Vega
editVega
editVega and Vega-Lite are both grammars for creating custom visualizations. They are recommended for advanced users who are comfortable writing Elasticsearch queries manually. Vega-Lite is a good starting point for users who are new to both grammars, but they are not compatible.
Vega and Vega-Lite panels can display one or more data sources, including Elasticsearch, Elastic Map Service, URL, or static data, and support Kibana extensions that allow you to embed the panels on your dashboard and add interactive tools.
Use Vega or Vega-Lite when you want to create visualizations with:
-
Aggregations that use
nestedorparent/childmapping - Aggregations without an index pattern
- Queries that use custom time filters
- Complex calculations
- Extracted data from _source instead of aggregations
- Scatter charts, sankey charts, and custom maps
- An unsupported visual theme
These grammars have some limitations: they do not support tables, and can’t run queries conditionally.
Both Vega and Vega-Lite use JSON, but Kibana has made this simpler to type by integrating HJSON. HJSON supports the following:
- Optional quotes
- Double quotes or single quotes
- Optional commas
- Comments using // or /* syntax
- Multiline strings
Tutorials: Create custom panels
editLearn how to connect Vega-Lite with Kibana filters and Elasticsearch data, then learn how to create more Kibana interaction using Vega.
As you edit the specs, work in small steps, and frequently save your work. Small changes can cause unexpected results. To save, click Save in the toolbar.
Before starting, add the eCommerce sample data that you’ll use in your spec, then create the dashboard.
- From the Kibana Home page, click Try our sample data.
- From eCommerce sample data, click Add data.
- Open the main menu, then click Dashboard.
- On the Dashboards page, click Create dashboard.
Open and set up Vega-Lite
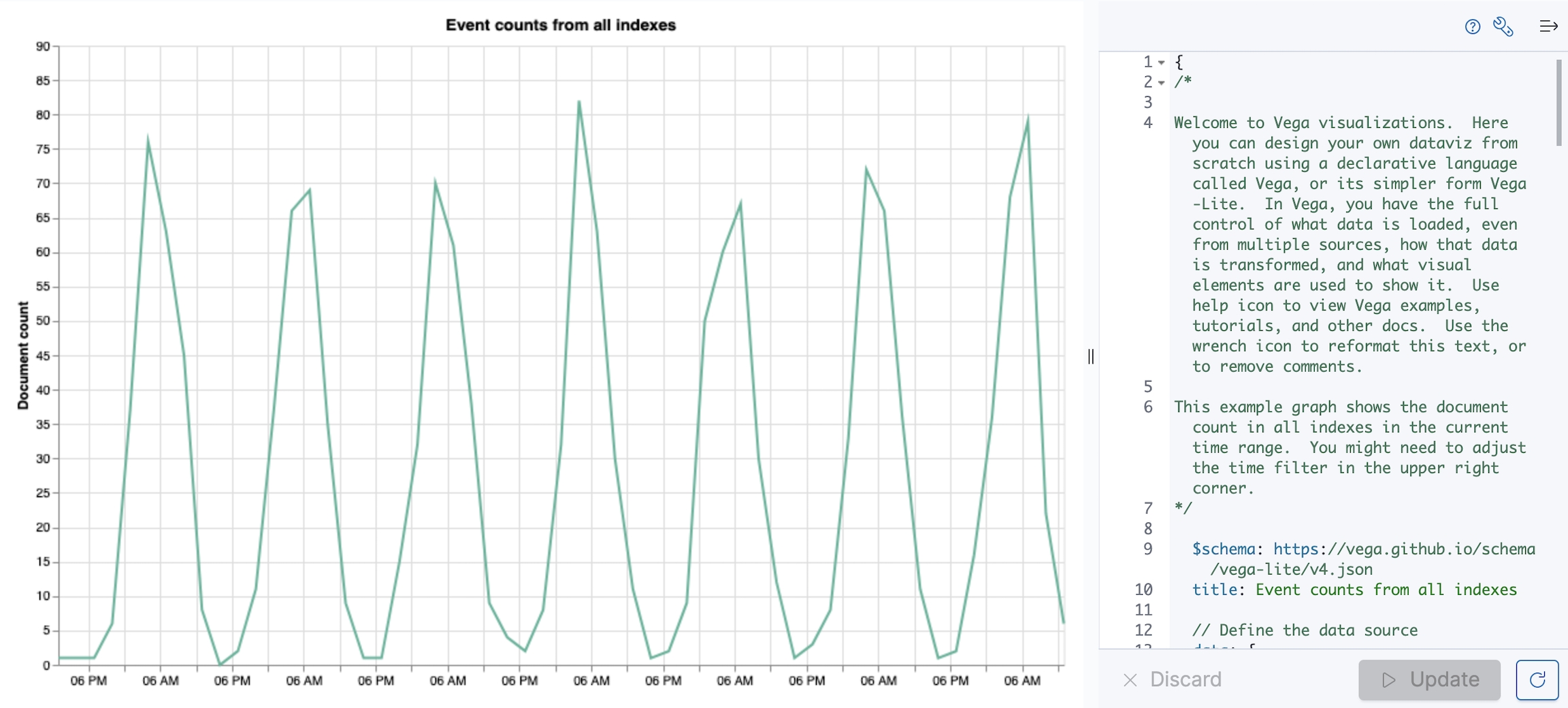
editOpen Vega-Lite and change the time range.
-
On the dashboard, click All types, then select Custom visualization.
A pre-populated line chart displays the total number of documents.
- Make sure the time filter is Last 7 days.
Tutorial: Create a stacked area chart from an Elasticsearch search query
editLearn how to query Elasticsearch from Vega-Lite, displaying the results in a stacked area chart.
-
In the Vega-Lite spec, replace
index: _allwith the following, then click Update:
index: kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
A flat line appears with zero results.
To add the data fields from the kibana_sample_data_ecommerce index, replace the following, then click Update:
-
%timefield%: @timestampwith%timefield%: order_date -
field: @timestampwithfield: order_date
Add the aggregations
editTo create the stacked area chart, add the aggregations.
To check your work, open and use the Console on a separate browser tab.
- Open Kibana on a new tab.
- Open the main menu, then click Dev Tools.
- On the Console editor, enter the aggregation, then click Click to send request:
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"order_date": {
"gte": "now-7d"
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"time_buckets": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "order_date",
"fixed_interval": "1d",
"extended_bounds": {
"min": "now-7d"
},
"min_doc_count": 0
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
Add the terms aggregation, then click Click to send request:
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"order_date": {
"gte": "now-7d"
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"categories": {
"terms": { "field": "category.keyword" },
"aggs": {
"time_buckets": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "order_date",
"fixed_interval": "1d",
"extended_bounds": {
"min": "now-7d"
},
"min_doc_count": 0
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
The response format is different from the first aggregation query:
{
"aggregations" : {
"categories" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [{
"key" : "Men's Clothing",
"doc_count" : 1661,
"time_buckets" : {
"buckets" : [{
"key_as_string" : "2020-06-30T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1593475200000,
"doc_count" : 19
}, {
"key_as_string" : "2020-07-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"key" : 1593561600000,
"doc_count" : 71
}]
}
}]
}
}
}
In the Vega-Lite spec, enter the aggregations, then click Update:
data: {
url: {
%context%: true
%timefield%: order_date
index: kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
body: {
aggs: {
categories: {
terms: { field: "category.keyword" }
aggs: {
time_buckets: {
date_histogram: {
field: order_date
interval: {%autointerval%: true}
extended_bounds: {
min: {%timefilter%: "min"}
max: {%timefilter%: "max"}
}
min_doc_count: 0
}
}
}
}
}
size: 0
}
}
format: {property: "aggregations.categories.buckets" }
}
For information about the queries, refer to reference for writing Elasticsearch queries in Vega.
