types.
Amazon SQS message payload
editThe forwarder can ingest logs contained within the payload of an Amazon SQS body record and send them to Elastic. The SQS queue serves as a trigger for the forwarder. When a new record gets written to an SQS queue, the Lambda function triggers.
You can set up a separate SQS queue for each type of log. The config parameter for Elasticsearch output es_datastream_name is mandatory. If this value is set to an Elasticsearch data stream, the type of log must be correctly defined with configuration parameters. A single configuration file can have many input sections, pointing to different SQS queues that match specific log types.