Generating alerts for anomaly detection jobs
editGenerating alerts for anomaly detection jobs
editThis functionality is in beta and is subject to change. The design and code is less mature than official GA features and is being provided as-is with no warranties. Beta features are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
Kibana alerting features include support for machine learning rules, which run scheduled checks on an anomaly detection job or a group of jobs to detect anomalies with certain conditions. If an anomaly meets the conditions, an alert is created and the associated action is triggered. For example, you can create a rule to check an anomaly detection job every fifteen minutes for critical anomalies and to notify you in an email. To learn more about Kibana alerting features, refer to Alerting and Actions.
Creating a rule
editYou can create machine learning rules in the anomaly detection job wizard after you start the job, from the job list, or under Stack Management > Alerts and Actions. On the Create rule window, select Anomaly detection alert under the machine learning section, then give a name to the rule and optionally provide tags.
Specify the time interval for the rule to check detected anomalies. It is
recommended to select an interval that is close to the bucket span of the
associated job. You can also select a notification option by using the Notify
selector. An alert remains active as long as anomalies are found for a
particular anomaly detection job during the check interval. When there is no anomaly
found in the next interval, the Recovered action group is invoked and the
status of the alert changes to OK. For more details, refer to the
documentation of
general rule details.
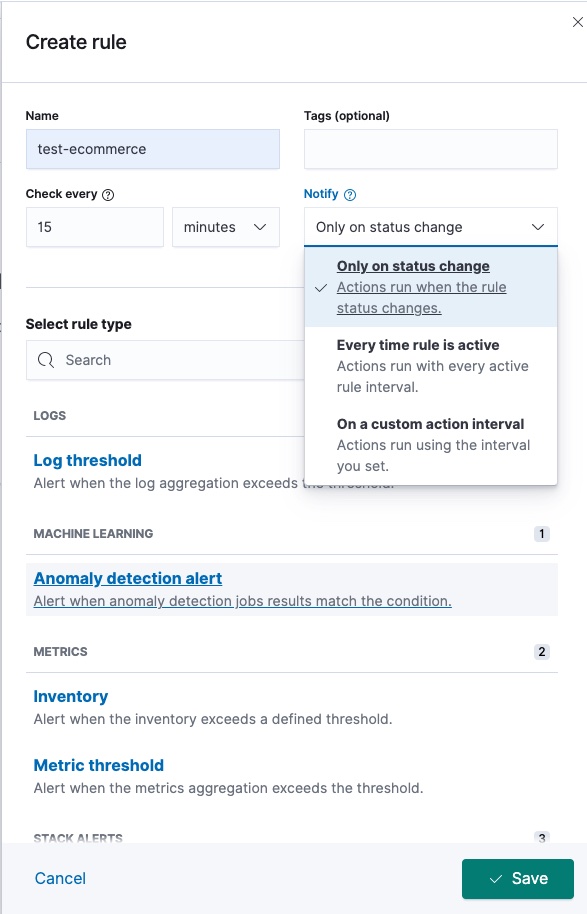
Select the anomaly detection job or the group of anomaly detection jobs that is checked against the rule. If you assign additional jobs to the group, the new jobs are automatically checked the next time the conditions are checked.
You can select the result type of the anomaly detection job that is checked against the rule. In particular, you can create rules based on bucket, record, or influencer results.
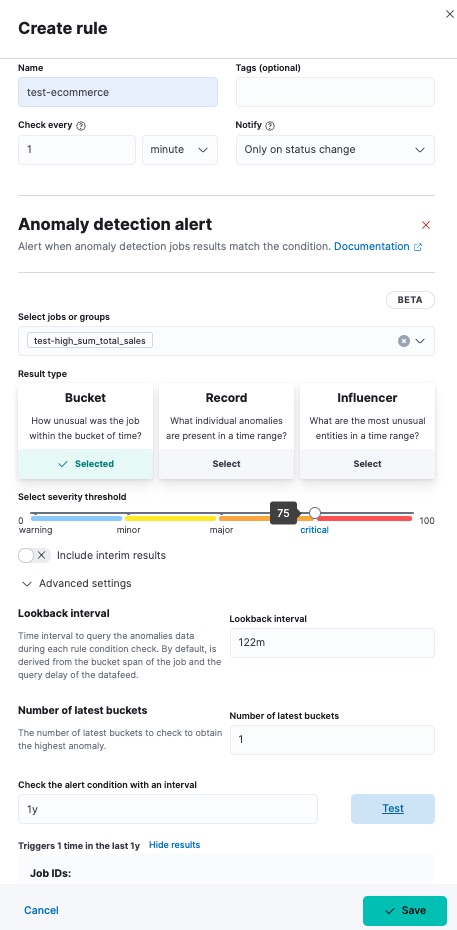
For each rule, you can configure the anomaly_score that triggers the action.