Debug the warning
editTo generate the data, Vega-Lite uses the source_0 and data_0. source_0 contains
the results from the Elasticsearch query, and data_0 contains the visually encoded results that are shown on the chart.
To debug the warning, compare source_0 and data_0.
- In the toolbar, click Inspect.
- From the View dropdown, select Vega debug.
-
From the dropdown, select source_0.
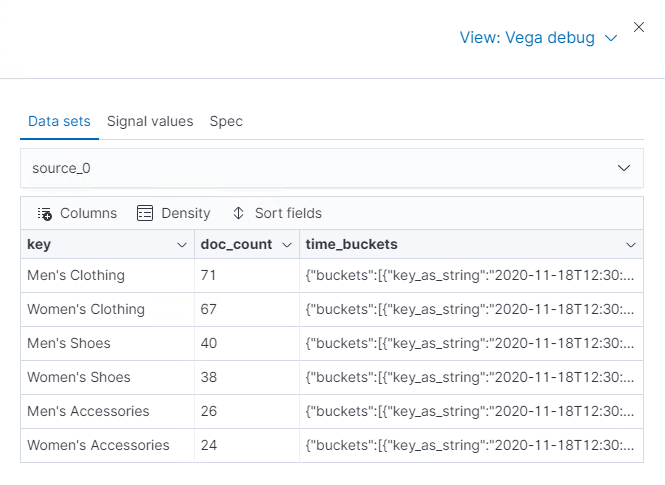
-
To compare to the visually encoded data, select data_0 from the dropdown.
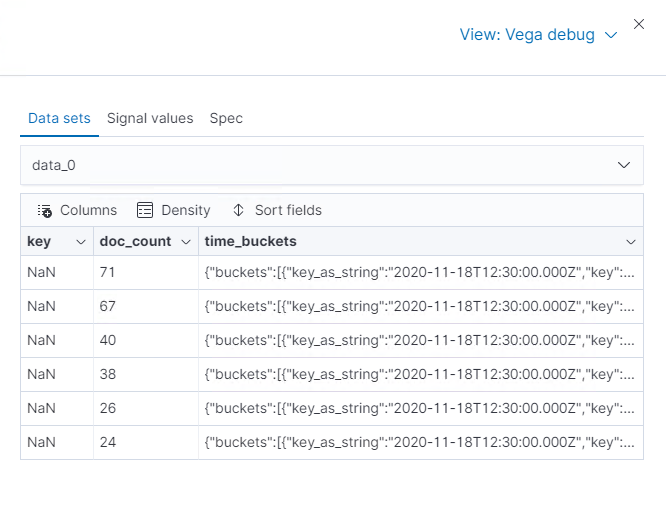
key is unable to convert because the property is category (
Men's Clothing,Women's Clothing, etc.) instead of a timestamp.
Add and debug the encoding block
editIn the Vega-Lite spec, add the encoding block:
encoding: {
x: {
field: time_buckets.buckets.key
type: temporal
axis: { title: null }
}
y: {
field: time_buckets.buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
axis: { title: "Document count" }
}
}
- Click Inspect, then select Vega Debug from the View dropdown.
-
From the dropdown, select data_0.
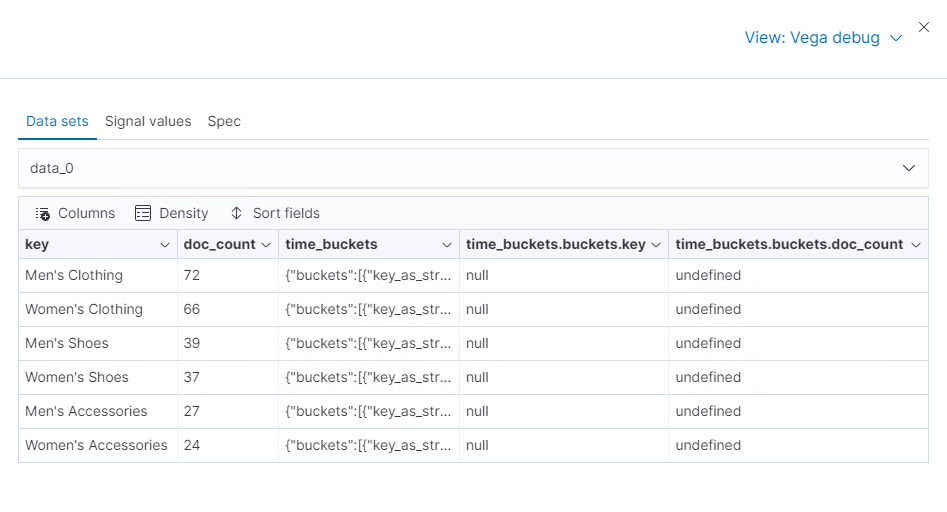
Vega-Lite is unable to extract the time_buckets.buckets inner array.
Extract the time_buckets.buckets inner array
editIn Kibana 7.9 and later, use the Vega-Lite flatten transformation to extract the time_buckets.buckets inner array.
If you are using Kibana 7.8 and earlier, the flatten transformation is available only in Vega.
In the Vega-Lite spec, add a transform block, then click Update:
transform: [{
flatten: ["time_buckets.buckets"]
}]
- Click Inspect, then select Vega Debug from the View dropdown.
-
From the dropdown, select data_0.
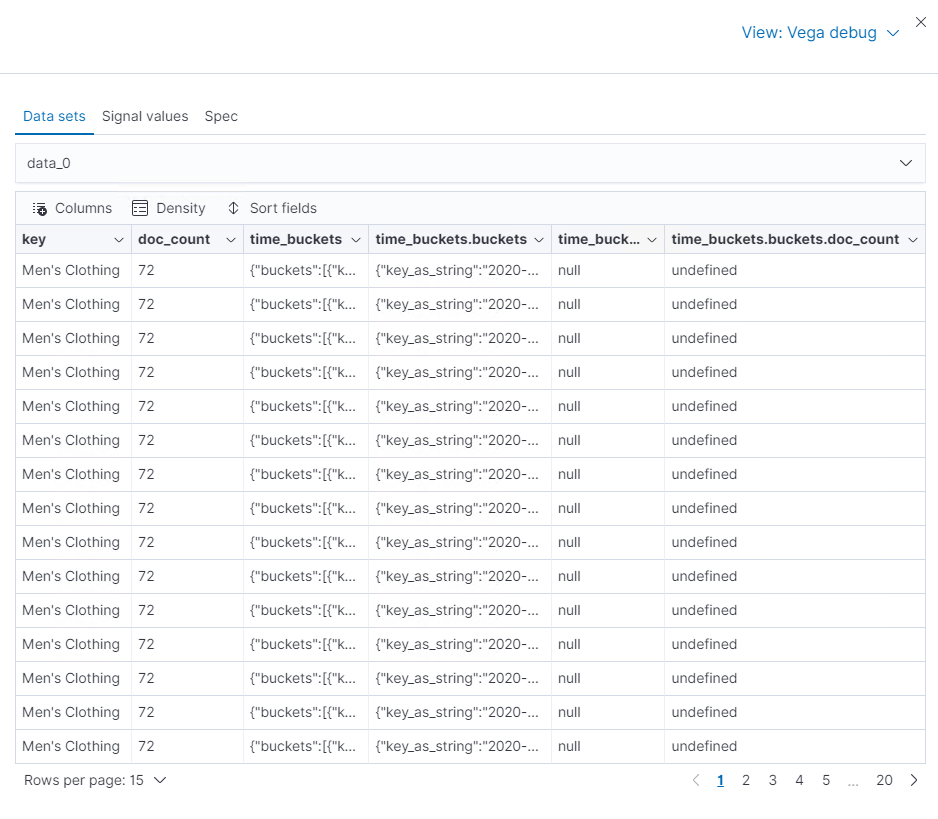
Vega-Lite displays undefined values because there are duplicate names.
