Getting started: Use Elastic Security for SIEM
editGetting started: Use Elastic Security for SIEM
editElastic Security combines Elastic SIEM, whose detection engine automates threat detection so you can quickly investigate and respond to threats, and Endpoint Security into a single solution that unifies prevention, detection, and response across your entire network.
This tutorial walks you through setting up an integration so you can collect data from your hosts. First, you’ll add the Network Packet Capture integration to an agent policy, then you’ll deploy the Elastic Agent on your host to collect network packet capture data. Elastic’s integrations not only provide an easy way to add new sources of data, but also contain built-in assets like dashboards, visualizations, and pipelines to extract specific data.
The following example walks through adding the Network Packet Capture integration, which displays flow information about network connections on a host.
Prerequisites
editTo get started, all you need is an internet connection, an email address, and a local or virtual machine from which you’d like to capture some network packet data.
Step 1: Create an Elastic Cloud deployment
editIf you’ve already signed up for a trial deployment you can skip this step.
An Elastic Cloud deployment offers you all of the features of the Elastic Stack as a hosted service. To test drive your first deployment, sign up for a free Elastic Cloud trial:
- Go to our Elastic Cloud Trial page.
-
Enter your email address and a password.

-
After you’ve logged in, you can create a deployment. Give your deployment a name and select Create deployment.

-
While the deployment sets up, make a note of your
elasticsuperuser password and keep it in a safe place. - Once the deployment is ready, select Continue. At this point, you access Kibana and a selection of setup guides.
Your deployment includes a pre-configured instance of Fleet Server, which manages the Elastic Agents that you can use to monitor a host system.
Step 2: Add the Network Packet Capture integration on your machine
edit- Log in to your cloud deployment, which will take you to Kibana Home. You can always return to Home by clicking the Elastic icon.
-
Click Add integrations.

- In the Search bar, enter Network Packet, then select the Network Packet Capture integration.
- Click Add Network Packet Capture.
-
Configure the integration with the following details:
-
Integration name: Give the integration a name. -
Description: Enter a brief description of the integration. -
New agent policy name: Since you’ll be creating a new agent policy, enter a name to identify it. Ensure that you leave the Collect system logs and metrics option selected. -
Click Save and continue to proceed. This step takes a minute or two to complete.

- On the following dialog that displays, click Add Elastic Agent to your hosts. The Add agent flyout is displayed.
-
Step 3: Install Elastic Agent on your machine
editThis integration is powered by Elastic Agent — a single, unified way to add monitoring for logs, metrics, and other types of data to a host. It can also protect hosts from security threats, query data from operating systems, and more. A single agent makes it easy and fast to deploy monitoring across your infrastructure. Each agent has a single policy (a collection of configuration settings) that you can update to add integrations for new data sources, security protections, and more.
The Add agent flyout has two tabs: Enroll in Fleet and Run standalone. The default is to enroll the agents in Fleet, as this reduces the amount of work on the person managing the hosts by providing a centralized management tool in Kibana.
- Skip the Select enrollment token step, but note that the enrollment token is specific to the agent policy you just created. When you run the command to enroll the agent, the enrollment token is included.
- Download, install, and enroll the Elastic Agent on your host by following the Install Elastic Agent on your host step.
-
After about a minute, your agent will have enrolled with the server, downloaded the configuration specified in the policy that you just created, and started collecting data. Close the Add agent flyout.

