Set up Enterprise Search with OpenID Connect single sign-on (SSO)
editSet up Enterprise Search with OpenID Connect single sign-on (SSO)
edit
OpenID Connect for Enterprise Search is a platinum feature. In addition, OpenID Connect is only supported in Enterprise Search in Kibana.
The following documentation describes the process of configuring Elasticsearch and Kibana:
There are two possible ways to configure auth sources in Enterprise Search:
Option 1: use Kibana as the authentication provider, and always log in via the Kibana UI. This is the preferred way, and it will become the only way in 8.x.
To use this way, within your Enterprise Search configuration settings, make sure that:
-
kibana.hostis set -
kibana.external_urlis set -
any
auth.sourceconfigurations are removed.
Option 2: explicitly configure auth sources in Enterprise Search config file. They should mirror the realms configured in Elasticsearch.
Using this way, it is still possible (but not obligatory) to log in using the Enterprise Search UI.
Example config settings:
ent_search.auth:
oidc1:
order: 1
source: elasticsearch-oidc
Instructions specific to Elastic Cloud users
editOn Elastic Cloud:
-
it’s not possible to remove
ent_search.authsection -
kibana.external_urlis applied automatically and is not part of user settings -
elasticsearch-nativeauth source is always added automatically to the list of sources, and should not be included in user settings.
Elastic Cloud users should explicitly configure auth sources in the Enterprise Search config, whether they intend to use Kibana or Enterprise Search UI to log in.
Configure Enterprise Search role mappings for OpenID Connect users
editWhen you configured Elasticsearch and Kibana for OpenID Connect using the documentation links above, one of the steps advised you to create a role mapping to be able to access Kibana. As a very simple and permissive example, you can give all users in oidc1 realm superuser role, and that will also give them full access to App Search and Workplace Search:
PUT /_security/role_mapping/oidc1_mapping
{
"roles": [ "superuser" ],
"enabled": true,
"rules": {
"all": [
{"field": { "realm.name": "oidc1"}}}
]
}
}
However, this might be too permissive. In the following example, users who successfully log in to the oidc1 realm get full access to Kibana, but no access to Enterprise Search:
PUT /_security/role_mapping/oidc1_mapping
{
"roles": [ "kibana_admin" ],
"enabled": true,
"rules": {
"all": [
{"field": { "realm.name": "oidc1"}}}
]
}
}
In this case, oidc1 users can be managed via Enterprise Search mappings. Before any mappings can be created, it is necessary to enable role-based access (RBAC) mode in either App Search or Workplace Search. After that, users can be mapped in Users and Roles:
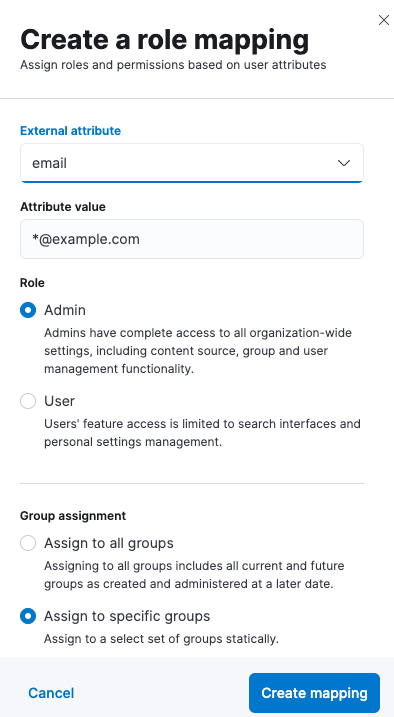
Mapping can use common Elasticsearch user attributes, such as username and email, but also anything provided in metadata that is returned by an OIDC provider. The data returned by an OIDC provider depends on what scopes were requested. For example, when openid and email scopes are requested, the Google OpenID Connect provider returns the following metadata:
{
"oidc(hd)": "example.com",
"oidc(id_token_hint)": "abcdef",
"oidc(iss)": "https://accounts.google.com",
"oidc(email)": "john.smith@example.com",
"oidc(email_verified)": true,
"oidc(sub)": "123456789",
"oidc(azp)": "app-id-here.apps.googleusercontent.com",
"oidc(at_hash)": "xyz",
"oidc(picture)": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/some-picture",
"oidc(nonce)": "xxx",
"oidc(aud)": [
"app-id-here.apps.googleusercontent.com"
]
}
This metadata can be extracted and assigned to Elasticsearch user’s properties. For example, this snippet in elasticsearch.yml:
xpack:
security:
authc:
realms:
oidc:
oidc1:
order: 2
claims.principal: email
claim_patterns.principal: "^([^@]+)@example\\.com$"
claims.mail: email
# more settings...
-
extracts
emailand assigns part of it to the Elasticsearch user’susername(principal) using a pattern -
also assigns
emailas-is to the Elasticsearch user’semail. Then, theseusernameandemailproperties, as well as the Elasticsearch user’sroleandmetadata, can be used to create a mapping specific to App Search or Workplace search.
Note that the snippet above is only a partial example of settings. For a full set of settings related to OpenID Connect, see the Elasticsearch documentation.