-
To resolve the duplicate names, add the
transformandencodingblocks, then click Update:
transform: [{
flatten: ["time_buckets.buckets"],
as: ["buckets"]
}]
mark: area
encoding: {
x: {
field: buckets.key
type: temporal
axis: { title: null }
}
y: {
field: buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
axis: { title: "Document count" }
}
color: {
field: key
type: nominal
}
}
Add hover states and tooltips
editWith the Vega-Lite spec, you can add hover states and tooltips to the stacked area chart with the selection block.
In the Vega-Lite spec, add the encoding block, then click Update:
encoding: {
tooltip: [{
field: buckets.key
type: temporal
title: "Date"
}, {
field: key
type: nominal
title: "Category"
}, {
field: buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
title: "Count"
}]
}
When you hover over the area series on the stacked area chart, a multi-line tooltip appears, but is unable to indicate the nearest point. To indicate the nearest point, add a second layer.
Add composite marks, then click Update:
layer: [{
mark: area
}, {
mark: point
}]
The points are unable to stack and align with the stacked area chart.
Change the y encoding:
y: {
field: buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
axis: { title: "Document count" }
stack: true
}
Add a selection block inside mark: point:
layer: [{
mark: area
}, {
mark: point
selection: {
pointhover: {
type: single
on: mouseover
clear: mouseout
empty: none
fields: ["buckets.key", "key"]
nearest: true
}
}
encoding: {
size: {
condition: {
selection: pointhover
value: 100
}
value: 5
}
fill: {
condition: {
selection: pointhover
value: white
}
}
}
}]
Move your cursor around the stacked area chart. The points are able to indicate the nearest point.
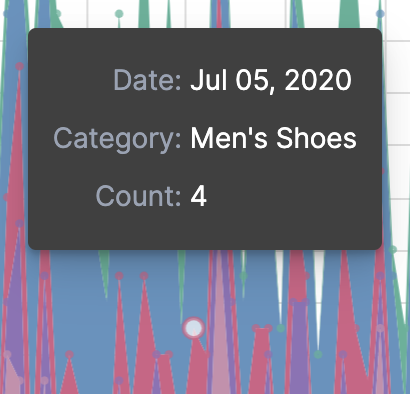
The selection is controlled by a signal. To view the signal, click Inspect in the toolbar.
Expand final Vega-Lite spec
{
$schema: https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v4.json
title: Event counts from ecommerce
data: {
url: {
%context%: true
%timefield%: order_date
index: kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
body: {
aggs: {
categories: {
terms: { field: "category.keyword" }
aggs: {
time_buckets: {
date_histogram: {
field: order_date
interval: {%autointerval%: true}
extended_bounds: {
min: {%timefilter%: "min"}
max: {%timefilter%: "max"}
}
min_doc_count: 0
}
}
}
}
}
size: 0
}
}
format: {property: "aggregations.categories.buckets" }
}
transform: [{
flatten: ["time_buckets.buckets"]
as: ["buckets"]
}]
encoding: {
x: {
field: buckets.key
type: temporal
axis: { title: null }
}
y: {
field: buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
axis: { title: "Document count" }
stack: true
}
color: {
field: key
type: nominal
title: "Category"
}
tooltip: [{
field: buckets.key
type: temporal
title: "Date"
}, {
field: key
type: nominal
title: "Category"
}, {
field: buckets.doc_count
type: quantitative
title: "Count"
}]
}
layer: [{
mark: area
}, {
mark: point
selection: {
pointhover: {
type: single
on: mouseover
clear: mouseout
empty: none
fields: ["buckets.key", "key"]
nearest: true
}
}
encoding: {
size: {
condition: {
selection: pointhover
value: 100
}
value: 5
}
fill: {
condition: {
selection: pointhover
value: white
}
}
}
}]
}
Tutorial: Update Kibana filters from Vega
editTo build an area chart using an Elasticsearch search query, edit the Vega spec, then add click and drag handlers to update the Kibana filters.
In the Vega spec, enter the following, then click Update:
{
$schema: "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega/v5.json"
data: [{
name: source_0
}]
scales: [{
name: x
type: time
range: width
}, {
name: y
type: linear
range: height
}]
axes: [{
orient: bottom
scale: x
}, {
orient: left
scale: y
}]
marks: [
{
type: area
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
}
}
}
]
}
Add the Elasticsearch search query with the data block, then click Update:
data: [
{
name: source_0
url: {
%context%: true
%timefield%: order_date
index: kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
body: {
aggs: {
time_buckets: {
date_histogram: {
field: order_date
fixed_interval: "3h"
extended_bounds: {
min: {%timefilter%: "min"}
max: {%timefilter%: "max"}
}
min_doc_count: 0
}
}
}
size: 0
}
}
format: { property: "aggregations.time_buckets.buckets" }
}
]
Change the x- and y-axes
editDisplay labels for the x- and y-axes.