To ensure your host was added, from the main left navigation menu, go to Security → Hosts, then confirm your hostname appears in the All hosts list.
Step 4: View your data
editOnce the Elastic Agent has been added, the integration installation is complete and you can now view data:
- From the main left navigation menu, go to Management → Integrations, then select the Installed integrations tab.
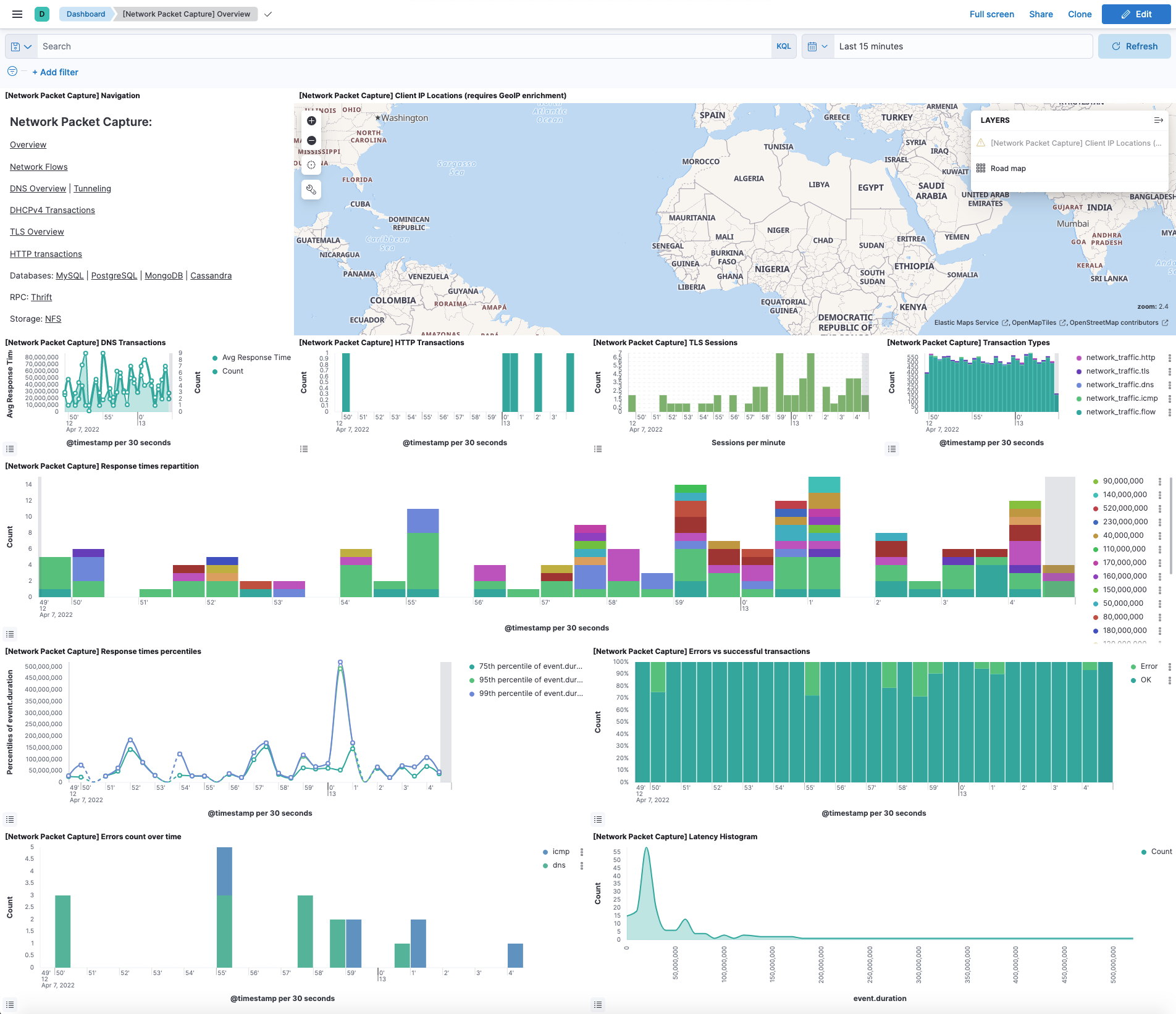
- Select Network Packet Capture, then select the Assets tab.
Assets for each integration are categorized by dashboards, saved searches, and visualizations. Expand each category and select an option to view specific data. The following image shows the Network Packet Capture DNS Overview dashboard, which provides a visual overview of DNS request and response metrics.
Step 5: Tidying up
editYou’ve now learned how to set up an Elastic Cloud deployment and bring in data from a host system. If you’d like to remove Elastic Agent from your system, run the uninstall command from the directory where it’s running and then follow the prompts.
You must run this command as the root user.
sudo /Library/Elastic/Agent/elastic-agent uninstall
You must run this command as the root user.
sudo /opt/Elastic/Agent/elastic-agent uninstall
Open a PowerShell prompt as an Administrator (right-click the PowerShell icon and select Run As Administrator).
From the PowerShell prompt, run:
C:\"Program Files"\Elastic\Agent\elastic-agent.exe uninstall
If you run into any problems, refer to Uninstall Elastic Agents from edge hosts for more information.
What’s next?
edit- If you prefer video tutorials, check out the Elastic Security Quick Start or Elastic Security How-to Series to learn how to get started using Elastic Security.
- Ready to monitor your network for suspicious activity? Create a rule that you can customize for your specific needs.
- Learn how to triage alerts that are generated once those rule conditions are met.
- If you want to block malware, ransomware, and other advanced threats, check out our other Getting started guide that shows you how to install the Endpoint Security integration so that you can not only detect threats, but prevent them before damage and loss occur.