The anomaly_score indicates the significance of a given anomaly compared to
previous anomalies. The default severity threshold is 75 which means every
anomaly with an anomaly_score of 75 or higher triggers the associated action.
You can select whether you want to include interim results. Interim results are created by the anomaly detection job before a bucket is finalized. These results might disappear after the bucket is fully processed. Include interim results if you want to be notified earlier about a potential anomaly even if it might be a false positive. If you want to get notified only about anomalies of fully processed buckets, do not include interim results.
You can also configure advanced settings. Lookback interval sets an interval that is used to query previous anomalies during each condition check. Its value is derived from the bucket span of the job and the query delay of the datafeed by default. It is not recommended to set the lookback interval lower than the default value as it might result in missed anomalies. Number of latest buckets sets how many buckets to check to obtain the highest anomaly from all the anomalies that are found during the Lookback interval. An alert is created based on the anomaly with the highest anomaly score from the most anomalous bucket.
You can also test the configured conditions against your existing data and check the sample results by providing a valid interval for your data. The generated preview contains the number of potentially created alerts during the relative time range you defined.
Defining actions
editAs a next step, connect your rule to actions that use supported built-in integrations by selecting a connector type. Connectors are Kibana services or third-party integrations that perform an action when the rule conditions are met.
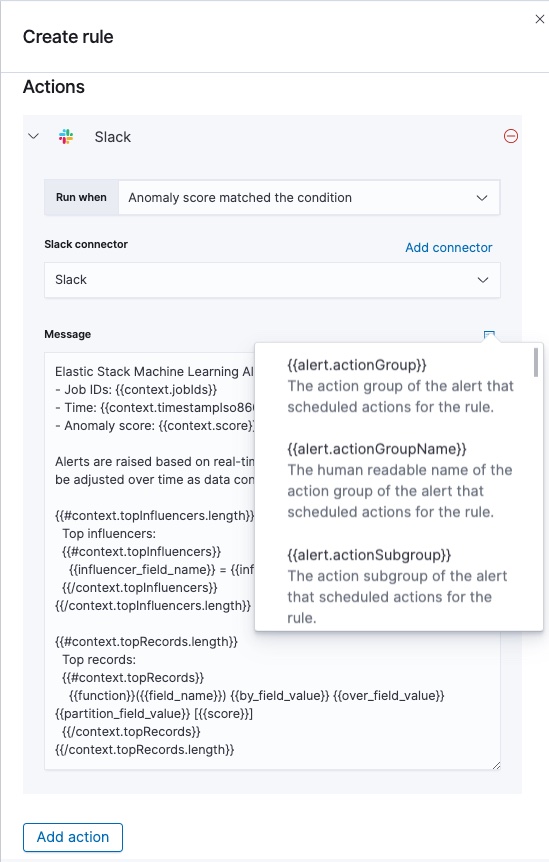
For example, you can choose Slack as a connector type and configure it to send a message to a channel you selected. You can also create an index connector that writes the JSON object you configure to a specific index. It’s also possible to customize the notification messages. A list of variables is available to include in the message, like job ID, anomaly score, time, or top influencers.
After you save the configurations, the rule appears in the Alerts and Actions list where you can check its status and see the overview of its configuration information.
The name of an alert is always the same as the job ID of the associated anomaly detection job that triggered it. You can mute the notifications for a particular anomaly detection job on the page of the rule that lists the individual alerts. You can open it via Alerts and Actions by selecting the rule name.