In the Vega spec, add the scales block, then click Update:
scales: [{
name: x
type: time
range: width
domain: {
data: source_0
field: key
}
}, {
name: y
type: linear
range: height
domain: {
data: source_0
field: doc_count
}
}]
Add the key and doc_count fields as the X- and Y-axis values, then click Update:
marks: [
{
type: area
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
x: {
scale: x
field: key
}
y: {
scale: y
value: 0
}
y2: {
scale: y
field: doc_count
}
}
}
}
]
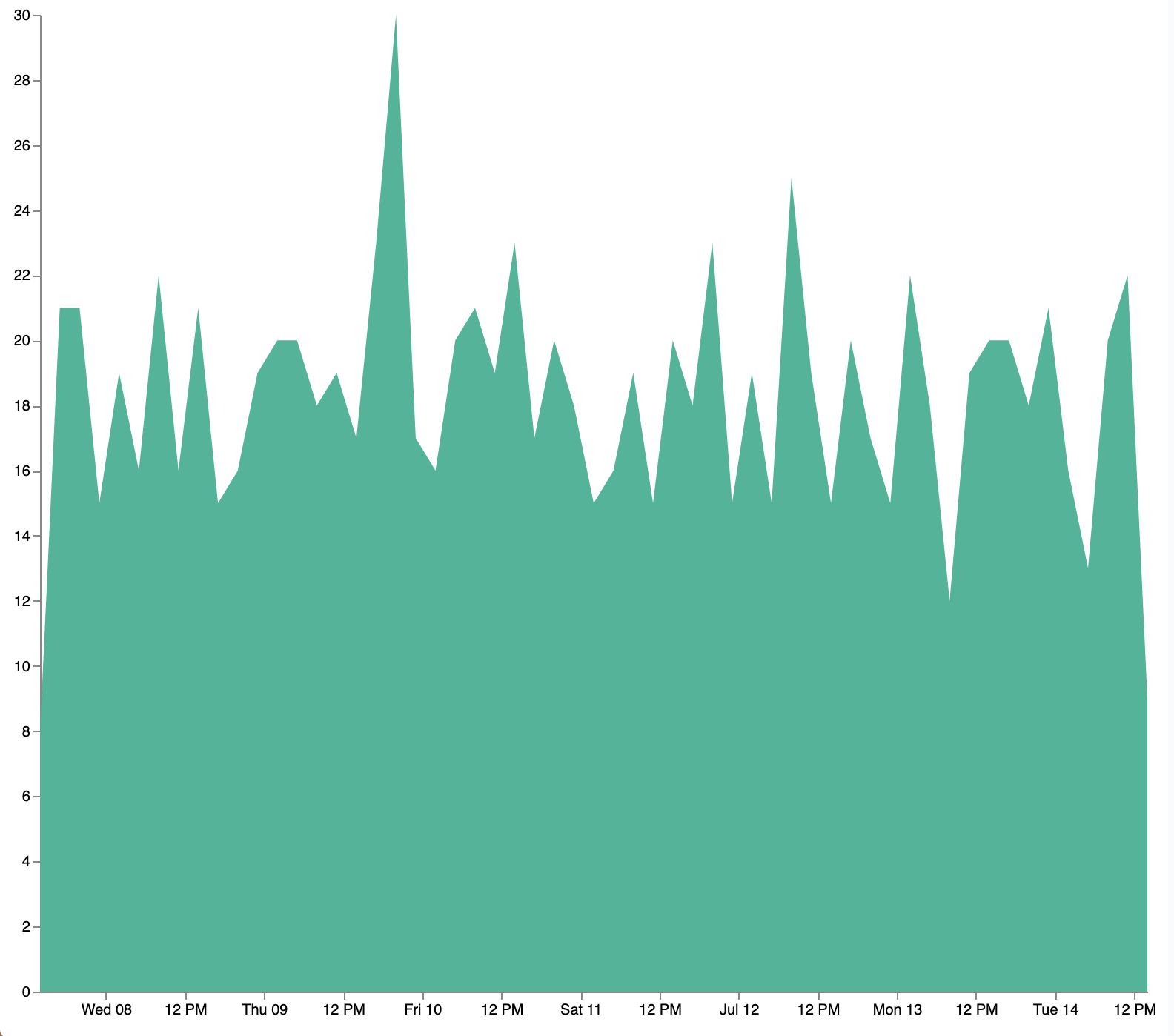
Add a block to the marks section
editShow the clickable points on the area chart to filter for a specific date.
In the Vega spec, add to the marks block, then click Update:
{
name: point
type: symbol
style: ["point"]
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
x: {
scale: x
field: key
}
y: {
scale: y
field: doc_count
}
size: {
value: 100
}
fill: {
value: black
}
}
}
}
Create a signal
editTo make the points clickable, create a Vega signal. You can access the clicked datum in the expression used to update.
In the Vega spec, add a signals block to specify that the cursor clicks add a time filter with the three hour interval, then click Update:
signals: [
{
name: point_click
on: [{
events: {
source: scope
type: click
markname: point
}
update: '''kibanaSetTimeFilter(datum.key, datum.key + 3 * 60 * 60 * 1000)'''
}]
}
]
The event uses the kibanaSetTimeFilter custom function to generate a filter that
applies to the entire dashboard on a click.
To make the area chart interactive, locate the marks block,
then update the point and add cursor: { value: "pointer" } to
encoding:
{
name: point
type: symbol
style: ["point"]
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
...
cursor: { value: "pointer" }
}
}
}
Add a drag interaction
editTo allow users to filter based on a time range, add a drag interaction, which requires additional signals and a rectangle overlay.
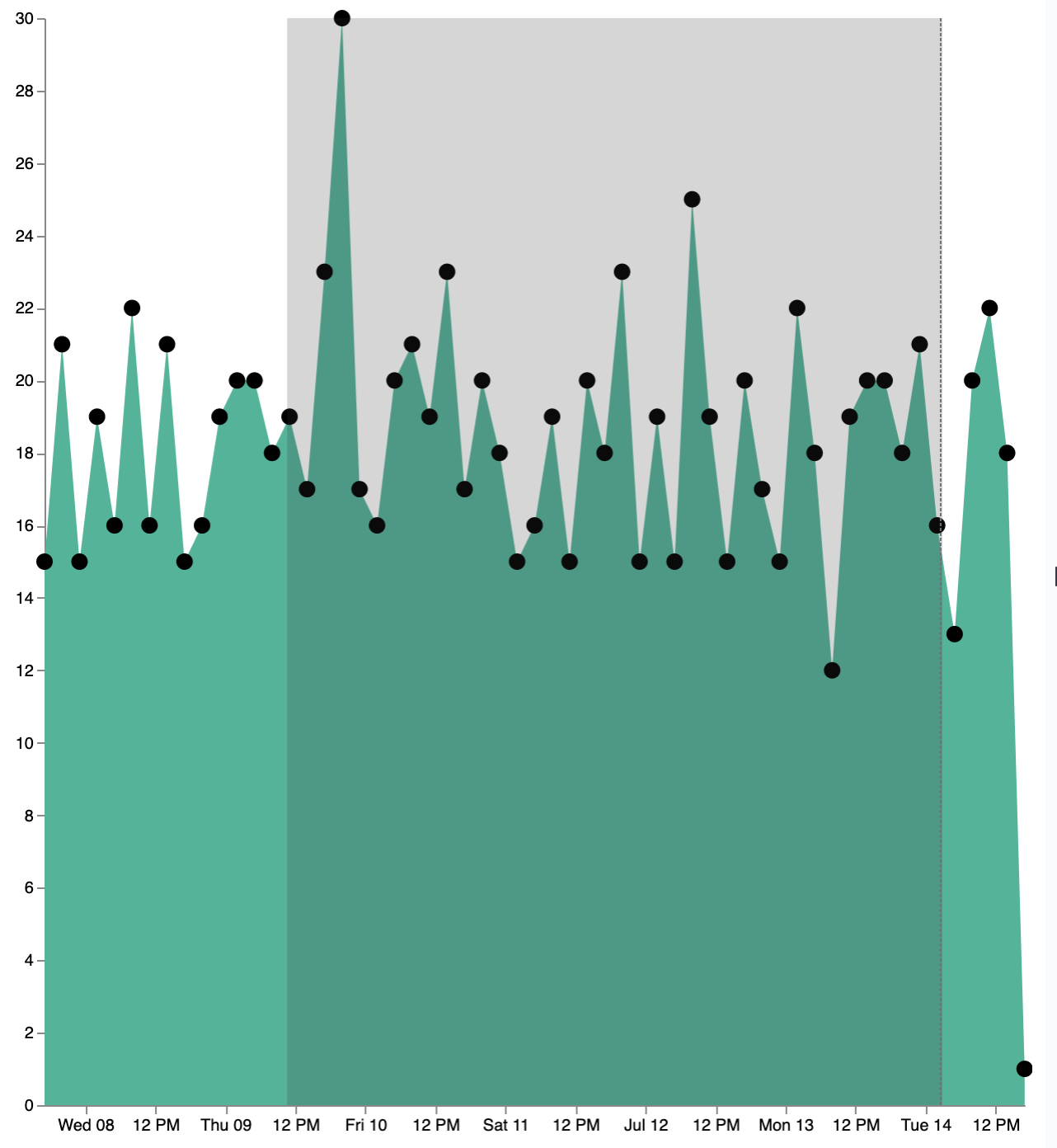
In the Vega spec, add a signal to track the X position of the cursor:
{
name: currentX
value: -1
on: [{
events: {
type: mousemove
source: view
},
update: "clamp(x(), 0, width)"
}, {
events: {
type: mouseout
source: view
}
update: "-1"
}]
}
To indicate the current cursor position, add a mark block:
{
type: rule
interactive: false
encode: {
update: {
y: {value: 0}
y2: {signal: "height"}
stroke: {value: "gray"}
strokeDash: {
value: [2, 1]
}
x: {signal: "max(currentX,0)"}
defined: {signal: "currentX > 0"}
}
}
}
To track the selected time range, add a signal that updates until the user releases their cursor or presses Return:
{
name: selected
value: [0, 0]
on: [{
events: {
type: mousedown
source: view
}
update: "[clamp(x(), 0, width), clamp(x(), 0, width)]"
}, {
events: {
type: mousemove
source: window
consume: true
between: [{
type: mousedown
source: view
}, {
merge: [{
type: mouseup
source: window
}, {
type: keydown
source: window
filter: "event.key === 'Escape'"
}]
}]
}
update: "[selected[0], clamp(x(), 0, width)]"
}, {
events: {
type: keydown
source: window
filter: "event.key === 'Escape'"
}
update: "[0, 0]"
}]
}
There is a signal that tracks the time range from the user.
