Get started with EDOT Android
Set up the Elastic Distribution of OpenTelemetry Android (EDOT Android) in your app and explore your app's data in Kibana.
| Requirement | Minimum version |
|---|---|
| Elastic Stack | 8.18 |
| Android API level | 26 (or 21 with desugaring) |
- If your application's minSdk value is lower than 26, you must add Java 8 desugaring support. Refer to Troubleshooting for more information.
- EDOT Android is meant to be used in Android projects only. Hybrid frameworks, such as React Native and Flutter, are not supported.
Add the EDOT Android agent plugin to your application’s build.gradle[.kts] file:
plugins {
id("com.android.application")
id("co.elastic.otel.android.agent") version "[latest_version]"
}
- You can find the latest version in the plugin portal.
After you've configured Gradle, initialize the agent within your app's code:
val agent = ElasticApmAgent.builder(application)
.setServiceName("My app name")
.setExportUrl("http://10.0.2.2:4318")
.setExportAuthentication(Authentication.ApiKey("my-api-key"))
.build()
- Your Application object. Get your application object.
- In OpenTelemetry, service means an entity that produces telemetry, so this is where your application name should go. Refer to Troubleshooting for more information.
- This is the Elastic endpoint where all your telemetry will be exported. Get your Elastic endpoint.
- Use an API key to connect the agent to the Elastic Stack. Create an API key.
If you'd like to provide these values from outside of your code, using an environment variable or a properties file for example, refer to Provide config values outside of your code.
With EDOT Android fully initialized, you can start sending telemetry to your Elastic Stack.
The following snippet shows how to generate telemetry through manual instrumentation:
val agent = ElasticApmAgent.builder(application)
.setServiceName("My app name")
//...
.build()
agent.span("My Span") {
Thread.sleep(500)
agent.span("My nested Span") {
Thread.sleep(500)
}
}
- Simulates some code execution for which we want to measure the time it takes to complete.
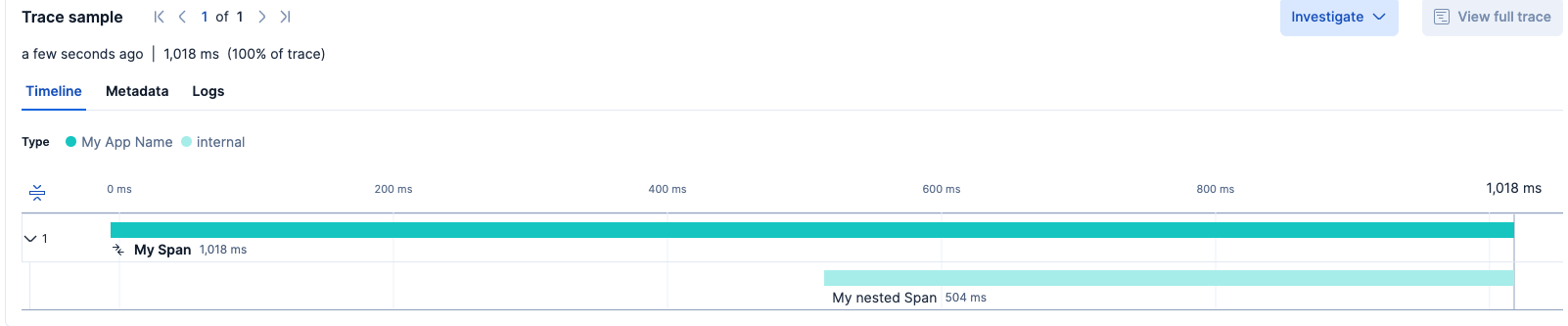
- Demonstrates what span hierarchies look like in Kibana.
After your app has sent telemetry data, either manually or automatically, view it in Kibana by navigating to Applications, Service Inventory, or by searching for Service Inventory in the global search field. You should find your application listed there.
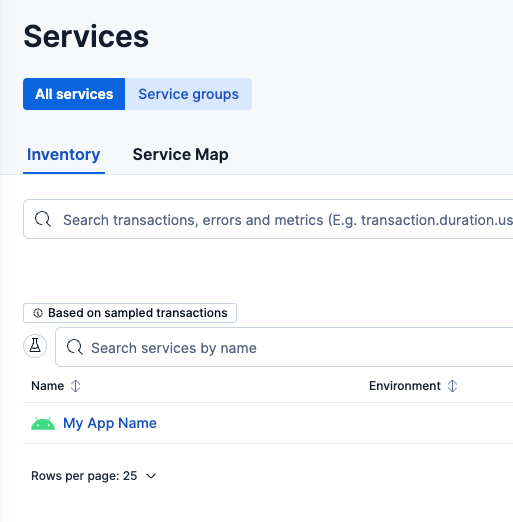
When you open it, go to the Transactions tab, where you should see your app's "outermost" spans listed.
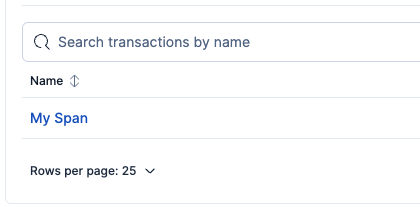
After clicking on the span, you should see it in detail.
This guide uses the minimum configuration options needed to initialize EDOT Android. If you'd like to explore what else you can customize, take a look at the configuration page.
In the example, you've manually sent a span, so you've created some manual instrumentation for your app. While this is helpful and flexible, EDOT Android can also create automatic instrumentations. This means that by simply initializing EDOT Android, it will start sending telemetry data on your behalf without you having to write code. For more details, refer to Automatic instrumentation.
Spans are a great way to measure how long some method, part of a method, or even some broader transaction that involves multiple methods takes to complete. However, spans aren't the only type of signal that you can send using the agent. You can send logs and metrics too! For more details, refer to Manual instrumentation.