API Keys
editAPI Keys
editAPI keys enable you to create secondary credentials so that you can send requests on behalf of a user. Secondary credentials have the same or lower access rights.
For example, if you extract data from an Elasticsearch cluster on a daily basis, you might create an API key tied to your credentials, configure it with minimum access, and then put the API credentials into a cron job. Or, you might create API keys to automate ingestion of new data from remote sources, without a live user interaction.
To manage API keys, open the main menu, then click Stack Management > API Keys.
Elasticsearch API key service
editThe Elasticsearch API key service is automatically enabled when you configure TLS on the HTTP interface. This ensures that clients are unable to send API keys in clear-text.
When HTTPS connections are not enabled between Kibana and Elasticsearch, you cannot create or manage API keys, and you get an error message. For more information, see the Elasticsearch API key documentation, or contact your system administrator.
Security privileges
editYou must have the manage_security, manage_api_key, or the manage_own_api_key
cluster privileges to use API keys in Kibana. To manage roles, open the main menu, then click
Stack Management > Roles, or use the Kibana Role Management API.
Create an API key
editTo create an API key, open the main menu, then click Stack Management > API Keys > Create API key.
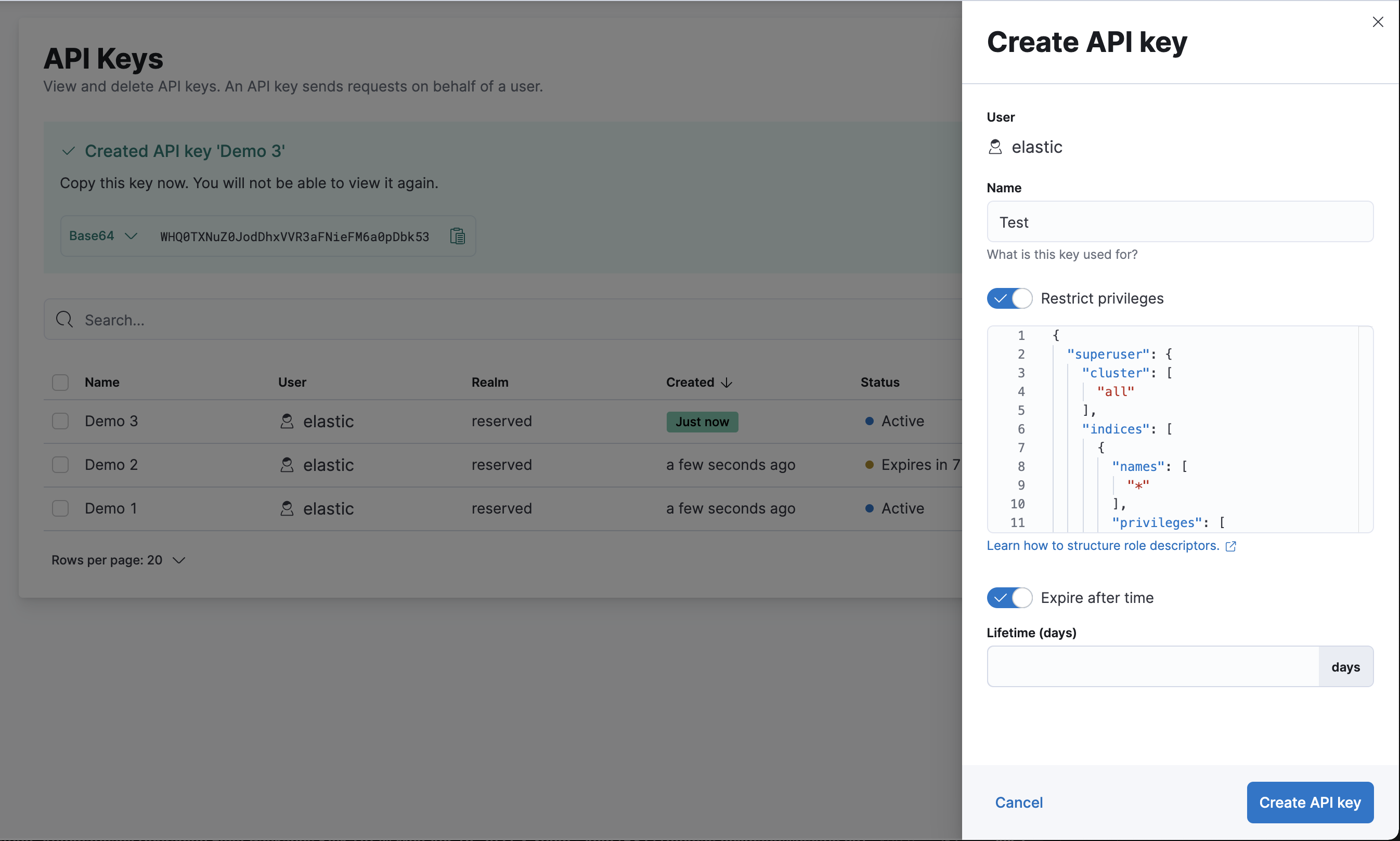
Once created, you can copy the API key (Base64 encoded) and use it to send requests to Elasticsearch on your behalf. For example:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:5601/api/security/role' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8' \ --header 'kbn-xsrf: true' \ --header 'Authorization: ApiKey aVZlLUMzSUJuYndxdDJvN0k1bU46aGxlYUpNS2lTa2FKeVZua1FnY1VEdw==' \
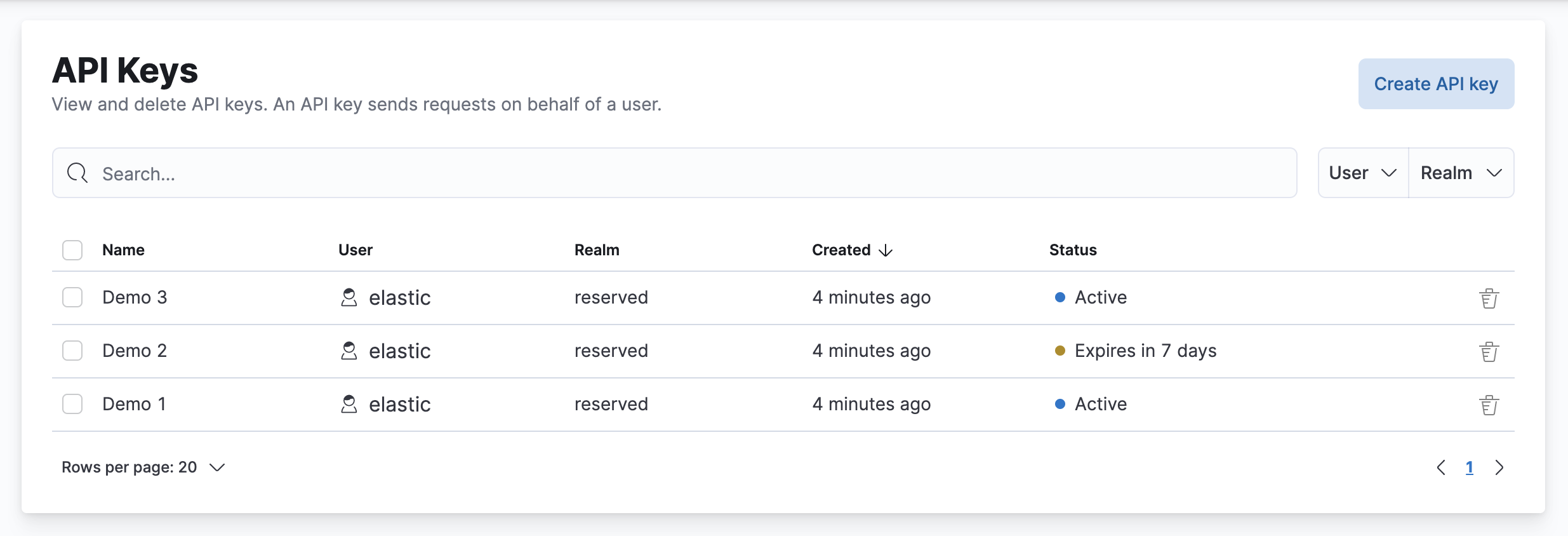
View and delete API keys
editThe API Keys feature in Kibana lists your API keys, including the name, date created, and status. If an API key expires, its status changes from Active to Expired.
If you have manage_security or manage_api_key permissions,
you can view the API keys of all users, and see which API key was
created by which user in which realm.
If you have only the manage_own_api_key permission, you see only a list of your own keys.
You can delete API keys individually or in bulk.
You cannot modify an API key. If you need additional privileges, you must create a new key with the desired configuration and invalidate the old key.