To indicate the range visually, add a mark that only appears conditionally:
{
type: rect
name: selectedRect
encode: {
update: {
height: {signal: "height"}
fill: {value: "#333"}
fillOpacity: {value: 0.2}
x: {signal: "selected[0]"}
x2: {signal: "selected[1]"}
defined: {signal: "selected[0] !== selected[1]"}
}
}
}
Add a signal that updates the Kibana time filter when the cursor is released while dragging:
{
name: applyTimeFilter
value: null
on: [{
events: {
type: mouseup
source: view
}
update: '''selected[0] !== selected[1] ? kibanaSetTimeFilter(
invert('x',selected[0]),
invert('x',selected[1])) : null'''
}]
}
Expand final Vega spec
{
$schema: "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega/v5.json"
data: [
{
name: source_0
url: {
%context%: true
%timefield%: order_date
index: kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
body: {
aggs: {
time_buckets: {
date_histogram: {
field: order_date
fixed_interval: "3h"
extended_bounds: {
min: {%timefilter%: "min"}
max: {%timefilter%: "max"}
}
min_doc_count: 0
}
}
}
size: 0
}
}
format: { property: "aggregations.time_buckets.buckets" }
}
]
scales: [{
name: x
type: time
range: width
domain: {
data: source_0
field: key
}
}, {
name: y
type: linear
range: height
domain: {
data: source_0
field: doc_count
}
}]
axes: [{
orient: bottom
scale: x
}, {
orient: left
scale: y
}]
marks: [
{
type: area
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
x: {
scale: x
field: key
}
y: {
scale: y
value: 0
}
y2: {
scale: y
field: doc_count
}
}
}
},
{
name: point
type: symbol
style: ["point"]
from: {
data: source_0
}
encode: {
update: {
x: {
scale: x
field: key
}
y: {
scale: y
field: doc_count
}
size: {
value: 100
}
fill: {
value: black
}
cursor: { value: "pointer" }
}
}
},
{
type: rule
interactive: false
encode: {
update: {
y: {value: 0}
y2: {signal: "height"}
stroke: {value: "gray"}
strokeDash: {
value: [2, 1]
}
x: {signal: "max(currentX,0)"}
defined: {signal: "currentX > 0"}
}
}
},
{
type: rect
name: selectedRect
encode: {
update: {
height: {signal: "height"}
fill: {value: "#333"}
fillOpacity: {value: 0.2}
x: {signal: "selected[0]"}
x2: {signal: "selected[1]"}
defined: {signal: "selected[0] !== selected[1]"}
}
}
}
]
signals: [
{
name: point_click
on: [{
events: {
source: scope
type: click
markname: point
}
update: '''kibanaSetTimeFilter(datum.key, datum.key + 3 * 60 * 60 * 1000)'''
}]
}
{
name: currentX
value: -1
on: [{
events: {
type: mousemove
source: view
},
update: "clamp(x(), 0, width)"
}, {
events: {
type: mouseout
source: view
}
update: "-1"
}]
}
{
name: selected
value: [0, 0]
on: [{
events: {
type: mousedown
source: view
}
update: "[clamp(x(), 0, width), clamp(x(), 0, width)]"
}, {
events: {
type: mousemove
source: window
consume: true
between: [{
type: mousedown
source: view
}, {
merge: [{
type: mouseup
source: window
}, {
type: keydown
source: window
filter: "event.key === 'Escape'"
}]
}]
}
update: "[selected[0], clamp(x(), 0, width)]"
}, {
events: {
type: keydown
source: window
filter: "event.key === 'Escape'"
}
update: "[0, 0]"
}]
}
{
name: applyTimeFilter
value: null
on: [{
events: {
type: mouseup
source: view
}
update: '''selected[0] !== selected[1] ? kibanaSetTimeFilter(
invert('x',selected[0]),
invert('x',selected[1])) : null'''
}]
}
]
}
Vega reference
editLearn more about Kibana extension, additional Vega resources, and examples.
Reference for Kibana extensions
editKibana has extended Vega and Vega-Lite with extensions that support:
- Automatic sizing
- Default theme to match Kibana
- Writing Elasticsearch queries using the time range and filters from dashboards
- [preview] This functionality is in technical preview and may be changed or removed in a future release. Elastic will work to fix any issues, but features in technical preview are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features. Using the Elastic Map Service in Vega maps
- Additional tooltip styling
- Advanced setting to enable URL loading from any domain
- Debugging support using the Kibana inspector or browser console
- (Vega only) Expression functions which can update the time range and dashboard filters
Automatic sizing
editMost users will want their Vega visualizations to take the full available space, so unlike
Vega examples, width and height are not required parameters in Kibana because your
spec will be merged with the default Kibana settings in most cases:
autosize: {
type: fit
contains: padding
}
width: container
height: container
These default settings are not applied if:
-
Your spec uses
type=map -
Your spec is Vega-Lite and contains a facet, row, column, repeat, or concat operator. In these
cases, providing
widthandheightwill affect the child size.
To set the width or height manually, set autosize: none and provide the exact pixel sizes, including
padding for the title, legend and axes.
autosize: none
width: 600
height: 200
padding: {
top: 20
bottom: 20
left: 55
right: 150
}
To learn more, read about Vega autosize and Vega-Lite autosize.
Autosize in Vega-Lite has several limitations
which can affect the height and width of your visualization, but these limitations do not exist in Vega.
If you need full control, convert your spec to Vega using the browser console
VEGA_DEBUG.vega_spec output.
To disable these warnings, you can add extra options to your spec.
Default theme to match Kibana
editKibana registers a default Vega color scheme
with the id elastic, and sets a default color for each mark type.
Override it by providing a different stroke, fill, or color (Vega-Lite) value.
Writing Elasticsearch queries in Vega
editKibana extends the Vega data elements
with support for direct Elasticsearch queries specified as url.
Kibana is unable to support dynamically loaded data, which would otherwise work in Vega. All data is fetched before it’s passed to the Vega renderer.
To define an Elasticsearch query in Vega, set the url to an object. Kibana parses
the object looking for special tokens that allow your query to integrate with Kibana.
Tokens include the following:
-
%context%: true: Set at the top level, and replaces thequerysection with filters from dashboard -
%timefield%: <name>: Set at the top level, integrates the query with the dashboard time filter -
{%timefilter%: true}: Replaced by an Elasticsearch range query with upper and lower bounds -
{%timefilter%: "min" | "max"}: Replaced only by the upper or lower bounds -
{%timefilter: true, shift: -1, unit: 'hour'}: Generates a time range query one hour in the past -
{%autointerval%: true}: Replaced by the string which contains the automatic Kibana time interval, such as1h -
{%autointerval%: 10}: Replaced by a string which is approximately dividing the time into 10 ranges, allowing you to influence the automatic interval -
"%dashboard_context-must_clause%": String replaced by object containing filters -
"%dashboard_context-filter_clause%": String replaced by an object containing filters -
"%dashboard_context-must_not_clause%": String replaced by an object containing filters
Vega supports the interval parameter, which is unsupported Elasticsearch 8.0.0 and later. To use intervals, use fixed_interval or calendar_interval instead.
For example, the following query counts the number of documents in a specific index:
// An object instead of a string for the URL value
// is treated as a context-aware Elasticsearch query.
url: {
// Specify the time filter.
%timefield%: @timestamp
// Apply dashboard context filters when set
%context%: true
// Which indexes to search
index: kibana_sample_data_logs
// The body element may contain "aggs" and "query" keys
body: {
aggs: {
time_buckets: {
date_histogram: {
// Use date histogram aggregation on @timestamp field
field: @timestamp
// interval value will depend on the time filter
// Use an integer to set approximate bucket count
interval: { %autointerval%: true }
// Make sure we get an entire range, even if it has no data
extended_bounds: {
min: { %timefilter%: "min" }
max: { %timefilter%: "max" }
}
// Use this for linear (e.g. line, area) graphs
// Without it, empty buckets will not show up
min_doc_count: 0
}
}
}
// Speed up the response by only including aggregation results
size: 0
}
}
The full result includes the following structure:
{
"aggregations": {
"time_buckets": {
"buckets": [{
"key_as_string": "2015-11-30T22:00:00.000Z",
"key": 1448920800000,
"doc_count": 28
}, {
"key_as_string": "2015-11-30T23:00:00.000Z",
"key": 1448924400000,
"doc_count": 330
}, ...
For most visualizations, you only need the list of bucket values. To focus on
only the data you need, use format: {property: "aggregations.time_buckets.buckets"}.
Specify a query with individual range and dashboard context. The query is
equivalent to "%context%": true, "%timefield%": "@timestamp",
except that the time range is shifted back by 10 minutes:
{
body: {
query: {
bool: {
must: [
// This string will be replaced
// with the auto-generated "MUST" clause
"%dashboard_context-must_clause%"
{
range: {
// apply timefilter (upper right corner)
// to the @timestamp variable
@timestamp: {
// "%timefilter%" will be replaced with
// the current values of the time filter
// (from the upper right corner)
"%timefilter%": true
// Only work with %timefilter%
// Shift current timefilter by 10 units back
shift: 10
// week, day (default), hour, minute, second
unit: minute
}
}
}
]
must_not: [
// This string will be replaced with
// the auto-generated "MUST-NOT" clause
"%dashboard_context-must_not_clause%"
]
filter: [
// This string will be replaced
// with the auto-generated "FILTER" clause
"%dashboard_context-filter_clause%"
]
}
}
}
}
When using "%context%": true or defining a value for "%timefield%" the body cannot contain a query. To customize the query within the VEGA specification (e.g. add an additional filter, or shift the timefilter), define your query and use the placeholders as in the example above. The placeholders will be replaced by the actual context of the dashboard or visualization once parsed.
The "%timefilter%" can also be used to specify a single min or max
value. The date_histogram’s extended_bounds can be set
with two values - min and max. Instead of hardcoding a value, you may
use "min": {"%timefilter%": "min"}, which will be replaced with the
beginning of the current time range. The shift and unit values are
also supported. The "interval" can also be set dynamically, depending
on the currently picked range: "interval": {"%autointerval%": 10} will
try to get about 10-15 data points (buckets).
Access Elastic Map Service files
edit[preview] This functionality is in technical preview and may be changed or removed in a future release. Elastic will work to fix any issues, but features in technical preview are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features. Access the Elastic Map Service files via the same mechanism:
url: {
// "type" defaults to "elasticsearch" otherwise
%type%: emsfile
// Name of the file, exactly as in https://maps.elastic.co
name: World Countries
}
// The result is either a topojson file or a geojson file.
// Refer to the Default format for the file at https://maps.elastic.co
// Get its features to use this data source with the "shape" marks
// https://vega.github.io/vega/docs/marks/shape/
// For a topojson file use
format: {type: "topojson", feature: "data"}
// For a geojson file use
format: {property: "features"}
Vega with a Map
edit
[preview]
This functionality is in technical preview and may be changed or removed in a future release. Elastic will work to fix any issues, but features in technical preview are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
To enable Maps, the graph must specify type=map in the host configuration:
{
"config": {
"kibana": {
"type": "map",
// Initial map position
"latitude": 40.7, // default 0
"longitude": -74, // default 0
"zoom": 7, // default 2
// Defaults to 'true', disables the base map layer.
"mapStyle": false,
// When 'mapStyle' is 'undefined' or 'true', sets the EMS-layer for the map.
// May either be: "road_map", "road_map_desaturated", "dark_map".
// If 'emsTileServiceId' is 'undefined', it falls back to the auto-switch-dark-light behavior.
"emsTileServiceId": "road_map",
// default 0
"minZoom": 5,
// defaults to the maximum for the given style,
// or 25 when base is disabled
"maxZoom": 13,
// Defaults to 'true', shows +/- buttons to zoom in/out
"zoomControl": false,
// Defaults to 'false', disables mouse wheel zoom. If set to
// 'true', map may zoom unexpectedly while scrolling dashboard
"scrollWheelZoom": false,
// When false, repaints on each move frame.
// Makes the graph slower when moving the map
"delayRepaint": true, // default true
}
},
/* the rest of Vega JSON */
}
The visualization automatically injects a "projection", which you can use to
calculate the position of all geo-aware marks.
Additionally, you can use latitude, longitude, and zoom signals.
These signals can be used in the graph, or can be updated to modify the
position of the map.
[preview]
This functionality is in technical preview and may be changed or removed in a future release. Elastic will work to fix any issues, but features in technical preview are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
You can use the Vega data element to access Elastic Maps Service (EMS) vector shapes of administrative boundaries in your Vega map by setting url.data to emsFile:
"data": [
{
"name": "countries",
"url": {
// "type" defaults to "elasticsearch" otherwise
%type%: emsfile
// Name of the file, exactly as in the Region map visualization
name: World Countries
},
// The result is a topojson file, get its features to use
// this data source with the "shape" marks
// https://vega.github.io/vega/docs/marks/shape/
"format": {"type": "topojson", "feature": "data"},
}
],
"marks": [
{
"type": "shape",
"from": {"data": "countries"},
"transform": [{"type": "geoshape", "projection": "projection"}]
}
]
Additional tooltip styling
editKibana has installed the Vega tooltip plugin, so tooltips can be defined in the ways documented there. Beyond that, Kibana also supports a configuration option for changing the tooltip position and padding:
{
config: {
kibana: {
tooltips: {
position: 'top',
padding: 15,
textTruncate: true,
}
}
}
}
Enable URL loading from any domain
editVega can load data from any URL. To enable, set vis_type_vega.enableExternalUrls: true in kibana.yml,
then restart Kibana.
Vega Inspector
editUse the contextual Inspect tool to gain insights into different elements.
Inspect Elasticsearch requests
editVega uses the Elasticsearch search API to get documents and aggregation results from Elasticsearch. To troubleshoot these requests, click Inspect, which shows the most recent requests. In case your specification has more than one request, you can switch between the views using the View dropdown.
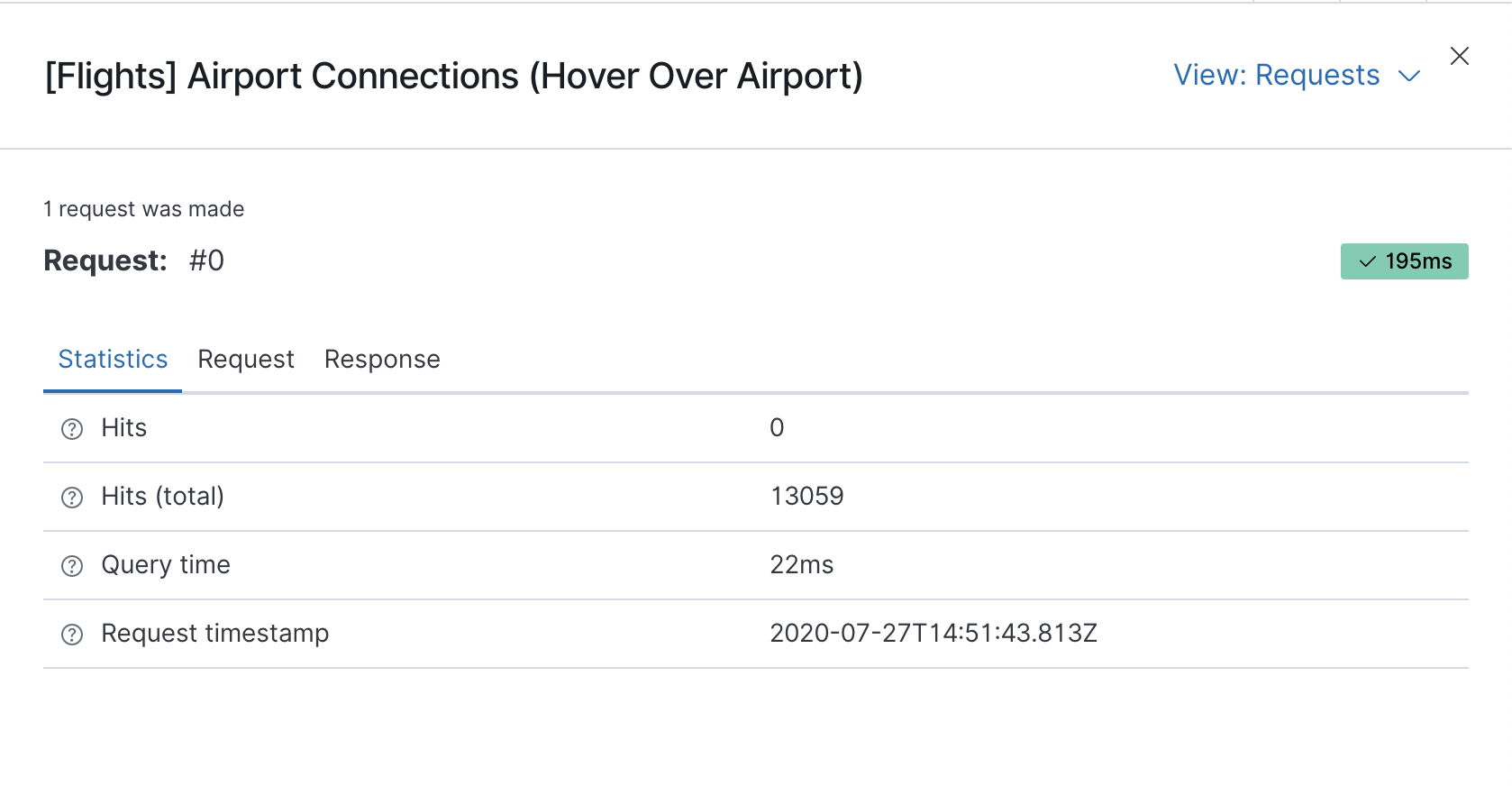
Vega debugging
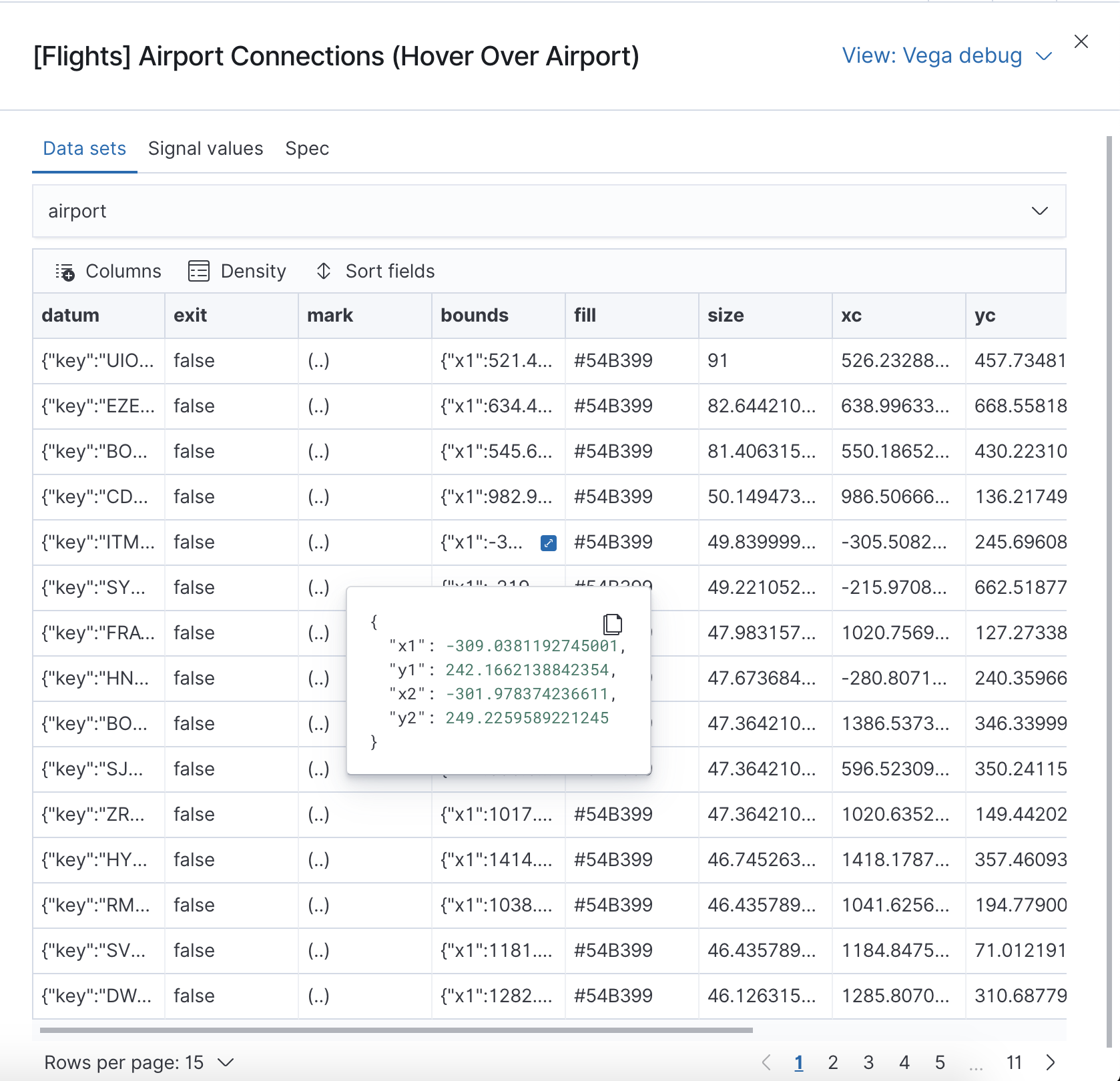
editWith the Vega debug view, you can inspect the Data sets and Signal Values runtime data.
The runtime data is read from the runtime scope.
To debug more complex specs, access to the view variable. For more information, refer to
the Vega browser debugging process.
Asking for help with a Vega spec
editBecause of the dynamic nature of the data in Elasticsearch, it is hard to help you with Vega specs unless you can share a dataset. To do this, click Inspect, select the Vega debug view, then select Spec.
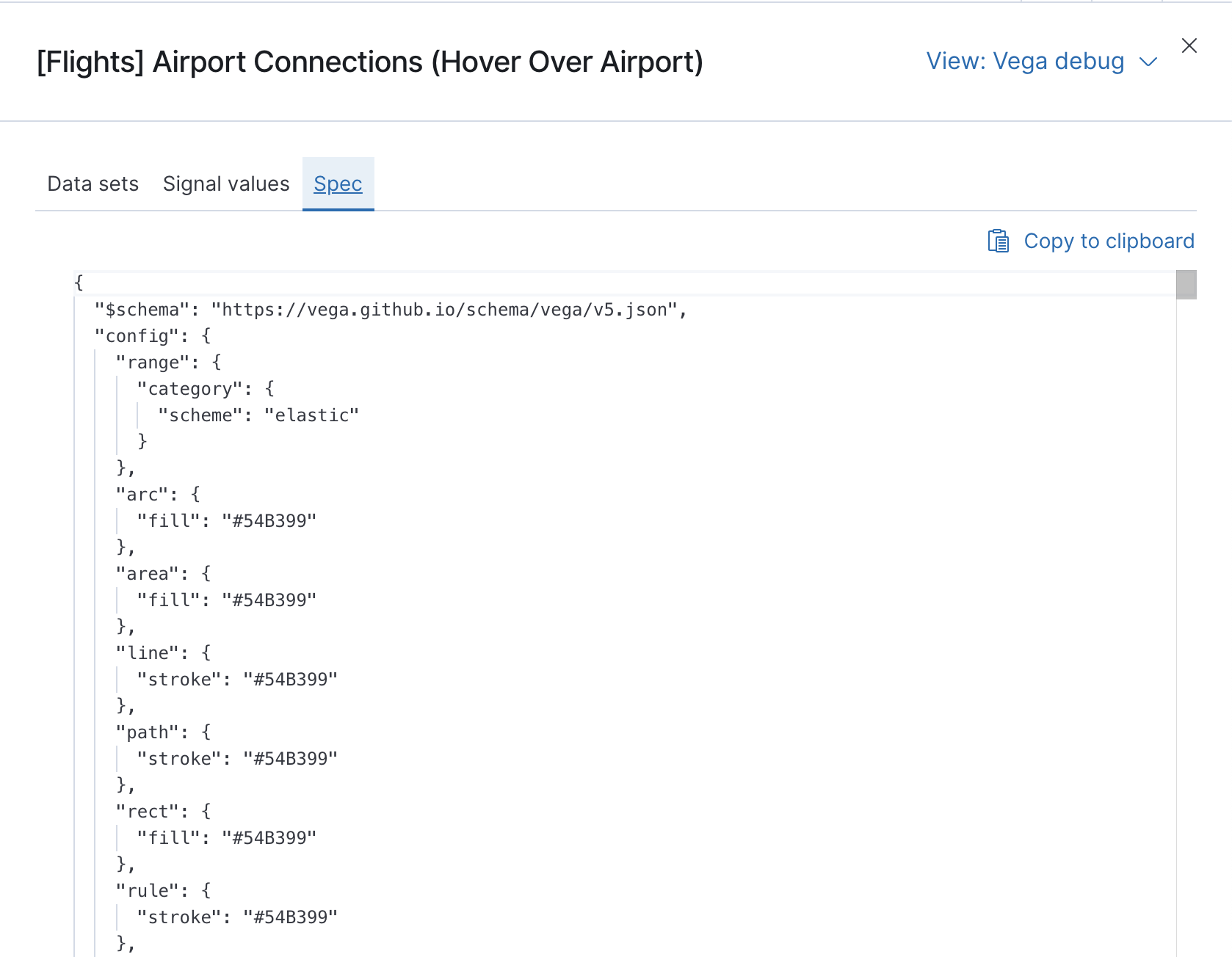
To copy the response, click Copy to clipboard. Paste the copied data to gist.github.com, possibly with a .json extension. Use the [raw] button, and share that when asking for help.
Browser debugging console
edit
[preview]
This functionality is in technical preview and may be changed or removed in a future release. Elastic will work to fix any issues, but features in technical preview are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
Use browser debugging tools (for example, F12 or Ctrl+Shift+J in Chrome) to
inspect the VEGA_DEBUG variable:
-
view— Access to the Vega View object. See Vega Debugging Guide on how to inspect data and signals at runtime. For Vega-Lite,VEGA_DEBUG.view.data('source_0')gets the pre-transformed data, andVEGA_DEBUG.view.data('data_0')gets the encoded data. For Vega, it uses the data name as defined in your Vega spec. -
vega_spec— Vega JSON graph specification after some modifications by Kibana. In case of Vega-Lite, this is the output of the Vega-Lite compiler. -
vegalite_spec— If this is a Vega-Lite graph, JSON specification of the graph before Vega-Lite compilation.
Expression functions which can update the time range and dashboard filters
editKibana has extended the Vega expression language with these functions.
These functions will trigger new data to be fetched, which by default will reset Vega signals.
To keep signal values set restoreSignalValuesOnRefresh: true in the Vega config.
/**
* @param {object} query Elastic Query DSL snippet, as used in the query DSL editor
* @param {string} [index] as defined in Kibana, or default if missing
*/
kibanaAddFilter(query, index)
/**
* @param {object} query Elastic Query DSL snippet, as used in the query DSL editor
* @param {string} [index] as defined in Kibana, or default if missing
*/
kibanaRemoveFilter(query, index)
kibanaRemoveAllFilters()
/**
* Update dashboard time filter to the new values
* @param {number|string|Date} start
* @param {number|string|Date} end
*/
kibanaSetTimeFilter(start, end)
Additional configuration options
edit{
config: {
kibana: {
// Placement of the Vega-defined signal bindings.
// Can be `left`, `right`, `top`, or `bottom` (default).
controlsLocation: top
// Can be `vertical` or `horizontal` (default).
controlsDirection: vertical
// If true, hides most of Vega and Vega-Lite warnings
hideWarnings: true
// Vega renderer to use: `svg` or `canvas` (default)
renderer: canvas
// Defaults to 'false', restores Vega signal values on refresh
restoreSignalValuesOnRefresh: false
}
}
}
Resources and examples
editTo learn more about Vega and Vega-Lite, refer to the resources and examples.
Vega editor
editThe Vega Editor includes examples for Vega & Vega-Lite, but does not support any Kibana-specific features like Elasticsearch requests and interactive base maps.
Vega-Lite resources
editVega resources
editWhen you use the examples in Kibana, you may
need to modify the "data" section to use absolute URL. For example,
replace "url": "data/world-110m.json" with
"url": "https://vega.github.io/editor/data/world-110m.json".